


1. Bornaprine Hydrochloride
2. Kr 339
3. Sormodren
1. 20448-86-6
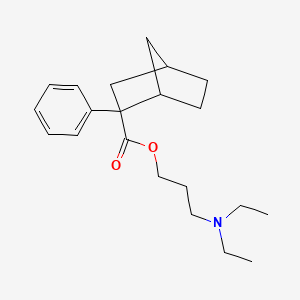
2. 3-(diethylamino)propyl 2-phenylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylate
3. Bornaprine (inn)
4. 3-(diethylamino)propyl 2-phenyl-2-norbornanecarboxylate
5. Schembl924755
6. Chembl4297087
7. Dtxsid20864944
8. Chebi:135406
9. D07302
10. Q4946040
| Molecular Weight | 329.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H31NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 329.235479232 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 329.235479232 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 414 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Muscarinic Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous ACETYLCHOLINE or exogenous agonists. Muscarinic antagonists have widespread effects including actions on the iris and ciliary muscle of the eye, the heart and blood vessels, secretions of the respiratory tract, GI system, and salivary glands, GI motility, urinary bladder tone, and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Muscarinic Antagonists.)
N - Nervous system
N04 - Anti-parkinson drugs
N04A - Anticholinergic agents
N04AA - Tertiary amines
N04AA11 - Bornaprine