

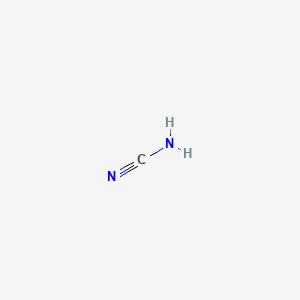

1. Carbimide
1. 420-04-2
2. Hydrogen Cyanamide
3. Amidocyanogen
4. Carbamonitrile
5. Cyanoamine
6. Cyanogenamide
7. Alzogur
8. Aminoformonitrile
9. Cyanogen Nitride
10. N-cyanoamine
11. Tsaks
12. Nh2cn
13. Usaf Ek-1995
14. Nsc 24133
15. Carbodiamide
16. Dtxsid9034490
17. Chebi:16698
18. 21cp7826lc
19. Nsc-24133
20. Dtxcid7014490
21. Aminonitrile
22. Calcium Cyanamide, Citrated
23. Cyanamide, Citrated Calcium
24. 206-992-3
25. H2ncn
26. Cyanamide [jan]
27. Deurbraak
28. Cyanamide Aq
29. Ch2n2
30. H2n-c#n
31. Mfcd00007572
32. Aminoformonitrile, 50% Aqueous Solution
33. Ncgc00164378-01
34. 2669-76-3
35. Caswell No. 485a
36. Cas-420-04-2
37. Hsdb 1550
38. Einecs 206-992-3
39. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 014002
40. Brn 1732569
41. Cyanamine
42. Unii-21cp7826lc
43. Cyanamide (tn)
44. Cyanamide, 99%
45. Cyanamide (jp18)
46. Cyanamide [mi]
47. Cyanamide [hsdb]
48. Wln: Zcn
49. Bmse000656
50. Ec 206-992-3
51. Cyanamide [who-dd]
52. Schembl1972
53. Schembl62011
54. 4-03-00-00145 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
55. Chembl56279
56. Schembl1336076
57. Nsc24133
58. Waa42037
59. Tox21_112109
60. Tox21_300678
61. Bbl027645
62. Nsc267195
63. Stl281853
64. Akos009031491
65. Db02679
66. Fc02553
67. Nsc-267195
68. Ncgc00164378-02
69. Ncgc00164378-03
70. Ncgc00254586-01
71. Ns00004630
72. En300-19848
73. C01566
74. D00123
75. Q414555
76. F8881-3984
| Molecular Weight | 42.040 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CH2N2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.8 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 29.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Cyanamide (carbimide or calcium carbimide) has been used to treat chronic alcoholism for more than 45 years.
PMID:15996348 Trebol I et al; Dermatitis 16 (1): 32-3 (2005)
A pharmacokinetic and dynamic study of cyanamide, an inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) used as an adjuvant in the aversive therapy of chronic alcoholism, has been carried out in man after oral administrations. ... Blood ALDH activity were estimated after oral administration of 0.3, 1 and 1.5 mg/kg of cyanamide. One i.v. administration of 1 mg/kg was performed in order to determine the absolute bioavailability and the main pharmacokinetic parameters. Elimination half life and total plasma clearance values were 51.7 8.8 min and 14.4 2.7 mL/kg/min respectively. After oral administrations of 0.3, 1 and 1.5 mg/kg a rapid absorption rate was estimated with a Tmax values range of 10.5 to 15.5 min. The extent of absorption was not complete, oral bioavailability being 53%, 70% and 81% respectively. The presence of a first pass-effect is suggested. The inhibitory activity of cyanamide on blood ALDH reached the maximum value 4 hr after its administration and decreased progressively throughout six days period. The cyanamide plasma levels time course did not correlated with the pharmacodynamic time course responses.
PMID:1820876 Obach R et al; Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet Spec No 3: 185-90 (1991)
Cyanide was detected as a product of cyanamide oxidation by bovine liver catalase in vitro under conditions that also produced an active aldehyde dehydrogenase (AlDH) inhibitor. Cyanide formation was directly related to both cyanamide and catalase concentrations and was also dependent on incubation time. The apparent Km for this reaction was 172 microM. Cyanide formation was blocked by ethanol, a known substrate for catalase Compound I. The toxic effects of cyanamide in the dog, a species with limited capacity to conjugate cyanamide by N-acetylation, may be causally related to enhancement of this catalase-mediated pathway for cyanamide metabolism.
PMID:3590232 Shirota FN et al; Toxicol Lett. 37 (1): 7-12 (1987)
The main urinary metabolite of hydrogen cyanamide (cyanamide) in rat and man is acetylcyanamide (n-acetylcyanamide). An analytical method was developed to determine acetylcyanamide in the urine with a limit of quantification of <10 ug/l (mean recovery 96.1% using spikes of 20 ug/l; relative standard deviation < 4%. This methodology is based upon ion chromatography using column-switch techniques and UV detection. It could be demonstrated that in rats an average of 45.6% of oral applied cyanamide (10 mg/kg) was excreted in the urine as acetylcyanamide. In male human volunteers a mean of 40% of oral admin cyanamide (mean dose 0.25 mg/kg body weight) was excreted via the urine as acetylcyanamide. The same group of volunteers participated in skin absorption study with dermal application of the above cyanamide dose onto a skin surface area of 32 sq cm. Within an application period of 6 hr an average cyanamide quantity of 2.3 mg, was available for skin absorption. A mean portion of 7.7% of this quantity was found as acetylcyanamide in the urine of the participants. Findings from literature state that cyanamide is metabolized in vitro to cyanide. According to examinations performed in vivo, however, such a metabolic pathway seems to be irrelevant for man. In comparisons with the control values there was no significant incr of both the cyanide concn in the blood and the thiocyanate concentrations in the urine of the above volunteers after the described oral cyanamide admin.
PMID:1953345 Mertschenk B et al; Arch Toxicol 65 (4): 268-72 (1991)
Organic nitriles are converted into cyanide ions through the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. Cyanide is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Cyanide is mainly metabolized into thiocyanate by either rhodanese or 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase. Cyanide metabolites are excreted in the urine. (L96)
... Elimination half life and total plasma clearance values were 51.7 8.8 min and 14.4 2.7 mL/kg/min respectively. ...
PMID:1820876 Obach R et al; Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet Spec No 3: 185-90 (1991)
