

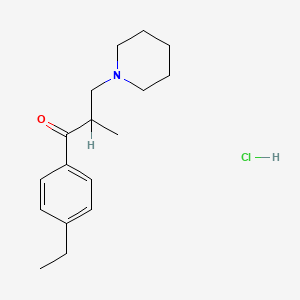

1. (4'-ethyl-2-methyl-3-piperidino)propiophenone
2. 4-empp
3. E-0646
4. Eperisone
1. 56839-43-1
2. Eperisone Hcl
3. Myonal
4. Mional
5. Empp
6. Eperisone, Hcl
7. E-646
8. 1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-one Hydrochloride
9. Eperisone Hydrochloride [jan]
10. 4'-ethyl-2-methyl-3-piperidinopropiophenone Hydrochloride
11. U38o8u7p6x
12. 1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-(1-piperidinyl)-1-propanone Hydrochloride
13. 1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-piperidin-1-ylpropan-1-one;hydrochloride
14. Dsstox_cid_27822
15. Dsstox_rid_82585
16. Dsstox_gsid_47844
17. Cas-56839-43-1
18. Ncgc00167973-01
19. (4'-ethyl-2-methyl-3-piperidino)propiophenone
20. Unii-u38o8u7p6x
21. E 0646
22. Epenard (tn)
23. 1-propanone, 1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-(1-piperidinyl)-, Hydrochloride
24. Eperisonehydrochloride
25. Dw-1030
26. Schembl218337
27. Chembl2360601
28. Dtxsid8047844
29. Eperisone Hydrochloride (jp17)
30. Chebi:31540
31. Bcp11969
32. Hy-b1901
33. Propiophenone, 4'-ethyl-2-methyl-3-piperidino-, Hydrochloride
34. Eperisone Hydrochloride [mi]
35. Tox21_112599
36. Mfcd00941459
37. Akos015843965
38. Tox21_112599_1
39. Ccg-267425
40. Eperisone Hydrochloride [mart.]
41. Ks-5241
42. Eperisone Hydrochloride [who-dd]
43. Ncgc00167973-02
44. Ac-15896
45. Db-052975
46. Cs-0013960
47. E2000
48. Ft-0602324
49. S4877
50. D01671
51. D95097
52. E-2000
53. A831198
54. Q27889924
55. 1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-onehydrochloride
56. 1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-(1-piperidyl)propan-1-one Hydrochloride;eperisone Hcl
| Molecular Weight | 295.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H26ClNO |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 295.1702921 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 295.1702921 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 20.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 275 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Muscle Relaxants, Central
A heterogeneous group of drugs used to produce muscle relaxation, excepting the neuromuscular blocking agents. They have their primary clinical and therapeutic uses in the treatment of muscle spasm and immobility associated with strains, sprains, and injuries of the back and, to a lesser degree, injuries to the neck. They have been used also for the treatment of a variety of clinical conditions that have in common only the presence of skeletal muscle hyperactivity, for example, the muscle spasms that can occur in MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. (From Smith and Reynard, Textbook of Pharmacology, 1991, p358) (See all compounds classified as Muscle Relaxants, Central.)
Parasympatholytics
Agents that inhibit the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system. The major group of drugs used therapeutically for this purpose is the MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Parasympatholytics.)
