


1. Calcium Resonium
2. Kalimate
3. Kayexalate
4. Poly(styrenesulfonate)
5. Polystyrene Sulfonate
6. Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid
7. Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid, Homopolymer, Calcium Salt
8. Psso3
9. Resonium-a
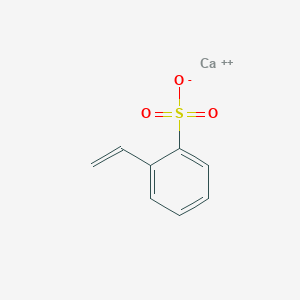
1. 37286-92-3
2. Calciumpolystyrenesulphonate
3. Calcium;2-ethenylbenzenesulfonate
4. Kalimate
5. Kmp-ca
6. Calcium Polystyrene Sulfonate [jan]
7. Calcium Salt Of Sulfonated Styrene Polymer
8. Unii-hui2s00793
9. Benzenesulfonic Acid, Ethenyl-, Homopolymer, Calcium Salt
10. Hui2s00793
11. B2699-019837
12. Calcium Polystyrene Sulfonate (poly(styrenesulfonic Acid) Calcium Salt)
| Molecular Weight | 223.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H7CaO3S+ |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 222.9741811 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 222.9741811 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 65.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 1 |
| Complexity | 237 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Cation Exchange Resins
High molecular weight insoluble polymers which contain functional anionic groups that are capable of undergoing exchange reactions with cations. (See all compounds classified as Cation Exchange Resins.)
Chelating Agents
Chemicals that bind to and remove ions from solutions. Many chelating agents function through the formation of COORDINATION COMPLEXES with METALS. (See all compounds classified as Chelating Agents.)
