



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
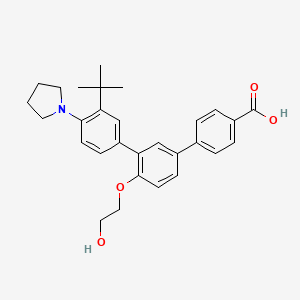

1. Aklief
2. Cd5789
1. 895542-09-3
2. Cd5789
3. Cd-5789
4. 0j8rn2w0hk
5. 4-[3-(3-tert-butyl-4-pyrrolidin-1-ylphenyl)-4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]benzoic Acid
6. 3''-(tert-butyl)-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4''-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-[1,1':3',1''-terphenyl]-4-carboxylic Acid
7. 3''-tert-butyl-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4''-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)(1,1':3',1'')terphenyl-4-carboxylic Acid
8. Aklief
9. Trifarotene [inn]
10. Trifarotene [usan:inn]
11. Unii-0j8rn2w0hk
12. (1,1':3',1''-terphenyl)-4-carboxylic Acid, 3''-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4''-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-
13. [1,1':3',1''-terphenyl]-4-carboxylic Acid, 3''-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4''-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-
14. Aklief (tn)
15. Cd 5789
16. Trifarotene [mi]
17. Trifarotene (usan/inn)
18. Trifarotene [usan]
19. Trifarotene [who-dd]
20. Schembl381493
21. Gtpl9962
22. Chembl3707313
23. Dtxsid30237781
24. Trifarotene [orange Book]
25. Bcp31392
26. Ex-a2704
27. Bdbm50457548
28. Akos037649283
29. At10456
30. Db12808
31. Compound 15b [pmid: 29706423]
32. Bs-17812
33. Bt166038
34. Hy-100256
35. Cs-0018407
36. D11225
37. Cd5789; Cd-5789; Cd 5789
38. Q27236856
| Molecular Weight | 459.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H33NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 6.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 459.24095853 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 459.24095853 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 70 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 647 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Trifarotene is indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris in patients 9 years of age and older.
Treatment of ichthyoses
Treatment of acne
Trifarotene exerts its effects via agonism at retinoid receptors - these receptors function to alter DNA transcription, resulting in downstream modulation of the expression of various genes involved in acne pathogenesis. It may be associated with skin irritation and should not be applied to cuts, abrasions, or otherwise damaged skin. As trifarotene may result in photosensitivity, patients should be cautioned to avoid excess sun exposure and to use sunscreen and/or protective clothing if exposure is unavoidable.
Dermatologic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders or for the routine care of skin. (See all compounds classified as Dermatologic Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D10 - Anti-acne preparations
D10A - Anti-acne preparations for topical use
D10AD - Retinoids for topical use in acne
D10AD06 - Trifarotene
Absorption
Systemic absorption of trifarotene is minimal. In a pharmacokinetic study involving 19 subjects, systemic concentrations were only quantifiable in 7 - steady state Cmax values ranged from undetectable (<5 pg/mL) to 10 pg/mL and AUC0-24h ranged from 75 to 104 pg.h/mL.
Route of Elimination
Trifarotene is eliminated primarily in the feces.
Trifarotene is rapidly metabolized in human hepatocytes - its observed half-life in human keratinocytes is >24 hours, whereas half-life in human liver microsomes is approximately 5 minutes. Metabolism of trifarotene is catalyzed primarily by CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP2C8, and, to a lesser extent, CYP2B6.
The terminal half-life of trifarotene is typically between 2 to 9 hours.
Trifarotene is a potent and selective agonist of retinoic acid receptor- (RAR-). It has significantly less activity at RAR- and RAR- (16- and 65-fold lower than activity at RAR-, respectively), and has no activity at retinoid X receptors (RXRs). Agonism at retinoic acid receptors results in dimerization, and the resulting receptor-ligand dimer binds to specific DNA regulatory sequences (retinoic acid response elements, or RAREs) in the promotor regions of retinoid-responsible genes. Downstream alterations to gene expression induced by binding to these regions is the principle mechanism through which trifarotene exerts its comedolytic, anti-inflammatory, and depigmenting effects. Like other retinoids, trifarotene influences the expression of a number of genes involved in retinoid metabolism, epidermal differentiation/proliferation, and epidermal response to stress. In addition, trifarotene appears to modulate retinoid-mediated pathways involved in proteolysis, skin hydration, and cell adhesion - modulation of these additional pathways has not been observed with other retinoids and may therefore be unique to trifarotene.


