


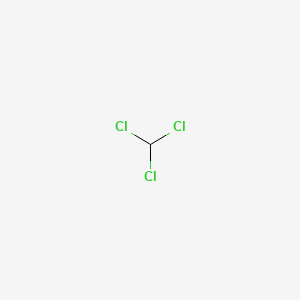

1. Trichloromethane
1. Trichloromethane
2. 67-66-3
3. Methane, Trichloro-
4. Trichlormethan
5. Formyl Trichloride
6. Trichloroform
7. Methenyl Trichloride
8. Methyl Trichloride
9. Methane Trichloride
10. Chloroforme
11. Chcl3
12. R 20 (refrigerant)
13. Cloroformio
14. Triclorometano
15. Trichloormethaan
16. Freon 20
17. 1,1,1-trichloromethane
18. Rcra Waste Number U044
19. Methenyl Chloride
20. Nci-c02686
21. Methylidyne Trichloride
22. Refrigerant R20
23. Hsdb 56
24. Chloroformum
25. Chloroform Bp
26. Trichloro-methane
27. Nsc 77361
28. R 20
29. Chloroform [un1888] [poison]
30. Hcc 20
31. Nsc-77361
32. Chebi:35255
33. 7v31yc746x
34. Ncgc00090794-01
35. Chloroform Chcl3
36. Chloroform, Hplc Grade
37. Dsstox_cid_306
38. Dsstox_rid_75501
39. Dsstox_gsid_20306
40. Chloroform, Analytical Standard
41. Chloroforme [french]
42. Caswell No. 192
43. Cloroformio [italian]
44. Trichlormethan [czech]
45. Chloroform [nf Xvii]
46. Trichloormethaan [dutch]
47. Triclorometano [italian]
48. Mfcd00000826
49. Cas-67-66-3
50. Chloroform [nf]
51. Ccris 137
52. Chloroform, Acs
53. Chloroformwith Amylene
54. Chloroformwith Ethanol
55. Einecs 200-663-8
56. Un1888
57. Rcra Waste No. U044
58. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 020701
59. Brn 1731042
60. Chlorform
61. Chloroforrn
62. Cloroform
63. Trichlormethane
64. Trichlorocarbon
65. Chloro Form
66. Chloro-form
67. Unii-7v31yc746x
68. Chloroform-
69. Ai3-24207
70. Chloroform, For Hplc, >=99.8%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
71. Trichloro- Methane
72. Chloroform Solution
73. Methane Trichloride
74. Tris(chloranyl)methane
75. Ccl3h
76. Hccl3
77. Chloroform, For Hplc
78. Trichloromethane, 9ci
79. Chloroform [ii]
80. Chloroform [mi]
81. Chloroform, Ethanol-free
82. Chloroformium Pro Narcosi
83. Wln: Gygg
84. Chloroform [hsdb]
85. Chloroform [iarc]
86. Chloroform [inci]
87. Aqualine™ Matrix K
88. Chloroform [vandf]
89. Chloroformum [hpus]
90. Ec 200-663-8
91. Chloroform [mart.]
92. Chloroform [usp-rs]
93. Chloroform [who-dd]
94. 4-01-00-00042 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
95. Chembl44618
96. Chloroform, Environmental Grade
97. Chloroform, P.a., 99.8%
98. Gtpl2503
99. Chloroform [green Book]
100. Chloroform - Reagent Grade Acs
101. Dtxsid1020306
102. R 20 (van)
103. Chloroform With Amylene Hplc Grade
104. Chloroform, Spectrophotometric Grade
105. Nsc77361
106. Zinc8214524
107. Chloroform (stabilized With Ethanol)
108. Tox21_111024
109. Tox21_202494
110. Chloroform, For Hplc, >=99.5%
111. Chloroform, For Hplc, >=99.8%
112. Akos000269026
113. Chloroform 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
114. Db11387
115. Un 1888
116. Chloroform 5000 Microg/ml In Methanol
117. Chloroform, Purification Grade, >=99%
118. Ncgc00090794-02
119. Ncgc00260043-01
120. F 20
121. Trichloromethane 10 Microg/ml In Methanol
122. Chloroform, Jis Special Grade, >=99.0%
123. Trichloromethane 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
124. C0819
125. Ft-0623661
126. Trichloromethane 5000 Microg/ml In Methanol
127. Chlorobutanol Impurity A [ep Impurity]
128. Chloroform, Hplc Grade Stabilized With Ethanol
129. Chloroform (stabilized With 2-methyl-2-butene)
130. Chloroform, Saj Super Special Grade, >=99.0%
131. A835850
132. L023971
133. Q172275
134. Brd-k88785477-001-01-8
135. Chloroform, For Hplc, >=99.8%, Amylene Stabilized
136. Chloroform, 99.8%, Acs Reagent Stabilized With Ethanol
137. Chloroform, Technical, Amylene Stabilized, >=99% (gc)
138. F0001-1775
139. Chloroform, Technical Grade, 95%, Contains 50 Ppm Amylene
140. Chloroform, Anhydrous, Contains Amylenes As Stabilizer, >=99%
141. Chloroform, For Hplc, >=99.8% (chloroform + Ethanol, Gc)
142. Chloroform, For Residue Analysis, Suitable For 5000 Per Jis
143. Chloroform Solution, 200 Mug/ml In Methanol, Analytical Standard
144. Chloroform Stabilized With 50-200 Ppm Amylene Acs Reagent Grade
145. Chloroform, >=99%, Pcr Reagent, Contains Amylenes As Stabilizer
146. Chloroform, Acs Reagent, >=99.8%, Contains Amylenes As Stabilizer
147. Chloroform, Ar, Contains 1-2% Ethanol As Stabilizer, >=99.5%
148. Chloroform, Ar, Contains 100 Ppm Amylene As Stabilizer, >=99.5%
149. Chloroform, Contains 100-200 Ppm Amylenes As Stabilizer, >=99.5%
150. Chloroform, Contains Amylenes As Stabilizer, Acs Reagent, >=99.8%
151. Chloroform, Contains Ethanol As Stabilizer, Acs Reagent, >=99.8%
152. Chloroform, Lr, Contains 100 Ppm Amylene As Stabilizer, >=99%
153. Chloroform, P.a., Acs Reagent, 99.8%, Contains 0.005% Amylene
154. Chloroform, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%, Contains 0.4-0.8% Ethanol
155. Chloroform, Uv Hplc Spectroscopic, 99.9%, Contains 50 Ppm Amylene
156. Chloroform Solution, Certified Reference Material, 5000 Mug/ml In Methanol
157. Chloroform, Acs Reagent, Reag. Ph. Eur., Contains Ethanol As Stabilizer
158. Chloroform, Anhydrous, >=99%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
159. Chloroform, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
160. Chloroform, Puriss. P.a., Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., 99.0-99.4% (gc)
161. Chloroform, Suitable For 300 Per Jis, >=99.0%, For Residue Analysis
162. Chloroform, Uv Hplc Spectroscopic, 99.0%, Contains 0.6-1.0% Ethanol
163. Chloroform Solution, Nist Standard Reference Material, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D)
164. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D)
165. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 3% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D)
166. Chloroform, Acs Reagent, >=99.8%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
167. Chloroform, Acs Spectrophotometric Grade, >=99.8%, Contains Amylenes As Stabilizer
168. Chloroform, Biotech. Grade, >=99.8%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
169. Chloroform, P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, 99.8%, Contains 50 Ppm Amylene
170. Chloroform, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, >=99.8% (chloroform + Ethanol, Gc)
171. Chloroform, Reagentplus(r), >=99.8%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
172. Residual Solvent Class 2 - Chloroform, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
173. 8013-54-5
174. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 0.3% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
175. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 0.3% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
176. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99,9 Atom % D), Tms 0.1 %, Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
177. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 10 Mm X 8 In.
178. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
179. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 4 Mm X 8 In.
180. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 1% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 8 Mm X 8 In.
181. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 10% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
182. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 2% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
183. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 2% In Chloroform-d (99.8 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
184. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 2% In Chloroform-d (99.8 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
185. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 20% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
186. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 3% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Tms 0.2 %, Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
187. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 3% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Tms 0.2 %, Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
188. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 5% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Chromium(iii) Acetylacetonate 0.2 %
189. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 5% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Chromium(iii) Acetylacetonate 2 %, Nmr Tube Size 10 Mm X 8 In.
190. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 5% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
191. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 5% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
192. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 50% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Chromium(iii) Acetylacetonate 0.2 %
193. Chloroform Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 50% In Acetone-d6 (99.9 Atom % D), Chromium(iii) Acetylacetonate 0.2 %, Nmr Tube Size 10 Mm X 8 In.
194. Chloroform, Acs Spectrophotometric Grade, >=99.8%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
195. Chloroform, Contains Ethanol As Stabilizer, Meets Analytical Specification Of Dab9, Bp, 99-99.4% (gc)
196. Chloroform, Hplc Plus, For Hplc, Gc, And Residue Analysis, >=99.9%, Contains 0.5-1.0% Ethanol As Stabilizer
197. Chloroform, Hplc Plus, For Hplc, Gc, And Residue Analysis, >=99.9%, Contains Amylenes As Stabilizer
198. Residual Solvent - Chloroform, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 119.37 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CHCl3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 117.914383 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 117.914383 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
MEDICATION (VET): As inhalation anesthetic in horses & now rarely in cattle, sheep, cats or dogs because of dangerous complications & superior alternatives; internally, well dilute in intestinal colic & flatulence; in expectorants, & less commonly as anthelmintic (swine, dogs) ... . /Former use/
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 104
MEDICATION (VET): Used/ externally, as liniment-type counterirritant for relief of deep seated pain, to expel screwworm larvae from wounds, as skin cleanser (fat solvent), & as skin coolant & local anesthetic due to its evaporation. ... Internally, it is given in various mixt well dilute to avoid gastric irritation ... . /Former use/
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 104
Has been used as an anesthetic and in pharmaceutical preparations.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 379
Chloroform was used chiefly as an anesthetic and in pharmaceutical preparation immediately prior to World War II. However, these uses have been banned.
Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 3rd ed., Volumes 1-26. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, 1978-1984., p. 5(79) 694
An increased incidence of cardiac arrhythmias has been demonstrated during surgery in patients anesthetized with chloroform as compared with other anesthetic agents at vapor concentrations of 22,500 ppm.
Mackison, F. W., R. S. Stricoff, and L. J. Partridge, Jr. (eds.). NIOSH/OSHA - Occupational Health Guidelines for Chemical Hazards. DHHS(NIOSH) Publication No. 81-123 (3 VOLS). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, Jan. 1981., p. 2
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Chloroform: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 140 (1994)
Fatal doses of liquid anesthetic agents by ingestion or inhalation are approx as follows: ... chloroform, 10 mL ... .
Dreisbach, R.H. Handbook of Poisoning. 12th ed. Norwalk, CT: Appleton and Lange, 1987., p. 314
The mean lethal dose for an adult is estimated to be about 45 g.
WHO; EHC163: Chloroform (1994) Available from, as of January 2, 2018: https://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc163.htm
Solvents
Liquids that dissolve other substances (solutes), generally solids, without any change in chemical composition, as, water containing sugar. (Grant and Hackh's Chemical Dictionary, 5th ed) (See all compounds classified as Solvents.)
N - Nervous system
N01 - Anesthetics
N01A - Anesthetics, general
N01AB - Halogenated hydrocarbons
N01AB02 - Chloroform
Chloroform can be absorbed through lung, from GI tract and to some extent through skin. Inhalation route is ... primary source of ... absorption in man.
Doull, J., C.D. Klaassen, and M. D. Amdur (eds.). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., 1980., p. 47
Chloroform is rapidly absorbed & distributed to all organs, with relatively high concn in nervous tissue. After intraduodenal injection of (14)C-chloroform to rats, 70% ... was found unchanged in expired air & 4% as (14)CO2(carbon dioxide) during 24 hr. ... Liver and, to much lesser extent, kidney were main organs in which CO2 was formed.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V20 414 (1979)
In man, pulmonary excretions of chloroform and its CO2 (carbon dioxide) metab account substantially for single oral dose of 0.5 or 1.0 g. Amongst 9 subjects, up to 68% of dose is excreted unchanged & up to 51% of CO2; not more than 4% of dose is excreted unchanged after 8 hr.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 329
... /Chloroform crosses/ placenta rapidly and enters fetal circulation.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 635
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Chloroform (50 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
When (14)C-chloroform was admin orally to mice, rats, & monkeys, radioactivity was found in expired air. Most of dose was excreted unchanged by monkeys, as (14)CO2 (carbon dioxide) by mice, & as both by rats. Three metabolites were detected in urine of rats & mice, one of which was identified as urea.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V20 414 (1979)
Haloforms are metabolized to carbon monoxide by hepatic microsomal mixed function oxidases & this reaction is markedly stimulated by sulfhydryl cmpd. Max stimulation occurred at 0.5 mmol glutathione. A mechanism for conversion to carbon monoxide is proposed.
PMID:526325 Stevens JL et al; Biochemical Pharmacology 28: 3189 (1979)
Trihalomethanes (haloforms) were metab to carbon monoxide by rat liver microsomal fraction requiring nadph & molecular oxygen. Metabolism followed halide order; thus, chloroform yielded smallest amt. Results suggest cytochrome p450 dependent system.
Ahmed AE et al; Drug Metabolism Disposition 5 (2): 198 (1976)
Deuterium-labeled chloroform was less toxic and less readily metabolized than /normal/ chloroform, suggesting that the cleavage of the C-H bond is the rate-limiting step in the process resulting in hepatotoxicity.
Pohl LR; Rev Biochem Toxicol 1: 79 (1979)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Chloroform (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Whole body: 1.5 hours; [TDR, p. 318]
TDR - Ryan RP, Terry CE, Leffingwell SS (eds). Toxicology Desk Reference: The Toxic Exposure and Medical Monitoring Index, 5th Ed. Washington DC: Taylor & Francis, 1999., p. 318
After inhalation of approximately 5 mg (38)Cl-chloroform, about 80% of the chloroform was found to have been absorbed ... . Eight volunteers expired 18 to 67% of an oral dose of 500 mg (13)C-chloroform (in capsules of olive oil) unchanged; in two subjects, about half of the dose was eliminated in the expired air as (13)CO2. The decline in the concentration of chloroform in blood was described by a two-compartment model, with initial and second-phase half-lives of 14 and 90 min, respectively, averaged over four subjects.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V73 153 (1999)
In humans given a single oral dose of 0.5 g chloroform, about 50-52% of the dose was absorbed, and virtually all of the absorbed dose was metabolized to carbon dioxide. Blood levels peaked after 1.5 hr and declined in line with a two-compartment model with half-lives of 13 and 90 min, respectively ...
WHO; Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 58-chloroform. 2004 Available from, as of August 26, 2008: https://www.inchem.org/documents/cicads/cicads/cicad58.htm
The feasibility of an oxygen-independent mechanism of chloroform bioactivation was indicated by the covalent binding to lipid and protein occurring in anaerobic incubations of chloroform and microsomes in the presence of NADPH. Under these conditions, the loss of cytochrome p450 and the inhibition of related mono-oxygenases were also observed. The chloroform anoxic biotransformation was negligible in uninduced microsomes and seemed to be catalyzed mainly by phenobarbital-inducible p450 isozymes. Biotransformation could also be supported by NADH as the source of reducing equivalents. Anaerobic metabolism of chloroform led to decreased levels of the main phenobarbital-induced p450 isozymes even at low chloroform concentration, and did not affect benzo(a)pyrene hydroxylase activity. These effects were not decreased by thiolic compounds. The oxidation products of chloroform caused a general impairment of the monoxygenase system, probably related to the formation of protein aggregates with very high molecular weight. In the presence of physiological concentrations of GSH, the targets of aerobically-produced metabolite were lipids, and, to a smaller extent, p450. At low chloroform concentrations and/or in the presence of GSH, the most changes to microsomal structures seemed to be produced by the reductively-formed intermediates.
PMID:3769050 Testai E, Vittozi L; Chem-Biol Interact 59 (2): 157-72 (1986)