




1. Agaroletten
2. Apo Bisacodyl
3. Apo-bisacodyl
4. Bekunis Bisacodyl
5. Bicol
6. Bisac Evac
7. Bisac-evac
8. Bisacodyl Tannex
9. Bisacodyl Uniserts
10. Bisacodyl, Bekunis
11. Bisacodyl, Fleet
12. Bisalax
13. Bisco Lax
14. Bisco Zitron
15. Bisco-lax
16. Bisco-zitron
17. Dulco Lax
18. Dulco Lax Perles
19. Dulco-lax
20. Dulco-lax Perles
21. Dulcolax
22. Dulcolax Perles
23. Durolax
24. Fleet Bisacodyl
25. Florisan N
26. Lnolax
27. Laxagetten
28. Laxanin
29. Laxans Ratiopharm
30. Laxans-ratiopharm
31. Laxbene
32. Laxysat Brger
33. Ratio Bisacodyl
34. Ratio-bisacodyl
35. Rytmil
36. Tannex, Bisacodyl
37. Ulcolax
38. Uniserts, Bisacodyl
1. 603-50-9
2. Dulcolax
3. Brocalax
4. Bicol
5. Durolax
6. Fenilaxan
7. Sanvacual
8. Theralax
9. Sk-bisacodyl
10. Dulcolan
11. Endokolat
12. Hillcolax
13. Stadalax
14. Eulaxan
15. Godalax
16. Ivilax
17. Laxadin
18. Laxans
19. Laxine
20. Laxorex
21. Neolax
22. Nigalax
23. Pyrilax
24. Telemin
25. Zetrax
26. Laxanin N
27. Laco
28. Modane
29. Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-, Diacetate (ester)
30. Evac-q-tabs
31. La96a
32. (pyridin-2-ylmethylene)bis(4,1-phenylene) Diacetate
33. Bis(p-acetoxyphenyl)-2-pyridylmethane
34. Di-(p-acetoxyphenyl)-2-pyridylmethane
35. Di-(4-acetoxyphenyl)-2-pyridylmethane
36. Feen-a-mint Tablets
37. Mls000069729
38. 2-(4,4'-diacetoxydiphenylmethyl)pyridine
39. 4,4'-(2-pyridylmethylene)diphenol Diacetate (ester)
40. (4,4'-diacetoxydiphenyl)(2-pyridyl)methane
41. 4,4'-(2-pyridylmethylene)diphenol Diacetate
42. [4-[(4-acetyloxyphenyl)-pyridin-2-ylmethyl]phenyl] Acetate
43. Correctol Tablets, Caplets
44. Nsc-755914
45. 4,4'-diacetoxydiphenylpyridyl-2-methane
46. Smr000058226
47. Mls002701749
48. Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridylmethylene)di-, Diacetate (ester)
49. Ulcolax
50. Nsc614826
51. 10x0709y6i
52. Ncgc00016522-05
53. Ncgc00016522-10
54. 4-{[4-(acetyloxy)phenyl](pyridin-2-yl)methyl}phenyl Acetate
55. Bisacodyl 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
56. Cas-603-50-9
57. Deficol
58. Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-, 1,1'-diacetate
59. Dsstox_cid_2681
60. Dsstox_rid_76689
61. Dsstox_gsid_22681
62. 4,4'-(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)bis(4,1-phenylene) Diacetate
63. Bisacodilo
64. Bisacodylum
65. Halflytely
66. Bisacodylum [inn-latin]
67. Bisacodilo [inn-spanish]
68. Hsdb 3016
69. (pyridin-2-ylmethylene)di-4,1-phenylene Diacetate
70. Sr-01000000233
71. Einecs 210-044-4
72. Brn 0323727
73. Horton
74. Ccris 8864
75. Unii-10x0709y6i
76. Bisacodyl [usp:inn:ban:jan]
77. Bisacodyl,(s)
78. Dulcolax (tn)
79. Prestwick_780
80. Mfcd00038039
81. Spectrum_000086
82. Halflytely (salt/mix)
83. Bisacodyl [inn]
84. Bisacodyl [jan]
85. Opera_id_884
86. Bisacodyl [mi]
87. Bisacodyl [hsdb]
88. Prestwick0_000419
89. Prestwick1_000419
90. Prestwick2_000419
91. Prestwick3_000419
92. Spectrum2_000149
93. Spectrum3_000318
94. Spectrum4_000256
95. Spectrum5_000898
96. Bisacodyl [vandf]
97. 4,4'-(2-pyridylmethylene)bisphenol Diacetate
98. Bisacodyl [mart.]
99. Chembl942
100. Ncichal_000004
101. Ncimech_000456
102. Bisacodyl [usp-rs]
103. Bisacodyl [who-dd]
104. Cid_2391
105. Regid_for_cid_2391
106. Schembl21044
107. Bspbio_000378
108. Bspbio_001916
109. Kbiogr_000692
110. Kbioss_000506
111. Divk1c_000347
112. Spectrum1500147
113. Spbio_000258
114. Spbio_002317
115. Bisacodyl (jp17/usp/inn)
116. Bpbio1_000416
117. Chebi:3125
118. Bisacodyl [orange Book]
119. Bisacodyl For System Suitability
120. Bisacodyl [ep Monograph]
121. Dtxsid1022681
122. Bdbm61400
123. Bisacodyl For Peak Identification
124. Hms501b09
125. Kbio1_000347
126. Kbio2_000506
127. Kbio2_003074
128. Kbio2_005642
129. Kbio3_001416
130. Bisacodyl [usp Monograph]
131. Ninds_000347
132. Hms1569c20
133. Hms1920g21
134. Hms2090k15
135. Hms2091o03
136. Hms2096c20
137. Hms2235i11
138. Hms3373l17
139. Hms3652e04
140. Hms3713c20
141. Pharmakon1600-01500147
142. Bcp18567
143. Hy-b0557
144. Zinc3830321
145. Tox21_110472
146. Tox21_200338
147. Ccg-35661
148. Ccg-36442
149. Halflytely Component Bisacodyl
150. Nsc755914
151. S4047
152. Stk293202
153. Akos001599884
154. Tox21_110472_1
155. Db09020
156. Nsc 755914
157. Nsc-614826
158. Bisacodyl Component Of Halflytely
159. Idi1_000347
160. 4,4'-diacetoxydiphenylpyrid-2-ylmethane
161. Bisacodyl, Active Ingredient Of Viraplex
162. Ncgc00016522-01
163. Ncgc00016522-02
164. Ncgc00016522-03
165. Ncgc00016522-04
166. Ncgc00016522-06
167. Ncgc00016522-07
168. Ncgc00016522-08
169. Ncgc00016522-09
170. Ncgc00016522-11
171. Ncgc00016522-12
172. Ncgc00023260-03
173. Ncgc00023260-04
174. Ncgc00023260-05
175. Ncgc00023260-06
176. Ncgc00257892-01
177. Ac-24284
178. As-15820
179. Nci60_004954
180. Sbi-0051297.p003
181. 4,4-(2-pyridylmethylene)diphenol Diacetate
182. Ab00051928
183. B1898
184. B5066
185. Ft-0603486
186. Sw196918-3
187. A14914
188. D00245
189. D81813
190. Ab00051928-17
191. Ab00051928_18
192. Ab00051928_19
193. Bisacodyl, Analytical Standard, For Drug Analysis
194. A832704
195. Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridylmethylene)di-, Diacetate
196. Q417874
197. Q-200726
198. Q-200727
199. Sr-01000000233-2
200. Sr-01000000233-3
201. (pyridin-2-ylmethanediyl)dibenzene-4,1-diyl Diacetate
202. Brd-k39987650-001-05-0
203. Brd-k39987650-001-15-9
204. Phenol, 4,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-, Diacetate
205. Phenol,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-, Diacetate (ester)
206. Phenol,4,4'-(2-pyridinylmethylene)bis-,1,1'-diacetate
207. 4-[[4-(acetyloxy)phenyl](2-pyridyl)methyl]phenyl Acetate
208. Bisacodyl, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
209. 4-[[4-(acetyloxy)phenyl](2-pyridinyl)methyl]phenyl Acetate #
210. Bisacodyl, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
211. [4-[(4-acetoxyphenyl)-(2-pyridyl)methyl]phenyl] Acetate;bisacodyl
212. Bisacodyl For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
213. Bisacodyl For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
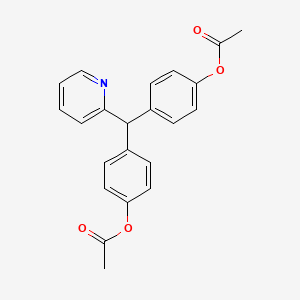
| Molecular Weight | 361.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H19NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 361.13140809 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 361.13140809 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 65.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 457 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Halflytely |
| Active Ingredient | sodium chloride; sodium bicarbonate; Bisacodyl; potassium chloride; polyethylene glycol 3350 |
| Dosage Form | For solution, tablet, delayed release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg,n/a; n/a,5.6gm; n/a,210gm; n/a,0.74gm; n/a,2.86gm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Braintree |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Halflytely |
| Active Ingredient | sodium chloride; sodium bicarbonate; Bisacodyl; potassium chloride; polyethylene glycol 3350 |
| Dosage Form | For solution, tablet, delayed release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg,n/a; n/a,5.6gm; n/a,210gm; n/a,0.74gm; n/a,2.86gm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Braintree |
Cathartics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Oral bulk-forming, lubricant, and stool softener laxatives are indicated prophylactically in patients who should not strain during defecation, such as those with an episiotomy wound, painful thrombosed hemorrhoids, fissures or perianal abscesses, body wall and diaphragmatic hernias , anorectal stenosis, or postmyocardial infarction. /Laxatives; Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1731
Oral laxatives are indicated for the short-term relief of constipation. Oral bulk-forming laxatives, stimulant laxatives, and carbon dioxide-releasing suppositories are indicated to facilitate defecation in geriatric patients with diminished colonic motor response... /Laxatives; Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1731
Bisacodyl is useful as a laxative for the occasional relief of constipation and in bowel cleansing preparation for x-ray or endoscopic examination. Bisacodyl may be used as a laxative in postoperative, antepartum, or postpartum care or in preparation for delivery
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 1285
In severe cases of constipation, such as with fecal impaction, mineral oil and stool softener laxatives administered orally or rectally are indicated to soften the impacted feces. To help complete the evacuation of the impacted colon, a rectal stimulant or saline laxative may follow. /Laxatives; Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1731
In therapeutic oral doses, all stimulant laxatives may produce some degree of abdominal discomfort, nausea, mild cramps, griping, and/or faintness. Rectal administration of bisacodyl suspensions ... may cause irritation and a sensation of burning of the rectal mucosa and mild proctitis. /Stimulant laxatives/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2784
Weakness, incoordination, and orthostatic hypotension may be exacerbated in elderly patients as a result of significant electrolyte loss when stimulant laxatives are used repeatedly to evacuate the colon. /Stimulant laxatives/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1732
Bisacodyl enteric-coated tablets are not recommenced for children up to 6 years of age since patients in this age group may have difficulty swallowing the tablet without chewing it. Gastric irritation may develop if the enteric coating is destroyed by chewing.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1732
Laxatives should not be given to young children unless prescribed by a physician. Since children are not usually able to describe their symptoms precisely, proper diagnosis should precede the use of laxatives. This will avoid the complication of an existing condition (eg appendicitis) or the appearance of more severe side effects. /Laxatives/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1732
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for BISACODYL (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Bisacodyl is indicated to relieve occasional constipation and irregularity.
FDA Label
Patients should be counselled regarding abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a change in bowel function that lasts longer than 2 weeks. It has a wide therapeutic index, as patients can take 5-15 mg orally. Patients taking bisacodyl should be counselled before taking the medication if they are already experiencing abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a change in bowel function lasting longer than 2 weeks. Patients should also be counselled to stop taking the medication if they experience rectal bleeding or no bowel movement in 12 hours.
Cathartics
Agents that are used to stimulate evacuation of the bowels. (See all compounds classified as Cathartics.)
Laxatives
Agents that produce a soft formed stool, and relax and loosen the bowels, typically used over a protracted period, to relieve CONSTIPATION. (See all compounds classified as Laxatives.)
A06AB02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A06 - Drugs for constipation
A06A - Drugs for constipation
A06AB - Contact laxatives
A06AB02 - Bisacodyl
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A06 - Drugs for constipation
A06A - Drugs for constipation
A06AG - Enemas
A06AG02 - Bisacodyl
Absorption
Oral formulations of bisacodyl are only 16% bioavailable. A 10 mg enteric coated oral tablet reaches a Cmax of 26 ng/mL with a Tmax of 8 hours, while a 10 mg oral solution reaches a Cmax of 237 ng/mL with a Tmax of 1.7 hours. A 10 mg suppository reaches a Cmax of 0-64 ng/mL. In lactating women, 10mg of oral bisacodyl reaches a Cmax of 20.5-195 ng/mL, with a Tmax of 3-4 hours, and a geometric mean AUC after a single dose of 471 h\*ng/mL. After multiple doses, the geometric mean AUC decreases to 311 h\*ng/mL.
Route of Elimination
The majority of bisacodyl is eliminated in the feces. 13.8-17.0% of a bisacodyl dose is eliminated in the urine as the active metabolite BHPM.
Volume of Distribution
Data regarding the volume of distribution of bisacodyl is not readily available. However, the volume of distribution of the active metabolite, BHPM, in lactating women is 181 L after a single dose and 289 L at steady state.
Clearance
Data regarding the clearance of bisacodyl is not readily available. The apparent plasma clearance of the active metabolite, BHPM, in lactating women after a single 10 mg oral dose is 272 mL/min and after multiple doses is 412 mL/min.
Absorption of bisacodyl ... is minimal following oral or rectal administration. Any bisacodyl that is absorbed is metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine and/or distributed in milk.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2787
Following oral administration of therapeutic dosages of diphenylmethane derivatives, /bowel/ evacuation is produced in 6 to 8 hours. Rectally administered bisacodyl ... produces evacuation of the colon in within 15 minutes to 1 hour.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2787
As much as 5% of orally administered dose is absorbed & excreted in urine as glucuronide.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1046
Excreted primarily in the feces ...
Cowl, C.T. Physician's Handbook 10th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA. 2003, p. 209
The absorption and plasma level profile and laxative effects of 10 mg bisacodyl as an experimental solution ... in 12 healthy volunteers are described. Results indicate only small amounts of drug were systemically available after administration of /solution/, dragee /(sugar coated capsule)/ and suppository. Urinary excretion was 43.4% for solution, 9.2% for dragee and 3.1% for suppository.
Roth W; Arzneim Forsch 39 (4): 570-74 (1988)
Bisacodyl is deacetylated to the active bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane (BHPM) by an intestinal deacetylase. A small amount of BHPM is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and is glucuronidated before elimination.
Following oral or rectal administration bisacodyl is converted to the active desacetyl metabolite bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)pyridyl-2-methane by intestinal and bacterial enzymes.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 1363
HPLC method which permits simultaneous detection of bisacodyl (BIS) & its monodesacetylated (mono) as well as totally desacetylated (DES) form, was used to study the intestinal handling of BIS (20 nmol/mL), when incubated for 60 min at the mucosal side of the preparations specified. In jejunal mucosa fluid, BIS disappeared completely in short time, & there was nearly equivalent rise in DES; mono was transitorily present. Hydrolysis was also rapid in mucosal fluid which had been in contact with jejunal sacs for 30 sec, but BIS was stable in blank incubations. Hydrolysis of BIS was slower by colonic than by jejunal sacs, & all 3 forms were present during incubation. It seemed still lower in mucosal fluid which had been in contact with colonic sac for 5 min. BIS & DES accumulate in jejunal & colonic serosal fluid mainly as conjugates (above 95%), & DES was in all cases the only conjugated metabolite present. Accumulation in jejunal serosal fluid was same whether BIS or DES was added.
Hillestad B et al; Intestinal Handling of Bisacodyl and Picosulphate by Everted Sacs of the Rat Jejunum and Stripped Colon; Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 51(4) 388 (1982)
Data regarding the half life of bisacodyl is not readily available. The half life of the active metabolite, BHPM, in lactating women was 7.3 h after a single 10 mg oral dose and 10.0 h after multiple doses.
Bisacodyl is deacetylated to the active bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane (BHPM) by an intestinal deacetylase. BHPM can stimulate parasympathetic nerves in the colon directly to increase motility and secretions. Bisacodyl stimulates adenylate cyclase, increasing cyclic AMP, leading to active transport of chloride and bicarbonate out of cells. Sodium ions, potassium ions, and water passively leave the cell; while sodium and chloride ions are unable to be reabsorbed. Water is also be transported from the luminal side of cells into the vasculature by aquaporin 3. Bisacodyl decreases expression of aquaporin 3, preventing water from moving into the vasculature, which may contribute to increased water in the colon. Bisacodyl directly stimulates parasympathetic nerves in the colon, stimulating contraction of longitudinal smooth muscle but not circular smooth muscle.
Bisacodyl is a stimulant laxative, ... acting directly on the colonic mucosa-where it stimulates sensory nerve endings to produce parasympathetic reflexes resulting in increased peristaltic contractions of the colon. The contact action of the drug is restricted to the colon, and motility of the small intestine is not appreciably influenced.
Physicians Desk Reference. 58th ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 2004., p. 1285
/Bisacodyl/ increases water retention in the stool by coating surfaces of stool and intestines with a water-immisicible film. Lubricant effect eases passage of contents through intestines. Emulsification of lubricant tends to enhance its ability to soften stool mass. /Laxatives/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1731
Recent studies show that these drugs alter fluid and electrolyte absorption producing net intestinal fluid accumulation and laxation. Some of these drugs may directly stimulate active intestinal ion secretion. Increased concentrations of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), occurring in colonic mucosa cells following administration of stimulant laxatives, may alter the permeability of these cells and mediate active ion secretion thereby producing net fluid accumulation and laxative action. /Stimulant Laxatives/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2782
Bisacodyl caused dose-dependent contractions in isolated guinea pig ileum & taenia coli which was not prevented by atropine or pheniramine. It prevented acetylcholine- & histamine-induced contractions. Bisacodyl-induced contractions were not caused by a decrease in endogenous cyclic amp level. However, both endogenous cyclic amp & verapamil (a calcium transport inhibitor) inhibited bisacodyl-induced contractions, suggesting site of action on calcium-dependent contractile system of smooth muscle cells.
Schubert et al; Mode of Action of Bisacodyl on the Smooth Muscle of the Small and Large Intestine of the Guinea Pig; Arzneim-Forsch 25(7) 1053 (1975)
Intestinal secretagogues as well as the laxative, bisacodyl, raise the K+ efflux rate across the mucosal border by 200-300%. Results suggest that laxatives may increase rate of K+ secretion into the colonic lumen by raising the K+ permeability of the mucosal border.
Moreto M et al; Effects of Secretagogues on the Potassium Ion Permeability of Mucosal and Serosal Borders of Rabbit Colonic Mucosa; Biochim Biophys Acta 648(29) 215 (1981)