
1. Ancef
2. Cefamedin
3. Cefamezine
4. Cefazolin Sodium
5. Cephamezine
6. Cephazolin
7. Cephazolin Sodium
8. Cephazolin, Sodium
9. Gramaxin
10. Kefzol
11. Sodium Cephazolin
12. Sodium, Cefazolin
13. Sodium, Cephazolin
14. Totacef
1. 25953-19-9
2. Cephazolin
3. Cephamezine
4. Cefazoline
5. Cefamezin
6. Cephazoline
7. Cephazolidin
8. Cefazolin Acid
9. Cefazolina
10. Cefazolinum
11. Cez
12. Kefzol
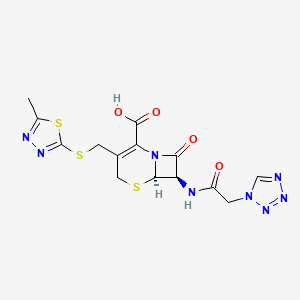
13. (6r,7r)-3-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-7-[[2-(tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
14. J01db04
15. Chebi:474053
16. Ihs69l0y4t
17. Elzogram
18. Cefazina
19. Firmacef
20. Liviclina
21. Atirin
22. Acef
23. (6r,7r)-3-{[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-7-[(1h-tetrazol-1-ylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
24. Ncgc00159465-02
25. Dsstox_cid_2753
26. Sk&f-41558
27. Dsstox_rid_76717
28. Cefazoline [inn-french]
29. Cefazolinum [inn-latin]
30. Dsstox_gsid_22753
31. (6r,7r)-7-(2-(1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido)-3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
32. Cefazolina [inn-spanish]
33. Cefazolin (usp)
34. (6r,7r)-7-(2-(1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido)-3-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-ylthio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
35. Smr000387025
36. Cas-25953-19-9
37. Skf 41558
38. Hsdb 3213
39. Einecs 247-362-8
40. Unii-ihs69l0y4t
41. Brn 4169371
42. Cefazolin [usp:inn:ban]
43. Cefazolin Acid,(s)
44. (6r,7r)-3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
45. (6r-trans)-3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-7-(((1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl)-amino)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
46. 7-(1-(1h-)-tetrazolylacetamido)-3-(2-(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazolyl)thiomethyl)delta3-cephem-4-carboxylic Acid
47. Nsc291561
48. Spectrum_000106
49. Cefazolin [inn]
50. Cefazolin [mi]
51. Cefazolin [hsdb]
52. Prestwick0_000736
53. Prestwick1_000736
54. Prestwick2_000736
55. Prestwick3_000736
56. Spectrum2_001140
57. Spectrum3_000330
58. Spectrum4_000267
59. Spectrum5_000665
60. Cefazolin [vandf]
61. Cefazolinfor Culture Media
62. Cefazolin [mart.]
63. Epitope Id:116197
64. Ec 247-362-8
65. Cefazolin [usp-rs]
66. Cefazolin [who-dd]
67. Schembl2841
68. Chembl1435
69. Lopac0_000274
70. Bspbio_000692
71. Bspbio_001939
72. Kbiogr_000734
73. Kbioss_000546
74. Mls001032060
75. Mls001049010
76. Divk1c_000014
77. Spbio_001039
78. Spbio_002631
79. Bpbio1_000762
80. Dtxsid2022753
81. Gtpl10935
82. Kbio1_000014
83. Kbio2_000546
84. Kbio2_003114
85. Kbio2_005682
86. Kbio3_001159
87. Cefazolin [usp Monograph]
88. Ninds_000014
89. Hms2268d15
90. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-[[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-7-[[2-(1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl]amino]-, (6r,7r)-
91. Hy-b1892
92. Zinc3830405
93. Tox21_111691
94. Bdbm50370587
95. S5936
96. Akos015962265
97. Tox21_111691_1
98. Db01327
99. Sdccgsbi-0050262.p005
100. Idi1_000014
101. Ncgc00022653-09
102. (6r,7r)-3-{[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio]methyl}-8-oxo-7-[(1h-tetrazol-1-ylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
103. 3-{[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-7beta-[(1h-tetrazol-1-ylacetyl)amino]-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic Acid
104. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-7-(((1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl)amino)-, (6r-trans)-
105. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido)-
106. Ac-16010
107. Bs-52943
108. Sbi-0050262.p004
109. Cs-0013954
110. C06880
111. D02299
112. 953c199
113. A818105
114. Q415739
115. W-107209
116. (6r, 7r)-3-[[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2- Yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-7-[[1h-tetrazol-1- Yl)acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2- Ene-2-carboxylic Acid
117. (6r,7r)-3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-7-(2-(1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido)5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
118. (6r,7r)-3-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-7-[[2-(tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid;cefazolin Acid
119. (6r,7r)-3-{[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-7-[2-(1h-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid
120. 5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic Acid, 3-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-7-(((1h-tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl)amino)-(6r-trans)
| Molecular Weight | 454.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H14N8O4S3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 454.03001448 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 454.03001448 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 235 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 740 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Kefzol |
| Active Ingredient | Cefazolin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 500mg base/vial; eq 10gm base/vial; eq 1gm base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Acs Dobfar |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Kefzol |
| Active Ingredient | Cefazolin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 500mg base/vial; eq 10gm base/vial; eq 1gm base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Acs Dobfar |
Mesh Heading: anti-bacterial agents
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Cefazolin (25953-19-9). Available from, as of April 14, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
Cephalosporins
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Cefazolin is indicated in the treatment of biliary tract infections caused by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 821
THERAP CAT: Antibacterial.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 326
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins are the most common side effects ... /and/ appear to be identical to those caused by the penicillins ... Patients who are allergic to one class of agents may manifest cross-reactivity when a member of the other class is admin. Immunological studies have demonstrated cross-reactivity in as many as 20% of patients who are allergic to penicillin, but clinical studies indicate a much lower frequency (about 1%) ... There are no skin tests that can reliably predict whether a patient will manifest an allergic reaction to the cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1212
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Cefazolin: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /From table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 140 (1994)
Positive direct and indirect antiglobulin (Coombs') test results have been reported in 3% or more of patients receiving a cephalosporin. The mechanism of this reaction is usually nonimmunologic in nature; a cephalosporin-globulin complex coats the erythrocytes and reacts nonspecifically with Coombs' serum. Nonimmunologic positive Coombs' test results are most likely to occur in patients who have received large doses of a cephalosporin or who have impaired renal function or hypoalbuminemia. /Cephalosporins/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 86
A positive Coombs reaction appears frequently in patients who receive large doses of a cephalosporin. Hemolysis is not usually associated with this phenomenon, although it has been reported. Cephalosporins have produced rare instances of bone-marrow depression, characterized by granulocytopenia ... Serious bleeding related either to ... thrombocytopenia, and/or platelet dysfunction has been reported with several beta-lactam antibiotics. This appears to be a particular problem with certain patients (elderly, poorly nourished, or those with renal insufficiency) who are receiving moxalactam. /Cephalosporins/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1212
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (38 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Mainly used to treat bacterial infections of the skin. It can also be used to treat moderately severe bacterial infections involving the lung, bone, joint, stomach, blood, heart valve, and urinary tract. It is clinically effective against infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci species of Gram positive bacteria. May be used for surgical prophylaxis; if required metronidazole may be added to cover B. fragilis.
FDA Label
Cefazolin (also known as cefazoline or cephazolin) is a semi-synthetic first generation cephalosporin for parenteral administration. Cefazolin has broad-spectrum antibiotic action due to inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. It attains high serum levels and is excreted quickly via the urine.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J01DB04
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01D - Other beta-lactam antibacterials
J01DB - First-generation cephalosporins
J01DB04 - Cefazolin
Absorption
Not absorbed from GI tract. Must be administered parenterally. Peak serum concentrations attained 1-2 hours post intramuscular injection.
Route of Elimination
Cefazolin is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers. Cefazolin is excreted unchanged in the urine. In the first six hours approximately 60% of the drug is excreted in the urine and this increases to 70%-80% within 24 hours.
CEFAZOLIN CROSSES INFLAMED SYNOVIAL MEMBRANES, YIELDING SYNOVIAL FLUID ANTIBIOTIC CONCN GREATER THAN THOSE IN SERUM WITHIN 2 HR OF IM DOSE... CLEARANCE OF CEFAZOLIN BY KIDNEY IS PREDOMINANTLY BY GLOMERULAR FILTRATION, & CLEARANCE RATES ARE LINEARLY RELATED TO CREATININE CLEARANCE...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 176
CEFAZOLIN RAPIDLY PENETRATES BODY TISSUES IN RATS, & DECLINE OF TISSUE ANTIBIOTIC LEVELS AFTER DOSING IS FIRST-ORDER. VERY SMALL AMT OF DRUG CROSS BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER & PLACENTAL TRANSFER APPEARS NEGLIGIBLE...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 176
...DURING STUDIES OF CEFAZOLIN TRANSFERENCE IN MAN, 92-100% OF ADMIN DOSE WAS ACCOUNTED FOR BY URINARY EXCRETION...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 106
... About 80% of cefazolin is reversibly bound to plasma protein ... is excreted in bile even when there is gallbladder disease ... concn may normally exceed that in plasma by 3 times.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1161
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CEFAZOLIN (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Not metabolized.
Metabolism of cefazolin is very limited in most of the animal species tested and in /humans/. After parenteral administration of cefazolin nearly 100% is excreted unchanged in urine with 24 hours in /humans/, dog and horse. No major metabolites seem to occur.
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Cefazolin, Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/0126/96-Final (July 1996). Available from, as of July 21, 2006: https://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/document_library/landing/document_library_search.jsp&murl=menus/document_library/document_library.jsp&mid
The serum half-life is approximately 1.8 hours following IV administration and approximately 2.0 hours following IM administration.
The serum half-life of cefazolin is 1.2-2.2 hr in adults with normal renal function. In one study, half-life was 6.8 hr in 1 adult with a creatinine clearance of 26 ml/min, 12 hr in 3 adults with creatinine clearances of 12-17 ml/min, and 57 hr in 3 adults with creatinine clearances less than 5 ml/min.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 93
In vitro tests demonstrate that the bactericidal action of cephalosporins results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, it inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins.
Bactericidal; action depends on ability to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins located in bacterial cytoplasmic membranes; cephalosporins inhibit bacterial septum and cell wall synthesis, probably by acylation of membrane-bound transpeptidase enzymes. This prevents cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains, which is necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. Also, cell division and growth are inhibited, and lysis and elongation of susceptible bacteria frequently occur. Rapidly dividing bacteria are those most susceptible to the action of cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 822