

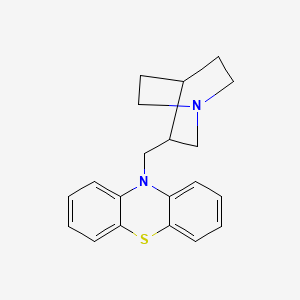

1. 3-methylquinuclidinyl-10-phenothiazine
2. Lm 209
3. Mequitazine Hydrochloride
4. Mequitazine Tartrate, (r-(r*,r*))-isomer
5. Mircol
6. Primalan
7. Quitadrill
1. 29216-28-2
2. Metaplexan
3. Primalan
4. Virginan
5. Mircol
6. Instotal
7. Vigigan
8. (r)-(+)-mequitazine
9. Mequitazina [spanish]
10. Kitazemin
11. Mequitazina
12. 10-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-ylmethyl)-10h-phenothiazine
13. Mequitazinum [inn-latin]
14. Mequitazina [inn-spanish]
15. Lm 209
16. Lm-209
17. 10-(3-quinuclidinylmethyl)phenothiazine
18. 10-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-ylmethyl)phenothiazine
19. Phenothiazine, 10-(3-quinuclidinylmethyl)-
20. Nsc 303612
21. 10-(quinuclidin-3-ylmethyl)-10h-phenothiazine
22. 10h-phenothiazine, 10-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-ylmethyl)-
23. Nsc303612
24. Butix
25. Nsc-303612
26. Mls000757058
27. Chebi:31821
28. Y463242ly2
29. Ncgc00183046-01
30. Mequitazinum
31. Zesulan
32. 10h-phenothiazine, 10-(1-azabicyclo(2.2.2)oct-3-ylmethyl)-
33. Dsstox_cid_3262
34. Dsstox_rid_76947
35. Dsstox_gsid_23262
36. Mequitazine [inn:ban:dcf:jan]
37. Kitazemin (tn)
38. Smr000528898
39. 3-methylquinuclidinyl-10-phenothiazine
40. Cas-29216-28-2
41. Einecs 249-521-7
42. Brn 1150945
43. Releas
44. Unii-y463242ly2
45. Mequitazine [mi]
46. Mequitazine [inn]
47. Mequitazine [jan]
48. Mequitazine (jp17/inn)
49. Mequitazine [mart.]
50. Schembl18207
51. Mequitazine [who-dd]
52. Mls001201790
53. Chembl73451
54. Dtxsid8023262
55. Hms2231i03
56. Hms3369o08
57. Hms3604k05
58. Hy-b2168
59. Tox21_113648
60. Mfcd00869383
61. S6435
62. Stk324459
63. Akos000424971
64. Akos022061643
65. Tox21_113648_1
66. Ac-2365
67. Cs-6222
68. Db01071
69. Ncgc00183046-03
70. Ls-14776
71. Nci60_002566
72. Db-047545
73. Ds-016113
74. Ft-0630547
75. Ft-0671023
76. M2807
77. V0162
78. D01324
79. Ab00691111-09
80. 216m282
81. A819820
82. L000704
83. 10-(quinuclidin-3-ylmethyl)phenothiazine;mequitazine
84. J-008412
85. J-017436
86. Q3333256
87. 10-{1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-ylmethyl}-10h-phenothiazine
88. (r)-10-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-ylmethyl)-10h-phenothiazine
89. 10h-phenothiazine,10-[(3s)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-ylmethyl]-
| Molecular Weight | 322.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H22N2S |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 322.15036988 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 322.15036988 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 31.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 398 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of Hay fever, urticaria (hives) and allergic rhinitis
In allergic reactions an allergen interacts with and cross-links surface IgE antibodies on mast cells and basophils. Once the mast cell-antibody-antigen complex is formed, a complex series of events occurs that eventually leads to cell-degranulation and the release of histamine (and other chemical mediators) from the mast cell or basophil. Once released, histamine can react with local or widespread tissues through histamine receptors. Histamine, acting on H1-receptors, produces pruritis, vasodilatation, hypotension, flushing, headache, tachycardia, and bronchoconstriction. Histamine also increases vascular permeability and potentiates pain. Mequitazine is a histamine H1 antagonist. It competes with histamine for the normal H1-receptor sites on effector cells of the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels and respiratory tract. It provides effective, temporary relief of sneezing, watery and itchy eyes, and runny nose due to hay fever and other upper respiratory allergies.
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
R - Respiratory system
R06 - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06A - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06AD - Phenothiazine derivatives
R06AD07 - Mequitazine
Mequitazine binds to the histamine H1 receptor sites on effector cells in the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract. This blocks the action of endogenous histamine, which subsequently leads to temporary relief of the negative symptoms brought on by histamine.
