



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
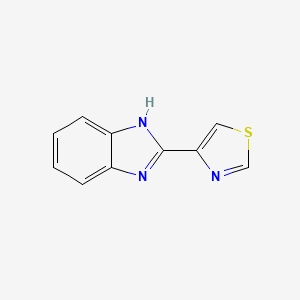

1. 2-(4'-thiazolyl)benzimidazole
2. Mintesol
3. Mintezol
4. Omnizole
5. Thibendole
6. Tiabendazol
1. 148-79-8
2. Tiabendazole
3. Mintezol
4. 2-(4-thiazolyl)benzimidazole
5. Omnizole
6. Thiabenzole
7. Equizole
8. Minzolum
9. Thiabendazol
10. Tiabendazol
11. Lombristop
12. Mintesol
13. Nemapan
14. Thibenzole
15. Bovizole
16. Thibenzol
17. Thiaben
18. Testo
19. Bioguard
20. Eprofil
21. Mertect
22. Mycozol
23. Pitrizet
24. Polival
25. Tebuzate
26. Tiabenda
27. Triasox
28. Mertec
29. Tobaz
30. Tbdz
31. Thibenzole Att
32. Apl-luster
33. Top Form Wormer
34. Cropasal
35. Sistesan
36. Thibendole
37. Ormogal
38. Storite
39. Thibenzole 200
40. Tecto Rph
41. 2-(4-thiazolyl)-1h-benzimidazole
42. Hokustar Hp
43. 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1h-benzimidazole
44. 4-(1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)thiazole
45. Mertect 160
46. Tecto 10p
47. Tecto 40f
48. Tecto 60
49. 1h-benzimidazole, 2-(4-thiazolyl)-
50. Sanaizol 100
51. Chemviron Tk 100
52. Thiabendazolum
53. Thiabendole
54. Tiabendazolum
55. Biogard
56. Drawipas
57. Mintezole
58. Tecto
59. Mertect Lsp
60. E-z-ex
61. Equizole A
62. Tbz 60w
63. 4-(2-benzimidazolyl)thiazole
64. Captan T
65. Metasol Tk 100
66. 2-(thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole
67. Helmindrax Octelmin
68. Thiabenzazole
69. Thiprazole
70. Tresaderm
71. Tubazole
72. 2-thiazole-4-ylbenzimidazole
73. Hymush
74. Nemacin
75. Mertect 340f
76. Metasol Tk-100
77. Syntol M100
78. Mk 360
79. Equivet Tz
80. Tecto B
81. Tibimix 20
82. Arbotect
83. 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole
84. Thiabendazole [bsi:iso]
85. Tbz 6
86. Benzimidazole, 2-(4-thiazolyl)-
87. 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1h-1,3-benzodiazole
88. Mk-360
89. 2-(4'-thiazolyl)benzimidazole
90. Mintezol (tn)
91. 4-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1,3-thiazole
92. Thiabendazole (usp)
93. Tiabendazole (jan/inn)
94. 4-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)thiazole
95. 1yvm
96. G 491
97. 5-(4-thiazolyl)benzimidazole
98. Tiabendazole [inn]
99. Rph
100. Nsc-90507
101. Chembl625
102. Nsc-525040
103. Mls000053094
104. N1q45e87dt
105. Chebi:45979
106. Nsc90507
107. Nsc525040
108. 2-(4-thiazolyl)-benzimidazole
109. Ncgc00016410-06
110. Ncgc00016410-13
111. Cas-148-79-8
112. E233
113. Smr000058170
114. 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1h-benzoimidazole
115. Rtu Flowable Fungicide
116. Dsstox_cid_1337
117. 4-(1h-1,3-benzodiazol-2-yl)-1,3-thiazole
118. Dsstox_rid_76091
119. Dsstox_gsid_21337
120. Metasol Tk 10
121. Tiabendazolum [inn-latin]
122. Thiabendazole [usan:ban]
123. Tbz-6
124. 2-[4-thiazoly]benzimidazole
125. Caswell No. 849a
126. Tiabendazol [inn-spanish, French]
127. Wln: T56 Bm Dnj C-et5n Csj
128. Metasol Tk 25
129. Ccris 4510
130. Thiabendazole [iso]
131. Hsdb 2027
132. 2-thiazol-4-yl-1h-benzoimidazole
133. Sr-01000000188
134. Einecs 205-725-8
135. Nsc 90507
136. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 060101
137. Nsc 525040
138. Thiabendazole [usan:usp]
139. Brn 0611403
140. Unii-n1q45e87dt
141. 2-(4-thiazoly)-benzimidazole
142. Ai3-50598
143. Tiabendazole, Inn
144. 2-(4-thiazolyl)-1h-benzoimidazole
145. Thiabendazole(usan)
146. Prestwick_813
147. Mfcd00005587
148. Thiabendazole, 98%
149. Spectrum_000039
150. Cpd000058170
151. Opera_id_336
152. Prestwick0_000524
153. Prestwick1_000524
154. Prestwick2_000524
155. Prestwick3_000524
156. Spectrum2_001331
157. Spectrum3_001407
158. Spectrum4_000354
159. Spectrum5_001009
160. Thiabendazole [mi]
161. Tiabendazole [jan]
162. Nciopen2_005709
163. Thiabendazole [hsdb]
164. Thiabendazole [inci]
165. Thiabendazole [usan]
166. Schembl19842
167. Bspbio_000507
168. Bspbio_003054
169. Kbiogr_000787
170. Kbioss_000399
171. Thiabendazole [vandf]
172. Tiabendazole [mart.]
173. 2(4-thiazolyl)-benzimidazole
174. Mls000069718
175. Bidd:er0372
176. Divk1c_000072
177. Spectrum1500570
178. Tiabendazole [who-dd]
179. Tiabendazole [who-ip]
180. Spbio_001481
181. Spbio_002428
182. Thiabendazole [usp-rs]
183. Bpbio1_000559
184. Gtpl7304
185. Dtxsid0021337
186. Thiabendazole, >=99%, Powder
187. Hms500d14
188. Kbio1_000072
189. Kbio2_000399
190. Kbio2_002967
191. Kbio2_005535
192. Kbio3_002274
193. Zinc73711
194. Ninds_000072
195. Hms1569j09
196. Hms1921e05
197. Hms2092m07
198. Hms2096j09
199. Hms2230f20
200. Hms3259e20
201. Hms3372e11
202. Hms3655e08
203. Hms3713j09
204. Pharmakon1600-01500570
205. Thiabendazole [green Book]
206. Tiabendazole [ep Impurity]
207. Thiabendazole [orange Book]
208. Tiabendazole [ep Monograph]
209. Albb-023635
210. Amy22461
211. Bcp19179
212. Hy-b0263
213. Tox21_110427
214. Tox21_202397
215. Tox21_300970
216. Bdbm50121347
217. Ccg-39633
218. Nsc757347
219. S1739
220. Stk394289
221. Thiabendazole [usp Monograph]
222. Akos000120940
223. Tox21_110427_1
224. Db00730
225. Nc00593
226. Nsc-757347
227. Sdccgmls-0002984.p003
228. Idi1_000072
229. Ncgc00016410-01
230. Ncgc00016410-02
231. Ncgc00016410-03
232. Ncgc00016410-04
233. Ncgc00016410-05
234. Ncgc00016410-07
235. Ncgc00016410-08
236. Ncgc00016410-09
237. Ncgc00016410-10
238. Ncgc00016410-11
239. Ncgc00016410-12
240. Ncgc00016410-14
241. Ncgc00016410-15
242. Ncgc00016410-18
243. Ncgc00016410-21
244. Ncgc00021671-04
245. Ncgc00021671-05
246. Ncgc00021671-06
247. Ncgc00021671-07
248. Ncgc00021671-08
249. Ncgc00021671-09
250. Ncgc00021671-10
251. Ncgc00254873-01
252. Ncgc00259946-01
253. Thiabendazole 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
254. Ac-10139
255. Ls-07459
256. Nci60_004280
257. Nci60_042006
258. Mls-0002984.p004
259. Sbi-0051531.p003
260. 2-(1,3-thiazole-4-yl)-1h-benzimidazole
261. Db-042952
262. Thiabendazole 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
263. Ab00052107
264. Ft-0608694
265. Sw196947-3
266. T0830
267. Thiabendazole 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
268. 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1h-benzimidazole #
269. Thiabendazole 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
270. Thiabendazole, Ban, Bsi, Iso, Jmaf, Usan
271. 48t798
272. C07131
273. D00372
274. E70385
275. Ab00052107_17
276. Ab00052107_18
277. Thiabendazole, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
278. A808809
279. Q424986
280. Sr-01000000188-2
281. Sr-01000000188-4
282. Sr-01000000188-5
283. W-108097
284. Brd-k77695569-001-05-2
285. Brd-k77695569-001-16-9
286. Brd-k77695569-001-28-4
287. Thiabendazole, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
288. Thiabendazole, Bioreagent, Plant Cell Culture Tested, Powder
289. Tiabendazole, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
290. Thiabendazole, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
291. Thiabendazole, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
292. 98002-42-7
| Molecular Weight | 201.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H7N3S |
| XLogP3 | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 201.03606841 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 201.03606841 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 212 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antinematodal Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
MEDICATION (VET): Thiabendazole is included in some otic preparations for treatment of yeast infections.
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 2102
MEDICATION (VET): The antifungal imidazoles also have some antibacterial action but are rarely used for this purpose. ... Thiabendazole is effective against Aspergillus and Penicillium spp , but its use has largely been replaced by the more effective imidazoles.
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 212
MEDICATION (VET): Imidazoles may have antibacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, and anthelmintic activity. ... The anthelmintic thiabendazole is also an imidazole with antifungal properties.
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 2101
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for THIABENDAZOLE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The clinical utility of thiabendazole in adults is compromised by its toxicity. Side effects frequently encountered with therapeutic doses include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Less frequently, diarrhea, fatigue, drowsiness, giddiness, or headache occur. Occasional fever, rashes, erythema multiforme, hallucinations, sensory disturbances, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported. Angioedema, shock, tinnitus, convulsions, and intrahepatic cholestasis are rare complications of therapy. Some patients excrete a metabolite that imparts an odor to the urine much like that occurring after ingestion of asparagus. Crystalluria without hematuria has been reported on occasion; it promptly subsides with discontinuation of therapy. Transient leukopenia has been noted in a few patients on thiabendazole therapy. There are no absolute contraindications to the use of thiabendazole. Because CNS side effects occur frequently, activities requiring mental alertness should be avoided during therapy. Thiabendazole has hepatotoxic potential and should be used with caution in patients with hepatic disease or decreased hepatic function.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 11th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2006., p. 1081
Hypersensitivity reactions consisting of pruritus, fever, facial flush, chills, conjunctival injection, rash (including perianal), angioedema, anaphylaxis, erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome with some fatalities), and lymphadenopathy have occurred.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 64
Because adverse CNS effects of thiabendazole may occur quite frequently, patients should be warned that the drug may impair their ability to perform activities requiring mental alertness or physical coordination (e.g., operating machinery, driving a motor vehicle) and that such activities should be avoided.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 64
Thiabendazole should be used with caution in patients in whom vomiting might be dangerous and in patients with severe malnutrition or anemia. Ideally, supportive therapy is indicated for anemic, dehydrated, or malnourished patients prior to administration of the drug.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 64
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for THIABENDAZOLE (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of strongyloidiasis (threadworm), cutaneous larva migrans (creeping eruption), visceral larva migrans, and trichinosis.
FDA Label
Thiabendazole is a fungicide and parasiticide. Thiabendazole is also a chelating agent, which means that it is used medicinally to bind metals in cases of metal poisoning, such as lead poisoning, mercury poisoning or antimony poisoning. Thiabendazole is vermicidal and/or vermifugal against Ascaris lumbricoides ("common roundworm"), Strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm), Necator americanus, Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm), Trichuris trichiura (whipworm), Ancylostoma braziliense (dog and cat hookworm), Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati (ascarids), and Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm). Thiabendazole also suppresses egg and/or larval production and may inhibit the subsequent development of those eggs or larvae which are passed in the feces.
Anthelmintics
Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of HELMINTHIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Anthelmintics.)
D - Dermatologicals
D01 - Antifungals for dermatological use
D01A - Antifungals for topical use
D01AC - Imidazole and triazole derivatives
D01AC06 - Tiabendazole
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P02 - Anthelmintics
P02C - Antinematodal agents
P02CA - Benzimidazole derivatives
P02CA02 - Tiabendazole
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed and peak plasma concentration is reached within 1 to 2 hours after the oral administration of a suspension. Some systemic absorption may occur from topical preparations applied to the skin.
Route of Elimination
It is metabolized almost completely to the 5-hydroxy form which appears in the urine as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates.
Investigations in mice, rats and dogs using (14)C-labelled thiabendazole indicated that oral doses were rapidly absorbed from the gut and were distributed throughout the body (including the brain). Only 0.01% of the (14)C-thiabendazole given to rats was recovered as (14)C-carbon dioxide. Thiabendazole readily crossed the placental barrier to expose the fetuses.
European Medicine Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Thiabendazole (148-79-8) EMEA/MRL/868/03, Summary Report (June 2004). Available from, as of June 10, 2009: https://www.ema.europa.eu/pdfs/vet/mrls/086803en.pdf
It becomes distributed throughout most of the body tissues, its highest concn in blood occurring at 4-7 hr after admin /in animals/.
Jones, L.M., et al. Veterinary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 4th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press, 1977., p. 1002
Absorption of thiabendazole by parasites is probably through the cuticle. Evidence from in vitro studies ... suggests that absorption ... is by means of passive diffusion of molecule through lipid barrier of nematode cuticle. This ... is not necessarily the case in vivo.
Jones, L.M., et al. Veterinary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 4th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press, 1977., p. 1003
Thiabendazole is rapidly absorbed and peak plasma concentrations occur within 1 to 2 hours. It is metabolized almost completely and appears in the urine as conjugates. In 48 hours, approximately 5% of the administered dose is recovered from feces and approximately 90% from urine. Most is excreted within the first 24 hours.
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons 59th Edition 2005. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2005., p. 1830
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for THIABENDAZOLE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic. Metabolized almost completely to the 5-hydroxy form which appears in the urine as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates.
In mice, rats and humans, the main pathway of metabolism of thiabendazole is an initial hydroxylation to form 5-hydroxythiabendazole, followed by conjugation to 5-hydroxythiabendazole glucuronide and 5-hydroxythiabendazole sulfate. In rats, 4-hydroxythiabendazole and 2-acetylbenzimidazole have been identified as minor metabolites or degradation products in urine.
European Medicine Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Thiabendazole (148-79-8) EMEA/MRL/868/03, Summary Report (June 2004). Available from, as of June 10, 2009: https://www.ema.europa.eu/pdfs/vet/mrls/086803en.pdf
... Treated beet leaves were exposed to sunlight for equiv of 14 8-hr days ... in addn to benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, benzimidazole and polar and polymer products were formed ... Thiabendazole was not metabolized by potatoes or cotton ...
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides, Update II. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish Wildlife Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 2l2. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1978., p. 259
A single oral dose of thiabendazole was administered to four male human subjects. Feces and urine were collected. After an oral dose of 1.0 g of (14)C thiabendazole, plasma levels peaked at 1 to 2 hr and large amounts of radioactivity appeared rapidly in the urine. More than 40% of the label was excreted within 4 hr and 80% in 24 hr. Most of the dose appeared in urine as the glucuronide (35%) and sulfate (13%) of 5-hydroxy-TBZ. A small amount of unchanged TBZ and unconjugated 5-HO-TBZ were also present. The same compounds were observed with rats and dogs. It has also been reported that (14)C-labeling of the benzene ring in thiabendazole gave rise to some (14)CO2 by rats, indicating ring cleavage.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides-Update III. Special Scientific Report- Wildlife No. 232. Washington, DC: U.S.Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, 1980., p. 507
Rat hepatic mixed function oxidase /activities in microsomal/ preparations hydroxylated thiabendazole. This activity seemed to be greatest in microsomal preparations > hepatocytes > slices.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides-Update III. Special Scientific Report- Wildlife No. 232. Washington, DC: U.S.Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, 1980., p. 507
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for THIABENDAZOLE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Thiabendazole has known human metabolites that include 5-hydroxythiabendazole.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The half-life for thiabendazole in both normal and anephric patients is 1.2 hours (range 0.9 to 2 hours). The half-life for the 5-hydroxythiabendazole metabolite in both normal and anephric patients is 1.7 hours (range 1.4 to 2 hours).
The precise mode of action of thiabendazole on the parasite is unknown, but it most likely inhibits the helminth-specific enzyme fumarate reductase.
Thiabendazole and other benzimidazole anthelmintics act by binding strongly to tubulin in the absorptive cells in the gut of parasitic worms. This interferes with the uptake of nutrients and the worms effectively starve to death. The host is less affected as the binding to mammalian tubulin is less strong and is reversible.
European Medicine Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Thiabendazole (148-79-8) EMEA/MRL/868/03, Summary Report (June 2004). Available from, as of June 10, 2009: https://www.ema.europa.eu/pdfs/vet/mrls/086803en.pdf
Although the exact mechanism of anthelmintic activity of thiabendazole has not been fully elucidated, the drug has been shown to inhibit the helminth-specific enzyme, fumarate reductase. In animals, thiabendazole has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic effects.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 65


