



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
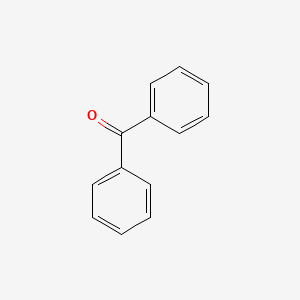

1. 119-61-9
2. Diphenylmethanone
3. Diphenyl Ketone
4. Benzoylbenzene
5. Methanone, Diphenyl-
6. Phenyl Ketone
7. Ketone, Diphenyl
8. Alpha-oxoditane
9. Benzene, Benzoyl-
10. Alpha-oxodiphenylmethane
11. Diphenylketone
12. Diphenyl-methanone
13. Kayacure Bp
14. .alpha.-oxoditane
15. Adjutan 6016
16. Fema No. 2134
17. .alpha.-oxodiphenylmethane
18. Diphenyl-methanon
19. 1dzp
20. Nsc 8077
21. Mfcd00003076
22. Chembl90039
23. 701m4ttv9o
24. Dtxsid0021961
25. Chebi:41308
26. Nsc-8077
27. Ncgc00090787-05
28. Dsstox_cid_1961
29. Dsstox_rid_76429
30. Dsstox_gsid_21961
31. Diphenylmethanone (benzophenone)
32. Caswell No. 081g
33. Cas-119-61-9
34. Ccris 629
35. Hsdb 6809
36. Wln: Rvr
37. Einecs 204-337-6
38. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 000315
39. Benzophenone (8ci)
40. Phenylketone
41. Unii-701m4ttv9o
42. Benzopheneone
43. Benzophenon
44. Benzophenone-
45. Benzoyl-benzene
46. A-oxoditane
47. Ai3-00754
48. Meta-benzophenone
49. Alpha -oxoditane
50. Fema 2134
51. Benzophenone Flakes
52. Di(phenyl)methanone
53. A-oxodiphenylmethane
54. Methanone, Diphenyl- (9ci)
55. Ph2co
56. Speedcure Bp
57. Darocur Bp
58. Diphenylmethanone, 9ci
59. Alpha -oxodiphenylmethane
60. Dimenhydrinate Impurity J
61. Benzophenone [mi]
62. Benzophenone [fcc]
63. Upcmld-dp071
64. Benzophenone [fhfi]
65. Benzophenone [hsdb]
66. Benzophenone [iarc]
67. Benzophenone [inci]
68. Ec 204-337-6
69. Bidd:pxr0008
70. Schembl17745
71. Mls001055400
72. Adk Stab 1413
73. Benzophenone [usp-rs]
74. Benzophenone [who-dd]
75. Bidd:er0022
76. Benzophenone (diphenyl-ketone)
77. Benzophenone (diphenylmethanone)
78. Upcmld-dp071:001
79. Bdbm22726
80. Benzophenone, Analytical Standard
81. Diphenhydramine Impurity E
82. Amy7704
83. Nsc8077
84. Hms2268a24
85. Zinc968233
86. Benzophenone [usp Impurity]
87. Benzophenone, >=99%, Fcc, Fg
88. Hy-y0546
89. Tox21_113465
90. Tox21_202425
91. Tox21_300058
92. Benzophenone, Reagentplus(r), 99%
93. S4438
94. Stl363250
95. Benzophenone, For Synthesis, 98.0%
96. Akos000119029
97. Tox21_113465_1
98. Benzophenone (diphenyl-ketone)
99. Db01878
100. Benzophenone 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
101. Benzophenone, Purum, >=99.0% (gc)
102. Benzophenone, Reagentplus(r), >=99%
103. Ncgc00090787-01
104. Ncgc00090787-03
105. Ncgc00090787-04
106. Ncgc00090787-06
107. Ncgc00090787-07
108. Ncgc00090787-08
109. Ncgc00254183-01
110. Ncgc00259974-01
111. Bp-21212
112. Smr000112143
113. Phenytoin Impurity A [ep Impurity]
114. Benzophenone, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
115. Db-061602
116. B0083
117. Cs-0015323
118. Ft-0622720
119. Ft-0693251
120. Benzophenone, Purified By Sublimation, >=99%
121. Benzophenone, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
122. C06354
123. D72506
124. Dimenhydrinate Impurity J [ep Impurity]
125. Phenytoin Sodium Impurity A [ep Impurity]
126. Q409482
127. Melting Point Standard 47-49c, Analytical Standard
128. Q-200691
129. Phenytoin Impurity Benzophenone [usp Impurity]
130. F0001-0309
131. Z1245792986
132. Benzophenone, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
133. Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride Impurity E [ep Impurity]
134. Mettler-toledo Calibration Substance Me 18870, Benzophenone
135. Phenytoin Sodium Impurity Benzophenone [usp Impurity]
136. Benzophenone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
137. Hydrocodone Hydrogen Tartrate 2.5-hydrate Impurity H [ep Impurity]
138. Benzophenone, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
139. Mettler-toledo Calibration Substance Me 18870, Benzophenone, For The Calibration Of The Thermosystem 900, Traceable To Primary Standards (lgc)
| Molecular Weight | 182.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H10O |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 182.073164938 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 182.073164938 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 17.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 165 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Photosensitizing Agents
Drugs that are pharmacologically inactive but when exposed to ultraviolet radiation or sunlight are converted to their active metabolite to produce a beneficial reaction affecting the diseased tissue. These compounds can be administered topically or systemically and have been used therapeutically to treat psoriasis and various types of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Photosensitizing Agents.)
The percutaneous absorption of benzophenone was determined in vivo in monkeys. Absorption through occluded skin was approximately 70% of the applied dose in 24 hr. Under unoccluded conditions skin penetration was reduced to 44%, presumably because of evaporation from the site of application.
European Commission/European Chemical Substances Information System; IUCLID Dataset, Benzophenone (CAS No. 119-61-9) (2000). Available from, as of March 18, 2015: https://esis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
/The authors/ gave /benzophenone/ orally ... (100 or 400 mg/kg) ... once per day for 3 days, to ovariectomized Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, and all rats were killed 24 h after being given the last dose. ... At 24 hr after the last dose, the mean serum concentrations of benzophenone, benzhydrol and p-hydroxybenzophenone in the high-dosed rats were 10.4+/-1.0, 1.5+/-0.3, and 0.7+/-0.2 (mean +/- SE) umol/L, respectively, whereas in the serum of low-dosed rats these compounds were not detected. When a single oral administration of benzophenone (100 or 400 mg/kg) was given to intact female rats, serum concentrations of benzophenone, benzhydrol and p-hydroxybenzophenone increased in a dose-dependent manner 6 hr later. ...
PMID:1245144 Nakagawa Y, Tayama K; Arch Toxicol 76 (12): 727-31 (2002)
... The percutaneous absorption of the fragrances benzyl acetate and five other benzyl derivatives (benzyl alcohol, benzyl benzoate, benzamide, benzoin and benzophenone) was determined in vivo in monkeys. Absorption through occluded skin was high for all cmpd (approx 70% of the applied dose in 24 hr) and no significant differences between the values for the different cmpd were observed. No correlations were seen between skin penetration of these cmpd and their octanol-water partition coefficients. Under unoccluded conditions skin penetration of the fragrances was reduced and there was great variability between cmpd, presumably because of variations in the rates of evaporation from the site of application.
PMID:2379896 Bronaugh RL et al; Food Chem Toxicol 28 (5): 369-73 (1990)
In male Sprague-Dawley rats that received benzophenone by gavage, 1% of the administered dose was detected as p-hydroxybenzophenone in enzymetreated urine samples, but not in unhydrolyzed urine (Stocklinski et al., 1979). No p-hydroxybenzophenone was detected in the feces.
DHHS/NTP; Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Benzophenone (CAS No. 119-61-9) Toxicity Report Series No. 61 NIH Pub No. 00-3943. Available from, as of March 18, 2015: https://ntp-server.niehs.nih.gov
The results from recent studies show that some benzophenones (BPs) and their hydroxylated metabolites can function as weak estrogens (E2) in the environment. However, little is known about the structure-activity relationship of these molecules. We have examined the effects of exposure to ten different BPs on the proliferation of estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer cells and on the transcriptional activity of E2-target genes. We analyzed two genes that are tightly linked with estrogen-mediated proliferation, the CXCL12 and amphiregulin genes and two classical estrogen-responsive genes, the pS2 and progesterone receptor. Significant differences in the BPs efficiency to induce cell proliferation and endogenous E2-target gene expressions were observed. Using ERE-, Sp1-, AP1- and C3-reporter genes that contain different ER-binding sites in their promoter, we also showed significant differences in the BPs efficiency in activation of the ER transactivation. Together, our analyzes showed that the most active molecule is 4-hydroxy-BP. Docking analysis of the interaction of BPs in the ligand-binding pocket of ERa suggests that the minimum structural requirement for the estrogenic activity of BPs is a hydroxyl (OH) group in the phenyl A-ring that allows interaction with Glu-353, Arg-394 or Phe-404, which enhances the stability between BPs and ERa. Our modeling also indicates a loss of interaction between the OH groups of the phenyl B-ring and His-524. In addition, the presence of some OH groups in the phenyl B-ring can create repulsion forces, which may constrain helix 12 in an unfavorable position, explaining the differential estrogenic effects of BPs. These results, together with our analysis of BPs for their potency in activation of cell proliferation and ER-mediated transcription, report an improved understanding of the mechanism and structure-activity relationship of BPs. /benzophenones/
Kerdivel G et al; PLoS One. 8(4):e60567 (2013)
Benzophenone's main metabolic pathway in the rabbit is by reduction to benzhydrol, which is excreted in urine conjugated with glucoronic acid. Small amount (1%) is converted to p-hydroxybenzophenone following oral administration to rats. No p-hydroxybenzohydrol was detected in urine or feces.
European Commission/European Chemical Substances Information System; IUCLID Dataset, Benzophenone (CAS No. 119-61-9) (2000). Available from, as of March 18, 2015: https://esis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
Benzophenone is a known human metabolite of cinnarizine.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560






