
1. Cyanonitrosylferrate
2. Disodium Salt Nitroprusside
3. Ketostix
4. Naniprus
5. Nipride
6. Nipruton
7. Nitriate
8. Nitroferricyanide
9. Nitropress
10. Nitroprussiat Fides
11. Nitroprusside
12. Nitroprusside, Disodium Salt
13. Nitroprusside, Disodium Salt, Dihydrate
14. Nitroprusside, Sodium
15. Sodium Nitroprusside
1. Nitroprusside [who-dd]
2. Dtxsid2046963
3. 169d1260km
| Molecular Weight | 215.94 g/mol |
|---|---|
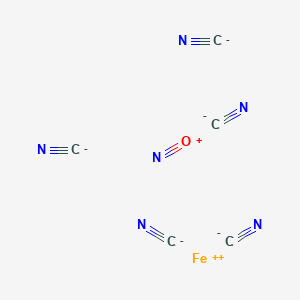
| Molecular Formula | C5FeN6O-2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 215.948294 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 215.948294 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 144 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | -2 |
| Complexity | 20 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 7 |
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Indicators and Reagents
Substances used for the detection, identification, analysis, etc. of chemical, biological, or pathologic processes or conditions. Indicators are substances that change in physical appearance, e.g., color, at or approaching the endpoint of a chemical titration, e.g., on the passage between acidity and alkalinity. Reagents are substances used for the detection or determination of another substance by chemical or microscopical means, especially analysis. Types of reagents are precipitants, solvents, oxidizers, reducers, fluxes, and colorimetric reagents. (From Grant and Hackh's Chemical Dictionary, 5th ed, p301, p499) (See all compounds classified as Indicators and Reagents.)
Nitric Oxide Donors
A diverse group of agents, with unique chemical structures and biochemical requirements, which generate NITRIC OXIDE. These compounds have been used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and the management of acute myocardial infarction, acute and chronic congestive heart failure, and surgical control of blood pressure. (Adv Pharmacol 1995;34:361-81) (See all compounds classified as Nitric Oxide Donors.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)