
1. Asl 8052
2. Asl-8052
3. Brevibloc
4. Esmolol
1. 81161-17-3
2. Esmolol Hcl
3. Brevibloc
4. Esmolol (hydrochloride)
5. Asl-8052
6. Esmolol Hydrochloride [usan]
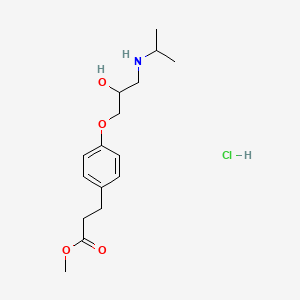
7. Methyl 3-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]propanoate;hydrochloride
8. Asl8052
9. V05260lc8d
10. Dsstox_cid_28929
11. Dsstox_rid_83195
12. Dsstox_gsid_49003
13. Benzenepropanoic Acid, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)-, Methyl Ester, Hydrochloride
14. Asl 8052
15. (+-)-methyl P-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)hydrocinnamate Hydrochloride
16. 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)benzenepropanoic Acid Methyl Ester Hcl
17. Chebi:4857
18. Cas-81161-17-3
19. Hsdb 6530
20. Ncgc00185766-01
21. Brevibloc In Plastic Container
22. Unii-v05260lc8d
23. Sr-01000763706
24. Methyl 3-(4-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)propanoate Hydrochloride
25. Methyl 3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy]phenyl}propanoate Hydrochloride
26. Brevibloc (tn)
27. Clol
28. Brevibloc Double Strength In Plastic Container
29. Schembl41086
30. Esmolol Hydrochloride- Bio-x
31. Mls001401393
32. Chembl1201115
33. Dtxsid7049003
34. Esmolol Hydrochloride (jan/usp)
35. Esmolol Hydrochloride [mi]
36. Esmolol Hydrochloride [jan]
37. Bcp28434
38. Hy-b1392
39. Esmolol Hydrochloride [hsdb]
40. Tox21_113496
41. Esmolol Hydrochloride [vandf]
42. Mfcd00941432
43. S4100
44. Esmolol Hydrochloride [mart.]
45. Akos015895316
46. Esmolol Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
47. Esmolol Hydrochloride [who-dd]
48. Tox21_113496_1
49. Ab07716
50. Ac-6972
51. Ccg-100972
52. Ccg-220890
53. Cs-4908
54. Ks-1353
55. Nc00222
56. Ncgc00185766-04
57. Be164425
58. Benzenepropanoic Acid, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)-, Methyl Ester, Hydrochloride, (+-)-
59. Smr000469141
60. Esmolol Hydrochloride [orange Book]
61. Esmolol Hydrochloride [usp Monograph]
62. Ft-0601541
63. Ft-0667970
64. Ft-0667971
65. Sw197602-3
66. D00644
67. Esmolol Hydrochloride, >=98% (hplc), Solid
68. F20655
69. 1-(3-methylphenyl)piperazinedihydrochloridehydrate
70. 598e034
71. 81161-17-3, 81147-92-4(free Base)
72. J-003862
73. Q-201070
74. Sr-01000763706-4
75. Q27106523
76. Esmolol Hcl; Brevibloc; Asl-8052; Asl 8052; Asl 805
77. Esmolol Hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
78. (+/-)-methyl P-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)hydrocinnamate Hydrochloride
79. (+/-)-methyl P-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino) Propoxy]hydrocinnamate Hydrochloride
80. Methyl 3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy]-phenyl}propanoate Hydrochloride
81. Benzenepropanoic Acid, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)-, Methyl Ester, Hydrochloride (1:1)
82. Benzenepropanoic Acid, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)-, Methyl Ester, Hydrochloride, (+/-)-
83. Methyl 3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy]phenyl}propanoate Hydrochloride (esmolol Hcl)
| Molecular Weight | 331.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H26ClNO4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 331.1550360 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 331.1550360 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 67.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 288 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Brevibloc |
| PubMed Health | Esmolol (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | BREVIBLOC (Esmolol Hydrochloride) is a beta adrenergic receptor blocker with a very short duration of action (elimination half-life is approximately 9 minutes). Esmolol hydrochloride is:()-Methyl p-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino) propoxy] hydrocinnam... |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Brevibloc double strength in plastic container |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 2gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Brevibloc in plastic container |
| Drug Label | Esmolol hydrochloride is a beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenergic receptor blocking agent with a very short duration of action (elimination half-life is approximately 9 minutes). Esmolol hydrochloride is:()-Methyl p-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylami... |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 2000mg/100ml (20mg/ml); 2500mg/250ml (10mg/ml); 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hq Speciality Pharma; Mylan Institutional; Eurohlth Intl |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Brevibloc |
| PubMed Health | Esmolol (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | BREVIBLOC (Esmolol Hydrochloride) is a beta adrenergic receptor blocker with a very short duration of action (elimination half-life is approximately 9 minutes). Esmolol hydrochloride is:()-Methyl p-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino) propoxy] hydrocinnam... |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Brevibloc double strength in plastic container |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 2gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Brevibloc in plastic container |
| Drug Label | Esmolol hydrochloride is a beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenergic receptor blocking agent with a very short duration of action (elimination half-life is approximately 9 minutes). Esmolol hydrochloride is:()-Methyl p-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylami... |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 1gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Active Ingredient | Esmolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 2000mg/100ml (20mg/ml); 2500mg/250ml (10mg/ml); 10mg/ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hq Speciality Pharma; Mylan Institutional; Eurohlth Intl |
Adrenergic Beta-Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Esmolol is used IV principally to provide rapid, temporary control of ventricular rate in patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (SVT) (eg, atrial flutter and/or fibrillation, sinus tachycardia).
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1748
Esmolol may be preferred to longer-acting B-adrenergic blocking agents for the short-term control of ventricular rate in patients with SVT because of the drug's rapid onset and short duration of effects, ... .
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1748
Esmolol is indicated for rapid and short-term control of ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter in perioperative, postoperative, or other emergency situations. It is also indicated in noncompensatory sinus tachycardia judged by the physician to need intervention. (Esmolol is used for control of heart rate in patients with myocardial ischemia. /NOT included in US product labeling/) It is not recommended for use in chronic situations where transfer to another agent is anticipated. /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1231
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Because of the risk of esmolol induced hypotension, blood pressure should be monitored closely during therapy with this drug, especially in patients with low pretreatment blood pressure (eg, systolic blood pressure less than 105 mm Hg). Hypotension can occur at any dose level with esmolol but usually is dose related, and doses exceeding 200 ug/kg per minute recommended by the manufacturer for the management of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Reversal of hypotension usually occurs within 30 minutes of discontinuing the drug or reducing the rate of IV infusion.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1751
... Esmolol is contraindicated in patients with second- or third-degree atrioventricular blocks, sinus bradycardia, cardiogenic shock, or overt cardiac failure.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1751
Esmolol may mask signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia (eg, tachycardia, palpitation, blood pressure changes, tremor, feelings of anxiety, but not sweating or dizziness) and may potentiate insulin-induced hypoglycemia; therefore, the drug should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1751
Because of de-esterified metabolite (ASL 8123) of esmolol is eliminated mainly by the kidneys, ... the drug should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment, especially severe impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1751
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Adrenergic beta-1 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to and block the activation of ADRENERGIC BETA-1 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-1 Receptor Antagonists.)
It is not known whether esmolol and/or ASL 8123 cross the placenta in humans, but the drug has been shown to cross the placenta in animals. In animals, fetal artery esmolol concentrations were about 10% of maternal concentrations at the completion of infusion. It also is not known whether esmolol and/or ASL 8123 are distributed into milk.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753
Following IV administration, esmolol is rapidly and widely distributed. The apparent volumes of distribution of esmolol and its de-esterifed metabolite (ASL 8123) in healthy adults are approximately 3.4 and 0.41 l/kg, respectively, following iv administration. In healthy adults, the volumes of distribution of esmolol in the central compartment and at steady state are approximately 0.87 and 1.2 l/kg, respectively, following IV administration. The apparent volume of distribution appears to be decreased in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery and increased in patients with renal impairment undergoing peritoneal dialysis and in patients with liver cirrhosis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753
Following IV administration in rats, esmolol is ditributed into liver and kidneys, but only minimally into CSF, spleen, or testes.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753
In vitro, esmolol is approximately 55% bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Protein binding of esmolol to alpha-1-acid glycoprotein does not appear to be concentration dependent at esmolol concentrations of 3-110 ug/ml. In vitro, ASL 8123 is approximately 10% bound to plasma proteins.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ESMOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Esmolol is rapidly and extensively metabolized via esterases (probably arylesterase), principally in the cytosol of erythrocytes. Metabolism of the drug also may occur in highly perfused tissues that contain esterases (eg, liver, kidneys). Hydrolysis of the methyl ester moiety results in formation of the de-esterified (free acid) metabolite, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino) propoxy)benzenepropanoic acid (ASL 8123), and methanol. Esmolol does not appear to be susceptible to hydrolysis via serum cholinesterase (pseudocholinesterase), acetylcholinesterase, or carbonic anhydrase. It is estimated that about 83% of an esmolol dose is metabolized to ASL 8123. ASL 8123 has a low affinity for beta-adrenergic receptors, exhibiting only minimal (about 1,000- to 1,500-fold less potent than esmolol) beta-blocking activity in animals and no appreciable blockade in humans. Unlike esmolol, ASL 8123 is eliminated principally by the kidneys, and the elimination half-life of the metabolite may be increased up to tenfold in patients with renal impairment; however, such accumulation is not thought to be clinically important since ASL 8123 has only minimal beta-blocking activity. The amount of methanol formed during hydrolysis of the drug does not appear to be clinically important. Following IV infusion of esmolol hydrochloride doses of 300 ug/kg per minute for up to l6 hours of 150 ug/kg per minute for 24 hours, blood methanol concentrations ranged from 2.8-5.9 or 2.9-13.2 ug/ml, respectively, being less than 2% of those usually associated with methanol toxicity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753
Following IV infusion in adults, the half life of esmolol averages about 2 minutes in the initial distribution phase and about 9 minutes (range: 5-23 minutes) in the terminal elimination phase, although considerable interindividual variation in blood elimination half life exists.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753
Free acid metabolite: approx 3.7 hr (increased up to tenfold in renal failure)
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1231
Esmolol selectively inhibits response to adrenergic stimuli by competitively blocking cardiac B1-adrenergic receptors, while having little effect on the B2-adrenergic receptors of bronchial and vascular smooth muscle. At high doses (e.g., greater than 300 ug/kg per minute), this selectivity of esmolol for B1-adrenergic receptors usually diminishes, and the drug will competitively inhibit B1-and B2-adrenergic receptors.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1752
By inhibiting myocardial beta1-adrenergic receptors, esmolol produces negative chronotropic and inotropic activity. Through its myocardial B1-adrenergic blocking action, esmolol decreases resting and exercise-induced heart rate, reflex orthostatic tachycardia, myocardial contractility, rate of left ventricular pressure rise (dp/dt), right ventricular contractility, and cardiac index.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1752
The decrease in myocardial contractility, arterial pressure, and heart rate produced by esmolol can lead to a reduction in myocardial oxygen consumption, which may account for the effectiveness of the drug in myocardial ischemia.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1753