

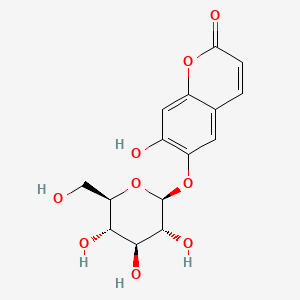

1. Aesculin
2. Esculoside
3. Venoplant
1. Aesculin
2. 531-75-9
3. Esculoside
4. Polychrome
5. Bicolorin
6. Enallachrome
7. (-)-esculin
8. Crataegin
9. Escosyl
10. Esculine
11. Polychrom
12. 6,7-dihydroxycoumarin 6-glucoside
13. Esculetin 6-o-glucoside
14. Vitamin C2
15. Esculetin 6-beta-d-glucoside
16. 6,7-dihydroxycoumarin-6-o-glucoside
17. Aesculinum
18. 6-(beta-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-cumarin
19. Chebi:4853
20. 7-hydroxy-6-cumarinyl-glucosid
21. Nsc-26665
22. 7-hydroxy-6-(((2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-2h-chromen-2-one
23. 6-(beta-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-2h-1-benzopyran-2-one
24. 1y1l18lqaf
25. 7-hydroxy-6-glucosyloxy-2h-chromene
26. Venoplant
27. 7-hydroxy-6-[(2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-2-one
28. Esculoside [jan]
29. 7-hydroxy-2-oxo-2h-chromen-6-yl Beta-d-glucopyranoside
30. 6-(.beta.-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-2h-1-benzopyran-2-one
31. Aesculetin Glukosid
32. 6-[(2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3,4,5-tris(oxidanyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-7-oxidanyl-chromen-2-one
33. 7-hydroxy-6-{[(2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy- 6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-tetrahydropyranyl]oxy}-2-chromenone
34. 66778-17-4
35. Unii-1y1l18lqaf
36. Schillerstoff
37. Esculina
38. Ccris 5724
39. Sr-01000633930
40. 2h-1-benzopyran-2-one, 6-(.beta.-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-
41. Esculetin Glukosid
42. Ncgc00016491-01
43. Cas-531-75-9
44. Aesculin (esculin)
45. Einecs 208-517-5
46. 7-hydroxy-6-glucosyloxy-2h-chromen
47. Nsc 26665
48. Spectrum_000361
49. Esculin [inci]
50. Esculin [mi]
51. Spectrum2_000576
52. Spectrum3_000731
53. Spectrum4_001923
54. Spectrum5_000845
55. Aesculinum [hpus]
56. Esculetin 6-b-d-glucoside
57. Schembl2893
58. Dsstox_cid_25318
59. Dsstox_rid_80798
60. Esculoside [who-dd]
61. Dsstox_gsid_45318
62. Bspbio_002282
63. Kbiogr_002266
64. Kbioss_000841
65. Divk1c_000956
66. Spectrum1500901
67. Spbio_000392
68. Chembl482581
69. Dtxsid7045318
70. Bcbcmap01_000202
71. Esculetin 6-.beta.-d-glucoside
72. Hms502p18
73. Kbio1_000956
74. Kbio2_000841
75. Kbio2_003409
76. Kbio2_005977
77. Kbio3_001502
78. Ninds_000956
79. Hms1921m16
80. 2h-1-benzopyran-2-one, 6-(beta-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-
81. Ex-a6781
82. Hy-n0188
83. Zinc3860441
84. Tox21_110453
85. Bdbm50480261
86. Ccg-38501
87. Mfcd00006879
88. S2258
89. Akos015895151
90. Db13155
91. Sdccgmls-0066653.p001
92. Idi1_000956
93. Smp1_000008
94. Ncgc00094874-04
95. Cs-0007892
96. N1766
97. 7-hydroxycoumarin-6-yl Beta-d-glucopyranoside
98. C09264
99. 6-(.beta.-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-hydroxy-cumarin
100. A829428
101. Q376432
102. Sr-01000633930-1
103. Sr-01000633930-3
104. Brd-k51742987-001-02-3
105. Brd-k51742987-002-02-1
106. Esculin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
107. 7-hydroxy-6-((2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yloxy)-2h-chromen-2-one
108. 7-hydroxy-6-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-chromen-2-one Hydrate;esculin Sesquihydrate
109. 7ou
| Molecular Weight | 340.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H16O9 |
| XLogP3 | -0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 340.07943208 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 340.07943208 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 146 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 495 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
As medication, esculin is sometimes used as a vasoprotective agent. Esculin is also used in a microbiology laboratory to aid in the identification of bacterial species (especially Enterococci and Listeria), as all strains of Group D Streptococci hydrolyze sculin in 40% bile.
Topically applied Esculine increases the capillary density (the number of capillaries open to flow per surface unit) and improves the morphological aspect of the smallest blood vessels.
Absorption
Rarely, absorbed into the blood stream if used as a combination with other ingredients in suppository form. But, Applying cream or ointment form to open wound or skin may lead this drug to absorb and circulate into blood stream.
After oral administration of esculin (100 mg/kg) for rats, plasma, urine, feces and bile samples were collected to screen metabolites. As a result, a total of 19 metabolites (10 phase I metabolites and 9 phase II metabolites) were found and identified. It was also found that after oral administration of esculin, the esculin could be metabolized to esculetin in vivo via deglycosylation, and esculetin was found in all biological samples.
Absorption half life about 1 hour and elimination half life about 20 hours
The main activities of Esculine focus on capillary protection, as it improves capillary permeability and fragility. It is reported to inhibit catabolic enzymes such as hyaluronidase and collagenase, thus preserving the integrity of the perivascular connective tissue. Esculine also showed good antioxidant properties, protecting triglycerides against auto-oxidation at high temperatures . The antioxidant property might as well explain some of the anti-inflammatory activity of the product, making it a suitable product for after sun treatments, for example.
