



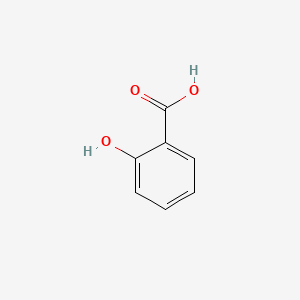

1. 2 Hydroxybenzoic Acid
2. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid
3. Acid, 2-hydroxybenzoic
4. Acid, O-hydroxybenzoic
5. Acid, Ortho-hydroxybenzoic
6. Acid, Salicylic
7. O Hydroxybenzoic Acid
8. O-hydroxybenzoic Acid
9. Ortho Hydroxybenzoic Acid
10. Ortho-hydroxybenzoic Acid
1. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid
2. 69-72-7
3. O-hydroxybenzoic Acid
4. 2-carboxyphenol
5. O-carboxyphenol
6. Rutranex
7. Salonil
8. Retarder W
9. Keralyt
10. Duoplant
11. Freezone
12. Saligel
13. Ionil
14. Psoriacid-s-stift
15. Stri-dex
16. Benzoic Acid, 2-hydroxy-
17. Salicylic Acid Soap
18. Salicylic Acid Collodion
19. Verrugon
20. Phenol-2-carboxylic Acid
21. 2-hydroxybenzenecarboxylic Acid
22. Acidum Salicylicum
23. Trans-ver-sal
24. Orthohydroxybenzoic Acid
25. Acido Salicilico
26. Ionil-plus
27. Salicylic Acid, Tech.
28. Kyselina Salicylova
29. Clear Away Wart Remover
30. Duofil Wart Remover
31. Domerine
32. Sebucare
33. Duofilm
34. Sebulex
35. Dr. Scholl's Callus Removers
36. Salicyclic Acid
37. Ionil Plus
38. Dr. Scholl's Corn Removers
39. Kyselina Salicylova [czech]
40. Dr. Scholl's Wart Remover Kit
41. Kyselina 2-hydroxybenzoova
42. Occlusal
43. Acido Salicilico [italian]
44. Advanced Pain Relief Corn Removers
45. Caswell No. 731
46. 2-hydroxy-benzoic Acid
47. Kyselina 2-hydroxybenzoova [czech]
48. Advanced Pain Relief Callus Removers
49. Salicylicum Acidum
50. Acido O-idrossibenzoico [italian]
51. Nsc 180
52. Salicylic Acid & Sulfur Soap
53. Ccris 6714
54. Hsdb 672
55. Ai3-02407
56. Mfcd00002439
57. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 076602
58. Brn 0774890
59. Chebi:16914
60. Nsc-180
61. Chembl424
62. O414pz4lpz
63. Mls000069653
64. Nsc180
65. Fema No. 3985
66. K 537
67. Ata Fraction 10, Ammonium Salt
68. Ncgc00159447-05
69. Smr000059163
70. Mediplast Pads
71. Akurza Lotion
72. Hydrisalic Gel
73. Akurza Cream
74. Salex Lotion
75. Salex Cream
76. Dsstox_cid_6368
77. Duoplant Gel
78. Dhs Sal Shampoo
79. Dsstox_rid_78106
80. P&s Shampoo
81. Dsstox_gsid_26368
82. Salicylic Acid [usan:jan]
83. Acido O-idrossibenzoico
84. Durasal
85. Cas-69-72-7
86. Propa Ph Peel-off Acne Mask
87. Nsc629474
88. Phenol Derivative, 7
89. Salicylic Acid (tn)
90. Benzoic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, Ion(1-)
91. Einecs 200-712-3
92. Unii-o414pz4lpz
93. Salicylic Acid [usp:jan]
94. Azurechelin
95. Salicylic Acid (6ci,8ci)
96. Salicylic-acid
97. Anti-blemish
98. Salicylic Acid Rs
99. Hydroxy-benzoic Acid
100. Ortho-salicylic Acid
101. Cmc_13852
102. Fostex (salt/mix)
103. Pernox (salt/mix)
104. Duofilm Wart Remover
105. Phenol-2-carboxylate
106. Duofilm (salt/mix)
107. Salicylic Acid,(s)
108. Sebulex (salt/mix)
109. 2-hydroxobenzoic Acid
110. Domerine (salt/mix)
111. Sebucare (salt/mix)
112. 2-hydroxybenzoate, I
113. Natural Salicylic Acid
114. O-hydroxy Benzoic Acid
115. Salicylic Acid Reagent
116. 2-hydroxy Benzoic Acid
117. Spectrum_000948
118. Opera_id_582
119. Salicylic Acid Acs Grade
120. Wln: Qvr Bq
121. Benzoic Acid, O-hydroxy-
122. Bazuka Extra Strength Gel
123. 2-hydroxybenzenecarboxylate
124. Bmse000252
125. C6h4(oh)cooh
126. Epitope Id:124929
127. Retarder Sax (salt/mix)
128. Upcmld-dp126
129. Ec 200-712-3
130. Salicylicacidinclusioncomplex
131. Schembl1967
132. Salicylic Acid [mi]
133. Oprea1_040343
134. Kbioss_001428
135. Salicylic Acid [jan]
136. Salicylic Acid [usp]
137. Bidd:er0602
138. Divk1c_000301
139. Salicylic Acid (jp17/usp)
140. Salicylic Acid [hsdb]
141. Salicylic Acid [inci]
142. Salicylic Acid [vandf]
143. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid, Natural
144. Fema3985
145. Gtpl4306
146. Sgcut00012
147. Zinc1554
148. Salicylic Acid [mart.]
149. Salicylic Acid Inclusion Complex
150. Salicylic Acid, >=99%, Fg
151. Salicylic Acid, Lr, >=99%
152. Component Of Tinver (salt/mix)
153. Dtxsid7026368
154. Salicylic Acid [usp-rs]
155. Salicylic Acid [who-dd]
156. Salicylic Acid [who-ip]
157. Upcmld-dp126:001
158. Bdbm26193
159. Component Of Keralyt (salt/mix)
160. Kbio1_000301
161. Kbio2_001428
162. Kbio2_003996
163. Kbio2_006564
164. Alpha/beta Hydroxy Acids (glycolic Acid, Salicylic Acid)
165. E9a559be-383b-4f83-bc02-3031d03d558a
166. Salicylicum Acidum [hpus]
167. Ninds_000301
168. Hms2233a10
169. Hms3373m19
170. Hms3885b08
171. Kuc106694n
172. Salicylic Acid, P.a., 99.0%
173. Benzoic Acid, 2-hydroxy- (9ci)
174. Bcp09067
175. Hy-b0167
176. Salicylic Acid [green Book]
177. To_000004
178. Lamivudine Impurity, Salicylic Acid-
179. Tox21_113453
180. Tox21_201471
181. Tox21_303109
182. S4539
183. Salicylic Acid [ep Impurity]
184. Stk258681
185. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid [fhfi]
186. Salicylic Acid [ep Monograph]
187. Akos000118979
188. Salicylic Acid [usp Monograph]
189. Salicylic Acid, Bioxtra, >=99.0%
190. Ccg-212792
191. Db00936
192. Pb48023
193. Idi1_000301
194. Smp2_000145
195. Ncgc00159447-01
196. Ncgc00159447-02
197. Ncgc00159447-04
198. Ncgc00159447-06
199. Ncgc00257065-01
200. Ncgc00259022-01
201. Acidum Salicylicum [who-ip Latin]
202. Bp-12826
203. Ksc-11-207-4
204. Lamivudine Related Compound Salicylic Acid
205. Salicylic Acid & Sulfur Soap (salt/mix)
206. Salicylic Acid, Acs Reagent, >=99.0%
207. Salicylic Acid, Plant Cell Culture Tested
208. Salicylic Acid, Reagentplus(r), >=99%
209. Ts-03583
210. Salicylic Acid 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
211. Salicylic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
212. Sbi-0051510.p003
213. Lamivudine Impurity C [ep Impurity]
214. Mesalazine Impurity H [ep Impurity]
215. Ft-0645123
216. Ft-0674502
217. Ft-0674503
218. H0206
219. H1342
220. Salicylic Acid, Tested According To Ph.eur.
221. Salicylic Acid 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
222. Salicylic Acid, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
223. Sulfasalazine Impurity H [ep Impurity]
224. C00805
225. D00097
226. D70842
227. Salicylic Acid, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
228. Ab00489876_15
229. Benzoic Acid,2-hydroxy Salicylic Acid
230. Salicylic Acid, Puriss. P.a., >=99.0% (t)
231. Q193572
232. Component Of Solarcaine First Aid Spray (salt/mix)
233. J-509667
234. Acetylsalicylic Acid Impurity C [ep Impurity]
235. Component Of Fostex Medicated Bar And Cream (salt/mix)
236. F2191-0216
237. Salicylic Acid, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
238. Salicylic Acid, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
239. Salicylic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
240. Salicylic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
241. Salicylic Acid, 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
242. Salicylic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
243. 8052-31-1
244. Salicylic Acid, Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Usp, 99.5-100.5% (calc. To The Dried Substance)
| Molecular Weight | 138.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 138.031694049 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 138.031694049 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 57.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 133 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Infective Agents; Antifungal Agents; Keratolytic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Cosmetic ingredient functions of Salicylic Acid and its salts. Ingredient: Salicylic Acid; Function: Antiacne agent, Antidanduff agent, Corn/callus/wart remover, Denaturant, Hair-conditioning agent, and Skin-conditioning agent (miscellaneous). /From table/
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report of the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Safety Assessment of Salicylic Acid, Butyloctyl Salicylate, Calcium Salicylate, C12-15 Alkyl Salicylate, Capryloyl Salicylic Acid, Hexyldodecyl Salicylate, Isocetyl Salicylate, Isodecyl Salicylate, Magnesium Salicylate, MET-Salicylate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Potassium Salicylate, Methyl Salicylate, Myristyl Salicylate, Sodium Salicylate, TEA-Salicylate, and Tridecyl Salicylate; p.9, (2003)
Salicylic acid has been present in OTC topical acne preparations (at concentrations of 2% to 5%), external analgesics and skin protectants used for poison ivy, oak and sumac, and topical antifungal drug products.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report of the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Safety Assessment of Salicylic Acid, Butyloctyl Salicylate, Calcium Salicylate, C12-15 Alkyl Salicylate, Capryloyl Salicylic Acid, Hexyldodecyl Salicylate, Isocetyl Salicylate, Isodecyl Salicylate, Magnesium Salicylate, MET-Salicylate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Potassium Salicylate, Methyl Salicylate, Myristyl Salicylate, Sodium Salicylate, TEA-Salicylate, and Tridecyl Salicylate; p.9, (2003)
MEDICATION (VET): Seborrhea is a skin disease in dogs that is characterized by a defect in keratinization or cornification. Clinically, it results in increased scale formation, occasionally excessive greasiness of the skin and hair coat, and often secondary inflammation and infection. ... Dogs with moderate to marked scaling and mild oiliness should be bathed with shampoos that contain sulfur and salicylic acid. Both agents are keratolytic, keratoplastic, antibacterial, and antipruritic.
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 799
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for SALICYLIC ACID (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Salicylic acid is not used systemically because of its severe irritating effect on GI mucosa and other tissues; therefore, better tolerated chemical derivatives have been prepared for systemic use.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 3545
Necrosis of normal skin has been associated with overuse of the drug. At high concentrations (e.g., 20%), salicylic acid has a caustic effect.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 3545
Prolonged use over large areas, especially in young children and those patients with significant renal or hepatic impairment, could result in salicylism. Limit the area to be treated and be aware of signs of salicylate toxicity (e.g., nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of hearing, tinnitus, lethargy, hyperpnea, diarrhea, psychic disturbances).
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons 59th Edition 2005. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2005., p. 2579
Contraindications: Sensitivity to salicylic acid; prolonged use, especially in infants, diabetics, and patients with impaired circulation; use on moles, birthmarks or warts with hair growing from them, genital or racial warts or warts on mucous membranes, irritated skin or any area that is infected or reddened.
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons 59th Edition 2005. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2005., p. 2579
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for SALICYLIC ACID (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Key additive in many skin-care products for the treatment of acne, psoriasis, callouses, corns, keratosis pilaris and warts.
Salicylic acid treats acne by causing skin cells to slough off more readily, preventing pores from clogging up. This effect on skin cells also makes salicylic acid an active ingredient in several shampoos meant to treat dandruff. Use of straight salicylic solution may cause hyperpigmentation on unpretreated skin for those with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick phototypes IV, V, VI), as well as with the lack of use of a broad spectrum sunblock. Subsalicylate in combination with bismuth form the popular stomach relief aid known commonly as Pepto-Bismol. When combined the two key ingredients help control diarrhea, nausea, heartburn, and even gas. It is also very mildly anti-biotic.
Keratolytic Agents
Agents that soften, separate, and cause desquamation of the cornified epithelium or horny layer of skin. They are used to expose mycelia of infecting fungi or to treat corns, warts, and certain other skin diseases. (See all compounds classified as Keratolytic Agents.)
Anti-Infective Agents
Substances that prevent infectious agents or organisms from spreading or kill infectious agents in order to prevent the spread of infection. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents.)
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D01 - Antifungals for dermatological use
D01A - Antifungals for topical use
D01AE - Other antifungals for topical use
D01AE12 - Salicylic acid
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01B - Antiinflammatory agents
S01BC - Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids
S01BC08 - Salicylic acid
Route of Elimination
About 10% is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution is about 170 mL/kg of body weight.
A single-center, single-sequence, two-period crossover study was performed to compare the systemic exposure to salicylic acid following facial application of a 30% salicylic acid cosmetic skin peel formulation applied for 5 min and an oral dose of 650 mg aspirin in nine healthy male and female subjects. The mean (SD) maximum salicylic acid concentration (C(max)) was 0.81 (0.32) ug/mL and 56.4 (14.2) ug/mL. The AUC-based safety margin ratio was 50:1. A depot effect was observed during topical application of the skin peel solution as the absorption of salicylic acid continued beyond the 5-min application period. Plasma salicylic acid C(max) values were achieved from 1.4 to 3.5 hr after topical application and from 0.5 to 1.5 hr after oral aspirin. The plasma concentrations in the present study (30%; 5 min) were similar to that of a low concentration (2%) applied in a leave-on product to the same body surface area.
Fung W et al; J Pharm Sci 97 (3): 1325-1328 (2007)
The absorption of reagent-grade salicylic acid through abdominal guinea pig skin was examined. The abdominal area was shaved and a recirculation apparatus was applied to determine the rate of absorption. Salicylic acid, pH 3.0, had a constant rate of absorption (approximately 4%) at concentrations of 250, 400, and 1000 ug/mL. Salicylic acid at a concentration of 500 ug/mL was used to examine the absorption as a function of pH. The percent absorbed from 1 to 6 hours was 6.1, 3.3, 0.6, and 0 at pH 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively, and 0, 1.8, 8.0, and 15.5 at pH 7, 8, 9, and 10, respectively.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report of the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Safety Assessment of Salicylic Acid, Butyloctyl Salicylate, Calcium Salicylate, C12-15 Alkyl Salicylate, Capryloyl Salicylic Acid, Hexyldodecyl Salicylate, Isocetyl Salicylate, Isodecyl Salicylate, Magnesium Salicylate, MET-Salicylate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Potassium Salicylate, Methyl Salicylate, Myristyl Salicylate, Sodium Salicylate, TEA-Salicylate, and Tridecyl Salicylate; p.15, (2003)
Salicylic acid is rapidly absorbed from the intact skin, especially when applied in oily liniments or ointments, ... .
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 700
The percutaneous absorption of salicylic acid through damaged guinea pig skin was studied using a recirculation apparatus. After the abdominal skin of male guinea pigs was clipped and the stratum corneum removed, a glass vessel was attached and used for continuous recirculation and the amount of salicylic acid, 500 ug/mL and pH 3.0, absorbed was calculated from the concentration remaining in the solution. Also, concentrations of 250, 500, and 1000 ug/mL salicylic acid at pH 3.0 and 500 ug/ml at a pH of 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 were used to determine the effect of concentration and pH, respectively, on absorption. The absorption rate of 500 ug/ml salicylic acid from the recirculating solution was 79.4% for damaged skin; the disappearance of salicylic acid from the solution was linear from the start of exposure. (This was 10 times the rate through intact skin; disappearance from intact skin was linear 1 hour after the start of exposure.) The rate of absorption from the recirculating solution was independent of concentration, but it did increase with an increasing fraction of un-ionized form. The amount of drug retained in damaged guinea pig skin after various exposure times was then determined. The animals were exposed to 500 ug/mL salicylic acid, pH 3.0, for 0.5, 1.0, 3.0, 4.5, or 6.0 hours, and then killed. The test area was wiped and the skin isolated to the corium. A peak in the amount of salicylic acid reserved in the skin was observed after 0.5 to 1 hour. ... These results were attributed to an increase in percutaneous absorption and rapid decrease in concentration in the test solution due to removal of the stratum corneum and a rapid decrease in skin concentration because of the decrease of salicylic acid in the solution. Varying the concentration of salicylic acid from 250 to 1000 ug/mL resulted in similar patterns of retention. Varying the pH from 3 to 6, the peak of the amount reserved became lower and broader with a decreasing fraction of unionized salicylic acid, and the time required to reach a peak had a later trend.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report of the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Safety Assessment of Salicylic Acid, Butyloctyl Salicylate, Calcium Salicylate, C12-15 Alkyl Salicylate, Capryloyl Salicylic Acid, Hexyldodecyl Salicylate, Isocetyl Salicylate, Isodecyl Salicylate, Magnesium Salicylate, MET-Salicylate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Potassium Salicylate, Methyl Salicylate, Myristyl Salicylate, Sodium Salicylate, TEA-Salicylate, and Tridecyl Salicylate; p.15, (2003)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for SALICYLIC ACID (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Salicylic acid is extensively metabolized.
At low dosage, approximately 80% of salicylic acid is metabolized in the liver. Conjugation with glycine, forms salicyluric acid and when conjugated with glucuronic acid, acyl and phenolic glucuronide are formed. Small amounts of salicylic acid are also hydroxylated to gentisic acid. With large doses, the kinetics switch from first order to zero order.
IPCS; Poisons Information Monograph 642: Salicylic Acid (September 1998). Available from, as of February 13, 2008: https://www.inchem.org/documents/pims/pharm/pim642.htm#PartTitle:5.%20%20ROUTES%20OF%20ENTRY
Dogs were dosed intravenously with 1 g (14)C-salicylic acid (containing 10 uCi) in sodium bicarbonate solution. Urine was collected for 30 to 36 hours. Urinary metabolite recovery from one animal, which was representative of all the dosed animals, was 50% unchanged salicylic acid, 25% glucuronates, 10% salicyluric acid, and 4% to 5% gentisic acid. Total recovery was > 90% of the dose.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report of the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Safety Assessment of Salicylic Acid, Butyloctyl Salicylate, Calcium Salicylate, C12-15 Alkyl Salicylate, Capryloyl Salicylic Acid, Hexyldodecyl Salicylate, Isocetyl Salicylate, Isodecyl Salicylate, Magnesium Salicylate, MET-Salicylate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Potassium Salicylate, Methyl Salicylate, Myristyl Salicylate, Sodium Salicylate, TEA-Salicylate, and Tridecyl Salicylate; p.29, (2003)
The major urinary metabolites identified after topical administeration differ from those after oral salicylate adminisration; those derived from percutaneous absorption contain more salicylate glucuronides (42%) and less salicyluric (52%) and salicylic acid (6%).
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons 59th Edition 2005. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2005., p. 2579
YIELDS O-CARBOXYPHENYL-B-D-GLUCURONIDE IN MAN; IN RABBIT; YIELDS O-CARBOXYPHENYL SULFATE IN RAT. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. S-3
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for SALICYLIC ACID (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Salicylic acid has known human metabolites that include 5-hydroxylation.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Groups of 3 and 25 month old male Fischer 344 rats were dosed iv with 5 or 50 mg/kg(14)C-salicylic acid ... . The half life value s in 3 month old animals were 4.08 and 30.1 hr with doses of 5 and 50 mg/kg, respectively; these values were 21.3 and 21.9 hr, respectively, in 25 month old animals.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; Final Report of the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Safety Assessment of Salicylic Acid, Butyloctyl Salicylate, Calcium Salicylate, C12-15 Alkyl Salicylate, Capryloyl Salicylic Acid, Hexyldodecyl Salicylate, Isocetyl Salicylate, Isodecyl Salicylate, Magnesium Salicylate, MET-Salicylate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Potassium Salicylate, Methyl Salicylate, Myristyl Salicylate, Sodium Salicylate, TEA-Salicylate, and Tridecyl Salicylate; p.29, (2003)
Salicylic acid directly irreversibly inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 to decrease conversion of arachidonic acid to precursors of prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Salicylate's use in rheumatic diseases is due to it's analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity. Salicylic acid is a key ingredient in many skin-care products for the treatment of acne, psoriasis, calluses, corns, keratosis pilaris, and warts. Salicylic acid allows cells of the epidermis to more readily slough off. Because of its effect on skin cells, salicylic acid is used in several shampoos used to treat dandruff. Salicylic acid is also used as an active ingredient in gels which remove verrucas (plantar warts). Salicylic acid competitively inhibits oxidation of uridine-5-diphosphoglucose (UDPG) with nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide (NAD) and noncompetitively with UDPG. It also competitively inhibits the transferring of the glucuronyl group of uridine-5-phosphoglucuronic acid (UDPGA) to a phenolic acceptor. Inhibition of mucopoly saccharide synthesis is likely responsible for the slowing of wound healing with salicylates.
Salicylic acid has a potent keratolytic action and a slight antiseptic action when applied topically to the skin. In low concentrations, the drug has keratoplastic activity (correction of abnormal keratinization) and in higher concentrations (i.e., 1% or higher, depending on the vehicle), the drug has keratolytic activity (causes peeling of skin). Salicylic acid softens and destroys the stratum corneum by increasing endogenous hydration (water concentration), probably because of decreased pH, which causes the cornified epithelium (horny layer) of the skin to swell, soften, and then desquamate.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 3545