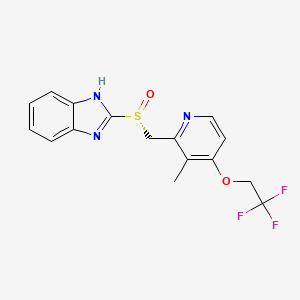

1. 2-((r)-((3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1h-benzimidazole
2. Dexilant
3. Dexlansoprazole Sesquihydrate
4. Lansoprazole, R Isomer
5. Lansoprazole, R-isomer
6. R Lansoprazole
7. R-isomer Lansoprazole
8. R-lansoprazole
9. T 168390
10. T-168390
11. T168390
12. Tak 390
13. Tak 390mr
14. Tak-390
15. Tak-390mr
16. Tak390
17. Tak390mr
1. (r)-lansoprazole
2. 138530-94-6
3. Kapidex
4. R-(+)-lansoprazole
5. Dexilant
6. Dexilant Solutab
7. Tak 390
8. Tak-390
9. Lansoprazole R-form
10. Lansoprazole, (r)-
11. T 168390
12. (r)-(+)-lansoprazole
13. T-168390
14. Uye4t5i70x
15. (r)-2-(((3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1h-benzo[d]imidazole
16. Nsc-758710
17. 2-((r)-((3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1h-benzimidazole
18. Tak-390mr
19. 1h-benzimidazole, 2-((r)-((3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl)methyl)sulfinyl)-
20. Dexlansoprazole [usan]
21. Unii-uye4t5i70x
22. Dexlansoprazole (inn/usan)
23. Dexlansoprazole [usan:inn]
24. (+)-lansoprazol
25. 2-[(r)-[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-1h-benzimidazole
26. Dexilant (tn)
27. (+)-2-((r)-((3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1h-benzimidazole
28. (+)-2-((r)-{(3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl)methyl}sulfinyl)-1h-benzimidazole
29. 1h-benzimidazole, 2-[(r)-[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-
30. Schembl44975
31. Dexlansoprazole [inn]
32. Dexlansoprazole [vandf]
33. Gtpl5487
34. Dexlansoprazole [mart.]
35. Chembl1201863
36. Dexlansoprazole [who-dd]
37. Lansoprazole R-form [mi]
38. 2-[(r)-[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl]-1h-benzimidazole
39. Chebi:135931
40. Hms3652c14
41. Zinc599734
42. Amy25226
43. Bdbm50247930
44. Dexlansoprazole [orange Book]
45. Hy-13662b
46. Mfcd13196699
47. S4099
48. Akos025290765
49. Ccg-213301
50. Db05351
51. Nsc 758710
52. Pb33188
53. 2-[(r)-[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridyl]methylsulfinyl]-1h-benzimidazole
54. Ncgc00386267-03
55. Ac-26449
56. As-18086
57. Sw219466-1
58. D08903
59. Ab01563023_01
60. Ab01563023_02
61. Q5268339
62. (r)-2-[[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-1h-benzimidazole
63. (r)-2-[[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]benzimidazole
64. (r)-2-[[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-1h-benzimidazole
65. (r)-2-[[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridyl]methyl]sulfinyl]benzimidazole
66. (r)-(+)2-([3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl)-1h-benzimidazole
67. 2-[(r)-{[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl]methane}sulfinyl]-1h-1,3-benzodiazole
| Molecular Weight | 369.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H14F3N3O2S |
| XLogP3 | 2.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 369.07588236 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 369.07588236 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 87.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 480 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexilant |
| PubMed Health | Dexlansoprazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | The active ingredient in DEXILANT (dexlansoprazole) delayed-release capsules, a proton pump inhibitor, is (+)-2-[(R)-{[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl] methyl} sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexlansoprazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, delayed release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 30mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Takeda Pharms Usa |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexlansoprazole |
| PubMed Health | Dexlansoprazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | The active ingredient in DEXILANT (dexlansoprazole) delayed-release capsules, a proton pump inhibitor, is (+)-2-[(R)-{[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl] methyl} sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexlansoprazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Par Pharm |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexilant |
| PubMed Health | Dexlansoprazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | The active ingredient in DEXILANT (dexlansoprazole) delayed-release capsules, a proton pump inhibitor, is (+)-2-[(R)-{[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl] methyl} sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexlansoprazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, delayed release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 30mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Takeda Pharms Usa |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Dexlansoprazole |
| PubMed Health | Dexlansoprazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | The active ingredient in DEXILANT (dexlansoprazole) delayed-release capsules, a proton pump inhibitor, is (+)-2-[(R)-{[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl] methyl} sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion... |
| Active Ingredient | Dexlansoprazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 60mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Par Pharm |
Dexlansoprazole is indicated for healing all grades of erosive esophagitis (EE), maintaining and healing of EE and relief of heartburn, and treating heartburn associated with symptomatic non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
FDA Label
Dexlansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and is included in the drug class of antisecretory compounds. It blocks the final step of gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the (H+, K+)-ATPase at the secretory surface of the parietal cells on gastric mucosa.
Anti-Ulcer Agents
Various agents with different action mechanisms used to treat or ameliorate PEPTIC ULCER or irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. This has included ANTIBIOTICS to treat HELICOBACTER INFECTIONS; HISTAMINE H2 ANTAGONISTS to reduce GASTRIC ACID secretion; and ANTACIDS for symptomatic relief. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Ulcer Agents.)
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit H(+)-K(+)-EXCHANGING ATPASE. They are used as ANTI-ULCER AGENTS and sometimes in place of HISTAMINE H2 ANTAGONISTS for GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX. (See all compounds classified as Proton Pump Inhibitors.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A02 - Drugs for acid related disorders
A02B - Drugs for peptic ulcer and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (gord)
A02BC - Proton pump inhibitors
A02BC06 - Dexlansoprazole
Absorption
After oral administration, the peak plasma concentration increases approximately dose proportionally. The dual delayed release formulation achieves two plasma concentration peaks, where the first peak occurs one to two hours after administration, followed by a second peak within four to five hours. The delivery technology of dexlansoprazole MR is designed to release the drug in two separate pH-dependent phases, the first in the proximal duodenum (25% of total drug dose) and the second (75% of total drug dose) in the more distal small intestine. The median time (Tmax) to peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of 30 mg dexlansoprazole was 4 hours and ranged from 1 to 6 hours with the Cmax value of 688 ng/mL. AUC was found to be 3275 (ngh/mL).
Route of Elimination
Dexlansoprazole is cleared from the body by either fecal excretion (50.7%) or renal excretion (47.6%) following oral ingestion, with no unchanged drug detected in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution after multiple doses in symptomatic GERD patients was 40.3 L.
Clearance
Apparent clearance (CL/F) in healthy subjects was 11.4 to 11.6 L/hour, respectively, after five days of 30 or 60 mg once daily administration.
Dexlansoprazole is extensively metabolized in the liver by oxidation, reduction, and subsequent formation of sulfate, glucuronide and glutathione conjugates to inactive metabolites. Oxidative metabolites are formed by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system including hydroxylation mainly by CYP2C19, and oxidation to the sulfone by CYP3A4. Dexlansoprazole is the major circulating component in plasma regardless of CYP2C19 metabolizer status. In CYP2C19 intermediate and extensive metabolizers, the major plasma metabolites are 5-hydroxy dexlansoprazole and its glucuronide conjugate, while in CYP2C19 poor metabolizers dexlansoprazole sulfone is the major plasma metabolite.
Lansoprazole has known human metabolites that include 5-Hydroxylansoprazole and Lansoprazole Sulfone.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Dexlansoprazole is eliminated with a half-life of approximately one to two hours in healthy subjects and in patients with symptomatic GERD.
Dexlansoprazole inhibits the H/K ATPase enzyme, which is involved in the secretion of hydrochloric acid, hydrolyzing ATP and exchanging H+ ions from the cytoplasm for K+ ions in the secretory canaliculus, which results in HCl secretion into the gastric lumen. Dexlansoprazole inhibits this effect of H/K ATPase by demonstrating a high degree of activation in the acidic environment. After passing through the liver and reaching the gastric parietal cells activated by a meal, PPIs undergo protonation in the acidic pH environment, followed by conversion to sulphenamide which represents the active form of the drug. Sulphenamide inhibits the activity of the proton pump and hence the transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen via covalent binding to the SH groups of the cysteine residues of H/K ATPase. The delivery technology of dexlansoprazole MR is designed to release the drug in two separate pH-dependent phases, the first in the proximal duodenum (25% of total drug dose) and the second (75% of total drug dose) in the more distal small intestine. Dexlansoprazole reduces both basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion.