

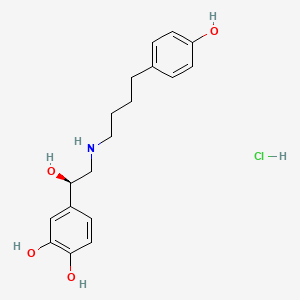

1. Arbutamine
2. Arbutamine Hydrochloride, (r)-isomer
3. Genesa
1. Genesa
2. Arbutamine Hcl
3. Arbutamine Hydrochloride [usan]
4. 125251-66-3
5. K0nf2cpj7f
6. Gp-2-121-3
7. (r)-3,4-dihydroxy-alpha-(((4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)methyl)benzyl Alcohol Hydrochloride
8. Arbutamine (hydrochloride)
9. Arbutamine Hydrochloride (usan)
10. Unii-k0nf2cpj7f
11. Genesa (tn)
12. Schembl40757
13. Chembl1200385
14. Dtxsid40154718
15. Arbutamine Hydrochloride [mi]
16. Hy-16056a
17. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)ethyl)-, (r)-hydrochloride
18. Arbutamine Hydrochloride [mart.]
19. Arbutamine Hydrochloride [vandf]
20. Arbutamine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
21. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)ethyl)-, (r)-, Hydrochloride
22. Cs-0108214
23. Arbutamine Hydrochloride [orange Book]
24. D02976
25. Q27281787
26. 4-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butylamino]ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol;hydrochloride
27. (r)-3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-(((4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)methyl)benzyl Alcohol Hydrochloride
28. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl)amino)ethyl)-, (r) Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 353.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H24ClNO4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 353.1393859 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 353.1393859 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 93 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 320 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Adrenergic beta-Agonists
Drugs that selectively bind to and activate beta-adrenergic receptors. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Agonists.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
