
1. Am 0715
2. Am 715
3. Am-0715
4. Am-715
5. Am0715
6. Mk 0366
7. Mk 366
8. Mk-0366
9. Mk-366
10. Mk0366
11. Mk366
12. Noroxin
1. 70458-96-7
2. Noroxin
3. Norfloxacine
4. Chibroxin
5. Baccidal
6. Sebercim
7. Mk-366
8. Norfloxacinum
9. Norfloxacino
10. Barazan
11. Fulgram
12. Nflx
13. Am-715
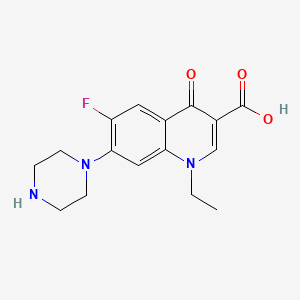
14. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
15. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
16. Lexinor
17. Zoroxin
18. Mfcd00079532
19. 1,4-dihydro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
20. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
21. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-
22. Mk-0366
23. Chembl9
24. Chebi:100246
25. 1-ethyl-6-fluor-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-chinolincarbonsaeure
26. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
27. Nsc-757250
28. Mls000069650
29. N0f8p22l1p
30. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
31. Ncgc00016916-01
32. Ncgc00016916-09
33. Smr000058200
34. Norfloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
35. Cas-70458-96-7
36. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-
37. Dsstox_cid_17680
38. Dsstox_rid_79353
39. Dsstox_gsid_37680
40. Norfloxacine [inn-french]
41. Norfloxacinum [inn-latin]
42. Norfloxacino [inn-spanish]
43. Am 715
44. Norphloxacine
45. Norflo
46. Mk 0366
47. Noroxin (tn)
48. Ccris 6302
49. Sr-01000000222
50. Einecs 274-614-4
51. Brn 0567897
52. Unii-n0f8p22l1p
53. Chibroxine
54. Chibroxol
55. Gonorcin
56. Nolicin
57. Noracin
58. Noraxin
59. Norocin
60. Noroxine
61. Norxacin
62. Uroxacin
63. Utinor
64. Noflo
65. Hsdb 8029
66. Norfloxacine,(s)
67. Prestwick_633
68. Norfloxacin [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
69. Norfloxacin (norxacin)
70. Norfloxacin - Norxacin
71. Spectrum_001017
72. Norfloxacin [mi]
73. Opera_id_1423
74. Prestwick0_000221
75. Prestwick1_000221
76. Prestwick2_000221
77. Prestwick3_000221
78. Spectrum2_001017
79. Spectrum3_000524
80. Spectrum4_000453
81. Spectrum5_001154
82. Norfloxacin [inn]
83. Norfloxacin [jan]
84. Norfloxacin [usan]
85. Epitope Id:119068
86. Norfloxacin [vandf]
87. Schembl3473
88. Norfloxacin [mart.]
89. Oprea1_375152
90. Bspbio_000261
91. Bspbio_002107
92. Kbiogr_000866
93. Kbioss_001497
94. Norfloxacin [usp-rs]
95. Norfloxacin [who-dd]
96. Mls006011446
97. Bidd:gt0725
98. Divk1c_000084
99. Spectrum1500440
100. Spbio_001173
101. Spbio_002182
102. Bpbio1_000289
103. Zinc3742
104. Norfloxacin (jp17/usp/inn)
105. Dtxsid7037680
106. Bcbcmap01_000218
107. Hms500e06
108. Kbio1_000084
109. Kbio2_001497
110. Kbio2_004065
111. Kbio2_006633
112. Kbio3_001607
113. Norfloxacin [orange Book]
114. Ninds_000084
115. Norfloxacin For System Suitability
116. Hms1568n03
117. Hms1920b16
118. Hms2090f03
119. Hms2091j16
120. Hms2095n03
121. Hms2235g03
122. Hms3712n03
123. Norfloxacin [ep Monograph]
124. Norfloxacin [usp Impurity]
125. Norfloxacin For Peak Identification
126. Pharmakon1600-01500440
127. Act02630
128. Albb-015911
129. Bcp27734
130. Hy-b0132
131. Rkl10074
132. Tox21_110682
133. Tox21_113441
134. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
135. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazinylhydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
136. Bbl005569
137. Bdbm50045000
138. Ccg-40235
139. Nsc757250
140. S1509
141. Stk177250
142. Akos000417391
143. Norfloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Ethanol
144. Tox21_110682_1
145. Ac-6855
146. Bcp9000993
147. Cs-1906
148. Db01059
149. Ks-5007
150. Nsc 757250
151. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
152. Idi1_000084
153. Smp1_000216
154. Ncgc00016916-02
155. Ncgc00016916-03
156. Ncgc00016916-04
157. Ncgc00016916-05
158. Ncgc00016916-06
159. Ncgc00016916-07
160. Ncgc00016916-08
161. Ncgc00016916-11
162. Ncgc00016916-12
163. Ncgc00021725-03
164. Ncgc00021725-04
165. Sy051390
166. Sbi-0051464.p002
167. Ft-0630800
168. Ft-0673085
169. N0817
170. C06687
171. D00210
172. N-8650
173. Ab00052059-18
174. Ab00052059-19
175. Ab00052059_20
176. Ab00052059_21
177. Norfloxacin, Analytical Standard, >=98% (tlc)
178. Norfloxacin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
179. 458n967
180. Norfloxacin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
181. Q417897
182. Sr-01000000222-2
183. Sr-01000000222-3
184. Brd-k11196887-001-05-5
185. Brd-k11196887-001-15-4
186. Z56926638
187. Norfloxacin, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
188. Norfloxacin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
189. 1-ethyl-3-carboxy-6-fluoro-7-(piperazinyl-1)-quinolin-4(1h)-one
190. Norfloxacin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
191. Norfloxacin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
192. (nflx)1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
193. 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
194. 1-ethyl-4-oxo-6-fluoro-7-(piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
195. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline Carboxylic Acid
196. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-quinoline-3-carboxylicacid
197. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
198. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinoline Carboxylic Acid
199. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(1-piperazinyl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
200. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid #
201. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
202. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
203. 7-(1-piperazinyl)-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
204. Norfloxacin For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
205. Norfloxacin For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
206. (norfloxacin)1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
207. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4,4a,8a-tetrahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid (norfloxacin)
208. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid (norfloxacin)
209. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid(1-norfloxacin)
210. 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid(norfloxacin)
| Molecular Weight | 319.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H18FN3O3 |
| XLogP3 | -1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 319.13321961 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 319.13321961 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 72.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 519 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Bacterial Agents; Enzyme Inhibitors; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Oral norfloxacin is used for the treatment of prostatitis caused by E. coli. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 397
Oral norfloxacin is used in adults for the treatment of complicated UTIs caused by susceptible E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, Ps. aeruginosa, S. marcescens, or E. faecalis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 397
Oral norfloxacin is used in adults for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) (including cystitis) caused by susceptible Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter aerogenes, E. cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, ... Proteus mirabilis, P. vulgaris, ... Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ... . The drug also is used orally in adults for the treatment of uncomplicated UTIs caused by susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococci), or Enterococcus faecalis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 397
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Norfloxacin (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Noroxin, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for NOROXIN (Norfloxacin) tablet, film coated (February 2012). Available from, as of March 2, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=36087c76-5da9-4fab-e88f-da1d5a579d8e
WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Noroxin, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid Noroxin in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for NOROXIN (Norfloxacin) tablet, film coated (February 2012). Available from, as of March 2, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=36087c76-5da9-4fab-e88f-da1d5a579d8e
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving quinolone therapy, including Noroxin. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, pharyngeal or facial edema, dyspnea, urticaria and itching. Only a few patients had a history of hypersensitivity reactions. If an allergic reaction to norfloxacin occurs, discontinue the drug. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management, including intubation, should be administered as indicated.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for NOROXIN (Norfloxacin) tablet, film coated (February 2012). Available from, as of March 2, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=36087c76-5da9-4fab-e88f-da1d5a579d8e
Other serious and sometimes fatal events, some due to hypersensitivity, and some due to uncertain etiology, have been reported rarely in patients receiving therapy with quinolones, including Noroxin. These events may be severe and generally occur following the administration of multiple doses. Clinical manifestations may include one or more of the following: fever, rash or severe dermatologic reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome); vasculitis; arthralgia; myalgia; serum sickness; allergic pneumonitis; interstitial nephritis; acute renal insufficiency or failure; hepatitis; jaundice; acute hepatic necrosis or failure; anemia, including hemolytic and aplastic; thrombocytopenia, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; leukopenia; agranulocytosis; pancytopenia; and/or other hematologic abnormalities.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for NOROXIN (Norfloxacin) tablet, film coated (February 2012). Available from, as of March 2, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=36087c76-5da9-4fab-e88f-da1d5a579d8e
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Norfloxacin (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of urinary tract infection
FDA Label
Norfloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Norfloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian.
Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP1A2. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors.)
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J01MA06
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA06 - Norfloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AE - Fluoroquinolones
S01AE02 - Norfloxacin
Absorption
Rapid
Route of Elimination
Norfloxacin is eliminated through metabolism, biliary excretion, and renal excretion. It is expected to undergo both glomerular filtration and tubular secretion during renal excretion, as shown by its high renal clearance rate of approximately 275 mL/min.
Norfloxacin crosses the placenta and is distributed into cord blood and amniotic fluid. It is not known whether the drug is distributed into milk. Norfloxacin was not detected in the milk of lactating women following a single 200-mg oral dose of the drug, but the possibility of distribution into milk following higher doses remains to be determined. Some other quinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin ofloxacin) are distributed into milk.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
In adults who received 400 mg of oral norfloxacin twice daily, prostatic tissue concentrations of the drug ranged from 0.24-4.65 ug/g in specimens obtained 1-4 hours after the second dose; concurrent serum concentrations ranged from 0.42-5.3 ug/mL. Norfloxacin is 10-15% bound to serum proteins.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
Biliary concentrations of norfloxacin may be up to 10 times higher than concurrent serum concentrations. In cholecystectomy patients who received a single 400-mg oral dose of norfloxacin prior to surgery, concentrations of the drug ranged from 0.6-15.6 ug/mL in gallbladder bile, from 0.4-7.5 mcg/g in gallbladder tissue, and from 0.4-1.8 ug/mL in serum in specimens obtained approximately 3.5-6 hours after the dose.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
There is limited information on the distribution of norfloxacin. Following oral administration in adults, norfloxacin is distributed into renal parenchyma, gallbladder, liver, prostatic tissue, testicles, seminal fluid, uterus, fallopian tubes, cervical and vaginal tissue, blister fluid, tonsils, maxillary sinus mucosa, sputum, and bile.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Norfloxacin (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Via liver and kidney
Norfloxacin is eliminated by renal and nonrenal mechanisms. The drug is partially metabolized by modification of the piperazinyl group to 6 metabolites, designated M-1, M-2, M-3, M-4(1), M-4(2), and M-5.2 Although some of the metabolites are microbiologically active, they are less active than the parent drug. It has been suggested that norfloxacin undergoes first-pass metabolism in the liver, but further study is needed to fully elucidate the metabolic fate of the drug.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
Pefloxacin, N-desmethyl is a known human metabolite of Pefloxacin.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
3-4 hours
In patients with impaired renal function, serum concentrations of norfloxacin are higher and its half-life is prolonged. In adults with renal impairment, the half-life of norfloxacin averaged 4.4, 6.6, or 7.6 hours in adults with creatinine clearances of 30-80, 10-29, or less than 10 mL/minute per 1.73 sq m, respectively. Limited data suggest that half-life of the drug is not substantially affected by hepatic impairment.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
The effective plasma or serum half-life of norfloxacin in adults with normal renal function is 2.3-4 hours. The effective half-life of the drug averages 4 hours in geriatric individuals 65-75 years of age with renal function normal for their age.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 404
The bactericidal action of Norfloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. Norfloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic agent that is shown to be effective against various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial species. The fluorine atom at the 6 position increases potency against gram-negative organisms, and the piperazine moiety at the 7 position is responsible for anti-pseudomonal activity
Norfloxacin usually is bactericidal in action. Like other fluoroquinolone anti-infectives, norfloxacin inhibits DNA synthesis in susceptible organisms via inhibition of type II DNA topoisomerases (DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 401
Fluoroquinolones prolong the QT interval by blocking voltage-gated potassium channels, especially the rapid component of the delayed rectifier potassium current I(Kr), expressed by HERG (the human ether-a-go-go-related gene). According to the available case reports and clinical studies, moxifloxacin carries the greatest risk of QT prolongation from all available quinolones in clinical practice and it should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors for Torsades de pointes (TdP).
PMID:22156660 Briasoulis A et al; Cardiology 120 (2): 103-10 (2011)