

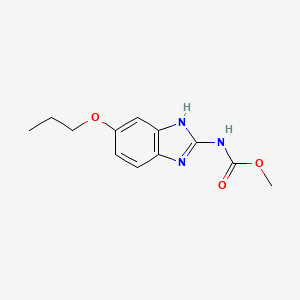

1. Methyl 5-n-propoxy-2-benzimidazolecarbamate
1. 20559-55-1
2. Loditac
3. Filaribits Plus
4. Anthelcide Eq
5. Oxibendazolo
6. Sk&f 30310
7. Methyl 5-propoxy-2-benzimidazolecarbamate
8. Methyl N-(6-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
9. Methyl (5-propoxy-1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)carbamate
10. Methyl 5-n-propoxy-2-benzimidazole Carbamate
11. Nsc-758459
12. 5-propoxy-2-benzimidazolecarbamic Acid Methyl Ester
13. Mls000069646
14. 2-benzimidazolecarbamic Acid, 5-propoxy-, Methyl Ester
15. Carbamic Acid, (5-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-, Methyl Ester
16. 022n12kj0x
17. Methyl (5-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
18. Methyl N-(5-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
19. Mfcd00133728
20. Sk&f-30310
21. Ncgc00018238-04
22. (5-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
23. Smr000058208
24. Carbamic Acid, N-(6-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-, Methyl Ester
25. Oxibendazole 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
26. Dsstox_cid_25625
27. Dsstox_rid_81010
28. Dsstox_gsid_45625
29. Oxibendazolum
30. Oxibendazolum [inn-latin]
31. Oxibendazolo [inn-spanish]
32. Aj119,(+)
33. Cas-20559-55-1
34. Einecs 243-877-7
35. Skf 30310
36. Oxybendazole
37. Unii-022n12kj0x
38. Oxibendazole [usan:inn:ban]
39. N-(2-(5-propoxybenzimidazolyl)) Methyl Carbamate
40. Anthelcide Eq (tn)
41. Oxibendazole, ~98%
42. Spectrum_001699
43. N-(propoxy-5, Benzimidazolyl)-2, Carbamate De Methyle [french]
44. Spectrum2_001556
45. Spectrum3_001951
46. Spectrum4_000836
47. Spectrum5_001219
48. Oxibendazole [mi]
49. Oxibendazole (usan/inn)
50. Oxibendazole [inn]
51. Oxibendazole [usan]
52. Cid_4622
53. Bspbio_003551
54. Kbiogr_001411
55. Kbioss_002179
56. Oxibendazole [mart.]
57. Mls006011733
58. Divk1c_000096
59. Schembl168101
60. Spectrum1503373
61. Spbio_001432
62. Chembl1087630
63. Dtxsid5045625
64. N-(propoxy-5, Benzimidazolyl)-2, Carbamate De Methyle
65. Bdbm31048
66. Chebi:92907
67. Hms500e18
68. Kbio1_000096
69. Kbio2_002179
70. Kbio2_004747
71. Kbio2_007315
72. Kbio3_002864
73. Oxibendazole [green Book]
74. Ninds_000096
75. Hms1922a22
76. Hms2090f21
77. Hms2094m09
78. Hms3713j18
79. Pharmakon1600-01503373
80. Hy-b0299
81. Zinc4685859
82. Tox21_110844
83. Ccg-39334
84. Nsc758459
85. S1851
86. Stl301145
87. Akos015895323
88. Tox21_110844_1
89. Ac-8714
90. Ccg-220608
91. Db04910
92. Nsc 758459
93. Idi1_000096
94. Oxibendazole 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
95. Ncgc00018238-01
96. Ncgc00018238-02
97. Ncgc00018238-03
98. Ncgc00018238-05
99. Ncgc00018238-06
100. Ncgc00018238-07
101. Ncgc00018238-08
102. Ncgc00018238-09
103. Ncgc00023557-03
104. Ncgc00023557-04
105. Ncgc00023557-05
106. As-12166
107. Sy067010
108. Db-045281
109. 5-propoxy-2-(carbomethoxyamino)benzimidazole
110. Albendazole Impurity I [ep Impurity]
111. Ft-0630464
112. O0499
113. C73898
114. D05293
115. Methyl 5-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
116. Ab00052350-06
117. Ab00052350_07
118. Ab00052350_08
119. Oxibendazole, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
120. 559o551
121. A814696
122. Aj-119/34637010
123. Sr-01000000182
124. Sr-05000002065
125. Q7115623
126. Sr-01000000182-2
127. Sr-05000002065-1
128. W-107609
129. Brd-k52075715-001-02-6
130. Brd-k52075715-001-03-4
131. Brd-k84514357-001-02-9
132. Methyl (6-propoxy-1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)carbamate
133. N-(6-propoxy-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
134. Oxibendazole, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 249.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H15N3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 249.11134135 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 249.11134135 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 76.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 288 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in infectious and parasitic disease (unspecified) and pediatric indications.
Anthelmintics
Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of HELMINTHIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Anthelmintics.)
Hepatic
Oxibendazole causes degenerative alterations in the tegument and intestinal cells of the worm by binding to the colchicine-sensitive site of tubulin, thus inhibiting its polymerization or assembly into microtubules. The loss of the cytoplasmic microtubules leads to impaired uptake of glucose by the larval and adult stages of the susceptible parasites, and depletes their glycogen stores. Degenerative changes in the endoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria of the germinal layer, and the subsequent release of lysosomes result in decreased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy required for the survival of the helminth. Due to diminished energy production, the parasite is immobilized and eventually dies.