



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
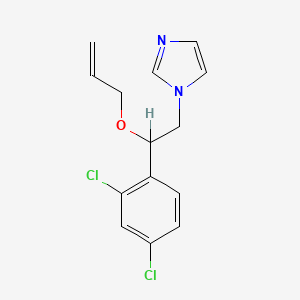

1. 1h-imidazole, 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propen-1-yloxy)ethyl)-, Sulfate (1:1)
2. Enilconazole Sulfate
3. Imazalil
4. Imazalil Mononitrate
5. Imazalil Phosphate
6. Imazalil Sulfate
7. Imazalil Sulfate (1:1)
8. Imazalil Sulphate
9. R 23979
1. Imazalil
2. 35554-44-0
3. Deccozil
4. Bromazil
5. Fungaflor
6. Imaverol
7. Clinafarm
8. Chloramizol
9. Florasan
10. Fungazil
11. Magnate
12. Eniloconazol (sp)
13. Deccozil S 75
14. Nuzone
15. Enilconazole (bpc)
16. Deccosil
17. Freshgard
18. 1h-imidazole, 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl]-
19. 1-(2-(allyloxy)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl)-1h-imidazole
20. Flopro Imz
21. R 23979
22. Amolden Mp 100
23. 1-[2-(allyloxy)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-1h-imidazole
24. Enilconazol
25. Cga 41333
26. Imazalil [ansi:bsi:iso]
27. 73790-28-0
28. Imazalil Sulphate
29. Chebi:83829
30. 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-prop-2-enoxyethyl]imidazole
31. Mfcd00055331
32. Enilconazole (usan/inn)
33. R-23979
34. Nsc-759313
35. 6k0nof3xq6
36. Enilconazole For Veterinary Use
37. Allyl-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-imidazol-1-ylethyl Ether
38. (+-)-1-(beta-(allyloxy)-2,4-dichlorophenethyl)-imidazole
39. (+ Or -)-1-(beta-allyloxy-2,4-dichlorophenylethyl)imidazole
40. 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl)-1h-imidazole
41. R 23,979
42. Cga-41333
43. Imazalil 1000 Microg/ml In Acetone
44. Imazalil 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
45. Imazalil 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
46. 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorphenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)aethyl)-1h-imidazol
47. Dsstox_cid_4151
48. Imazalil Phosphate
49. Dsstox_rid_77305
50. Dsstox_gsid_24151
51. Imazalil Mononitrate
52. Chloramizole
53. Caswell No. 497ab
54. 1h-imidazole, 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl)-
55. 1-[2-allyloxy-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]imidazole
56. Enilconazole [usan:ban:inn]
57. 1398065-91-2
58. Hsdb 6672
59. Einecs 252-615-0
60. Imazalil Sulfate (1:1)
61. Unii-6k0nof3xq6
62. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 111901
63. Brn 0545683
64. Eniloconazol
65. Freshguard
66. Fecundal
67. Imaversol
68. Rappor Plus
69. Fung-azil
70. Enilconazole [usan:inn:ban]
71. Imazalil-d5
72. Deccozil S75
73. Flo Pro Imz
74. Cas-35554-44-0
75. Fecundal (salt/mix)
76. Imazalil (enilconazole)
77. Imazalil [iso]
78. Rappor Plus (salt/mix)
79. (.+/-.)-imazalil
80. 33586-66-2
81. Prestwick0_000963
82. Prestwick1_000963
83. Prestwick2_000963
84. Prestwick3_000963
85. Enilconazole [mi]
86. Enilconazole [inn]
87. Imazalil Sulphate (1:1)
88. (+ Or -)-1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenylethyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl)-1h-imidazole
89. 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorphenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)aethyl)-1h-imidazol [german]
90. Enilconazole [hsdb]
91. Enilconazole [usan]
92. Schembl22498
93. Bspbio_000965
94. Enilconazole [mart.]
95. Imazalil, Analytical Standard
96. Mls002154075
97. Imazalil, Ansi, Bsi, Iso
98. Spbio_002886
99. Bpbio1_001063
100. Chembl356918
101. 1-[2-(allyloxy)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]imidazole
102. Dtxsid8024151
103. Pzbpkyovpcnpjy-uhfffaoysa-
104. Hms1571a07
105. Hms2094c13
106. Hms2098a07
107. Hms3041c20
108. Hms3715a07
109. Pharmakon1600-01506067
110. Albb-035652
111. Amy22447
112. Hy-b1134
113. Tox21_201551
114. Tox21_300720
115. Bdbm50051843
116. Imazalil 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
117. Nsc759313
118. S5053
119. Imazalil 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
120. Imazalil 100 Microg/ml In N-hexane
121. 1h-imidazole, 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl)-, (+-)-
122. Akos015895066
123. Ccg-220963
124. Cs-4739
125. Nsc 759313
126. Ncgc00163778-01
127. Ncgc00163778-03
128. Ncgc00163778-04
129. Ncgc00163778-05
130. Ncgc00163778-06
131. Ncgc00163778-07
132. Ncgc00254626-01
133. Ncgc00259100-01
134. Ac-15959
135. As-10962
136. Smr000777988
137. Sy104743
138. Ab00513978
139. Ft-0658775
140. Imazalil, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
141. C18739
142. D03997
143. Ab00513978_06
144. 554i440
145. A822869
146. Q421576
147. Sr-01000855376
148. Sr-01000855376-2
149. Brd-a11776908-001-03-6
150. Brd-a11776908-001-06-9
151. Enilconazole For Veterinary Use [ep Monograph]
152. 1-[2-(allyloxy)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-1h-imidazole #
153. 1-[2-allyloxy-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]imidazole;imazalil
154. Enilconazole, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
155. (.+/-.)-1-(.beta.-(allyloxy)-2,4-dichlorophenethyl)imidazole
156. (rs)-1-(.beta.-allyloxy-2,4-dichlorophenethyl)imidazole
157. (+/-)-1-(.beta.-(allyloxy)-2,4-dichlorophenethyl)-imidazole
158. (.+/-.)-1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl]-1h-imidazole
159. 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl]-1h-imidazole, 9ci
160. 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(prop-2-en-1-yloxy)ethyl]-1h-imidazole
161. (r,s)-1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl)-1h-imidazole
162. 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propen-1-yloxy)ethyl)-1h-imidazole
163. 1h-imidazole, 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propen-1-yloxy)ethyl)-
164. 1h-imidazole, 1-(2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl)-, (+/-)-
165. 1h-imidazole, 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2-propenyloxy)ethyl]-, (.+/-.)-
| Molecular Weight | 297.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H14Cl2N2O |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 296.0483185 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 296.0483185 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 27 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 291 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Mesh Heading: fungicides, industrial
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Imazalil (35554-44-0). Available from, as of April 14, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
MEDICATION (VET): Antifungal
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 634
... Used in the therapy of human alternariosis, an uncommon infection.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1459
Fungicides, Industrial
Chemicals that kill or inhibit the growth of fungi in agricultural applications, on wood, plastics, or other materials, in swimming pools, etc. (See all compounds classified as Fungicides, Industrial.)
Comparison of the excretion patterns after oral and intravenous dosing suggests that the bioavailability, and therefore the absorption, of imazalil given orally is high.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues on Imazalil (35554-44-0). Available from, as of July 7, 2006: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
Imazalil technical (purity = 98.7%) and 14C-imazalil (117.1 uCi/mL; purity = 99.9%) was administered to 4 groups of 6-8 Wistar rats. Group A: 5 rats/sex & reserve group I (1/sex) were injected in tail vein with 1.25 mg 14C-imazalil/kg (single dose). Group B: 5/sex were dosed by gastric intubation at 1.25 mg 14C-imazalil/kg (single dose). Group C: 5/sex & reserve group K (3/sex) were dosed by gastric intubation at 1.25 mg imazalil/kg/day for 14 days. At 24 hours after the last unlabelled dose, 5/sex received a single oral dose of 14C-imazalil at 1.25 mg/kg. Group D: 5/sex & reserve group L (1/sex) were dosed by gastric intubation at 20 mg 14C imazalil/kg (single dose). At 96 hours post-dosing (Groups B, C & D) were sacrificed for tissue collection. Group A & reserve rats (those not used) were sacrificed & disposed of. Distribution showed that after 96 hrs only 1% of 14C-imazalil was recovered in tissues and carcass. There was a dose-response in tissue levels of compound but there was no accumulation after multiple dosing. There were no sex differences. Approximately 50% of tissue 14C-imazalil was recovered in liver 96 hrs after gavage, levels in liver were approximately 20 times higher and kidney, lung and adrenals 4-10 times higher than corresponding blood levels. All other tissues examined had concentrations of 14C-imazalil < that of blood, with none detected in brain. By all routes and methods of administration, the majority (approximately 90%) of radioactivity was excreted within 24 hrs (primarily in urine & slightly higher in females).
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Toxicology Data Review Summaries. Available from: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/toxsums/toxsumlist.htm on Imazalil (35554-44-0) as of July 7, 2006.
A striking decrease was found in the effectiveness of thiabendazole (TBZ), benomyl, imazalil and prochloraz in controlling blue and green molds as a result of delaying the fungicidal treatments. Although imazalil and prochloraz gave low protective activity, they had high antisporulation efficiency. On the other hand, thiabendazole and benomyl protected fruits against subsequent infection. Storage was found to have a pronounced effect on the residual activity of imazalil compared with thiabendazole. Residues of imazalil and thiabendazole were found in orange jam made from fungicide-treated fruits.
Abdel Lateef M FA et al; Egyptian Journal of Phytopathology 22 (1): 59-73 (1994)
Imazalil is absorbed, distributed, and metabolized rapidly in rodent species. It is a sulfate, of which approximately 90% is excreted within 96 hours.
Sullivan, J.B., Krieger G.R. (eds). Clinical Environmental Health and Toxic Exposures. Second edition. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 1999., p. 1114
... Little imazalil was excreted unchanged /in rats/: less than 1% of the administered dose in the feces and trace amounts in the urine. The compound was metabolized to at least 25 metabolites. Three major metabolites were identified, (+/-)-1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2,3-dihydroxypropyloxy)ethyl]-imidaxolidine-2,5-dione (metabolite 8), (+/-)-1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(2,3-dihydroxypropyloxy)ethyl]-1H-imidazole (metabolite 10), and (+/-)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-imidazol-1-ylethanol (metabolite 11). The main routes of metabolism were epoxidation, epoxide hydratation, oxidative O-dealkylation, oxidation, and scission and oxidative N-dealkylation. The metabolic pattern was similar after oral and intravenous administration and in animals of each sex.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues on Imazalil (35554-44-0). Available from, as of July 7, 2006: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
The half-time was about 2 hrs /in humans/.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues on Imazalil (35554-44-0). Available from, as of July 7, 2006: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
Two single-copy genes, designated atrA and atrB (ATP-binding cassette transporter A and B), were cloned from the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans and sequenced. Based on the presence of conserved motifs and on hydropathy analysis, the products encoded by atrA and atrB can be regarded as novel members of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily of membrane transporters. Both products share the same topology as the ABC transporters PDR5 and SNQ2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and CDR1 from Candida albicans, which are involved in multidrug resistance of these yeasts. Significant homology also occurs between the ATP-binding cassettes of atrA and atrB, and those of mammalian ABC transporters (P-glycoproteins). The transcription of atrA and, i particular, atrB in mycelium of A. nidulans is strongly enhanced by treatment with several drugs, including antibiotics, azole fungicides and plant defense toxins. The enhanced transcription is detectable within a few minutes after drug treatment and coincides with the beginning of energy-dependent drug efflux activity, reported previously in the fungus for azole fungicides. Transcription of the atr genes has been studied in a wild-type and in a series of isogenic strains carrying the imaA and/or imaB genes, which confer multidrug resistance to various toxic compounds such as the azole fungicide imazalil. atrB is constitutively transcribed at a low level in the wild-type and in strains carrying imaA or imaB. Imazalil treatment enhances transcription of atrB to a similar extent in all strains tested. atrA, unlike atrB, displays a relatively high level of constitutive expression in mutants carrying imaB. Imazalil enhances transcription of atrA more strongly in imaB mutants, suggesting that the imaB locus regulates atrA. Functional analysis demonstrated that cDNA of atrB can complement the drug hypersensitivity associated with DPR5 deficiency in S. cerevisiae.
PMID:9180695 Del Dorbo G et al; Mol Gen Genet 254 (4): 417-26 (1997)


