



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
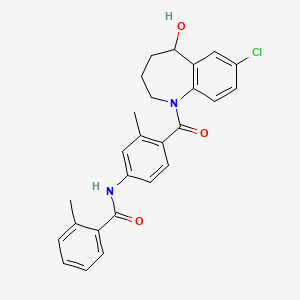

1. 7-chloro-5-hydroxy-1-(2-methyl-4-(2-methylbenzoylamino)benzoyl)2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-1-benzazepine
2. Opc 41061
3. Opc-41061
4. Opc41061
5. Samsca
1. 150683-30-0
2. Samsca
3. Opc-41061
4. Opc 41061
5. N-(4-(7-chloro-5-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-benzo[b]azepine-1-carbonyl)-3-methylphenyl)-2-methylbenzamide
6. N-[4-(7-chloro-5-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1-benzazepine-1-carbonyl)-3-methylphenyl]-2-methylbenzamide
7. (r)-(+)-tolvaptan
8. Tolvaptan (opc-41061)
9. Chembl344159
10. Opc-41061(tolvaptan)
11. Ncgc00183001-01
12. 21g72t1950
13. Benzamide, N-(4-((7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1h-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl)-3-methylphenyl)-2-methyl-
14. Jinarc
15. N-(4-(7-chloro-5-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-benzo[b]-azepine-1-carbonyl)-3-methylphenyl)-2-methylbenzamide
16. Unii-21g72t1950
17. Benzazepine Derivative, 32
18. Tolvaptan [usan:inn:ban]
19. Hsdb 8196
20. Tolvaptan [inn]
21. Tolvaptan- Bio-x
22. Benzamide, N-[4-[(7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1h-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl]-3-methylphenyl]-2-methyl-
23. Jynarque
24. 7-chloro-5-hydroxy-1-(2-methyl-4-(2-methylbenzoylamino)benzoyl)2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-1-benzazepine
25. Tolvaptan [jan]
26. Tolvaptan [mi]
27. Tolvaptan [usan]
28. Tolvaptan [vandf]
29. Tolvaptan [mart.]
30. Tolvaptan [who-dd]
31. Dsstox_cid_28706
32. Dsstox_rid_82975
33. Dsstox_gsid_48780
34. Tolvaptan [ema Epar]
35. Schembl242421
36. Gtpl2226
37. Tolvaptan [orange Book]
38. Dtxsid3048780
39. Bdbm35723
40. Chebi:32246
41. Hms3604l08
42. Hms3656k20
43. Hms3744a09
44. (r)-n-(4-(7-chloro-5-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-benzo[b]azepine-1-carbonyl)-3-methylphenyl)-2-methylbenzamide
45. Tox21_113256
46. Mfcd09838782
47. Pdsp1_001738
48. Pdsp2_001721
49. S2593
50. Akos015994735
51. Tolvaptan, >=98% (hplc), Powder
52. Ccg-269223
53. Cs-0572
54. Ks-1315
55. Ac-22748
56. Bt164486
57. Hy-17000
58. Am20090726
59. Cas-150683-30-0
60. Ft-0675287
61. Ft-0675288
62. Sw219182-1
63. Ab01565822_02
64. 683t300
65. A809063
66. L001628
67. Q426132
68. Sr-01000942265
69. Sr-01000942265-1
70. H-d-phe-pro-arg-5-amido-isophthalicacid-dimethylesteracetatesalt
71. (+-)-4'-((7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1h-1-benzazepin-1-yl) Carbonyl)-o-tolu-m-toluidide
72. (+-)-4'-((7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1h-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl)-o-tolu-m-toluidide
73. (+/-)-4'-((7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1h-1-benzazepin-1-yl) Carbonyl)-o-tolu-m-toluidide
74. 5-hydroxy-7-chloro-1-[2-methyl-4-(2-methylbenzoylamino)benzoyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-benzazepine
75. 7-chloro-5-hydroxy-1-[2-methyl-4-(2-methyl Benzoyl Amino) Benzoyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-1-benzazepine
76. 7-chloro-5-hydroxy-1-[2-methyl-4-(2-methylbenzoylamino) Benzoyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-1-benzazepine
77. 7-chloro-5-hydroxy-1-[2-methyl-4-(2-methylbenzoylamino)benzoyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1h-1-benzazepine
78. N-[4-(7-chloro-5-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepine-1-carbonyl)-3-methyl-phenyl]-2-methyl-benzamide
79. N-[4-(7-chloro-5-hydroxy2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1-benzazepine-1-carbonyl)-3-methylphenyl]-2-methylbenzamide
80. N-[4-[(7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1h-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl]-3-methylphenyl]-2-methylbenzamide
| Molecular Weight | 448.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H25ClN2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 4.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 448.1553704 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 448.1553704 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 674 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Samsca |
| PubMed Health | Tolvaptan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Tolvaptan is ()-4'-[(7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl) carbonyl]-o-tolu-m-toluidide. The empirical formula is C26H25ClN2O3. Molecular weight is 448.94. The chemical structure is:SAMSCA tablets for oral use contain 15mg o... |
| Active Ingredient | Tolvaptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Otsuka America Pharm |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Samsca |
| PubMed Health | Tolvaptan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Tolvaptan is ()-4'-[(7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl) carbonyl]-o-tolu-m-toluidide. The empirical formula is C26H25ClN2O3. Molecular weight is 448.94. The chemical structure is:SAMSCA tablets for oral use contain 15mg o... |
| Active Ingredient | Tolvaptan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Otsuka America Pharm |
Vasopressin V2 Receptor Antagonist
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Lite Record for Tolvaptan (150683-30-0). Available from, as of May 30, 2014: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
Samsca is indicated for the treatment of clinically significant hypervolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia (serum sodium <125 mEq/L or less marked hyponatremia that is symptomatic and has resisted correction with fluid restriction), including patients with heart failure and Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH). /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
EXPL Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is characterized by bilateral renal cysts, kidney pain, hypertension, and progressive loss of renal function. It is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease and the most common inherited kidney disease in the United States. Despite its prevalence, disease-modifying treatment options do not currently exist. Tolvaptan is an orally active, selective arginine vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist already in use for hyponatremia. Tolvaptan exhibits dose-proportional pharmacokinetics with a half-life of approximately 12 hours. Metabolism occurs through the cytochrome P450 3A4 isoenzyme, and tolvaptan is a substrate for P-glycoprotein, resulting in numerous drug interactions. Recent research has highlighted the beneficial effect of tolvaptan on delaying the progression of ADPKD, which is the focus of this review. Pharmacologic, preclinical, and phase II and III clinical trial studies have demonstrated that tolvaptan is an effective treatment option that targets underlying pathogenic mechanisms of ADPKD. Tolvaptan delays the increase in total kidney volume (surrogate marker for disease progression), slows the decline in renal function, and reduces kidney pain. However, tolvaptan has significant adverse effects including aquaretic effects (polyuria, nocturia, polydipsia) and elevation of aminotransferase enzyme concentrations with the potential for acute liver failure. Appropriate patient selection is critical to optimize long-term benefits while minimizing adverse effects and hepatotoxic risk factors. Overall, tolvaptan is the first pharmacotherapeutic intervention to demonstrate significant benefit in the treatment of ADPKD, but practitioners and regulatory agencies must carefully weigh the risks versus benefits. Additional research should focus on incidence and risk factors of liver injury, cost-effectiveness, clinical management of drug-drug interactions, and long-term disease outcomes.
PMID:24706579 Baur BP et al; Pharmacotherapy. 2014 Apr 7. doi: 10.1002/phar.1421. (Epub ahead of print)
Tolvaptan is not indicated for the treatment of hypovolemic hyponatremia. The manufacturer states that tolvaptan should not be used in patients who require urgent intervention to raise serum sodium concentrations to prevent or treat serious neurologic manifestations. In addition, it has not been established that using tolvaptan to increase serum sodium concentrations provides symptomatic benefit to patients
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 2853
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: INITIATE AND RE-INITIATE IN A HOSPITAL AND MONITOR SERUM SODIUM. Samsca should be initiated and re-initiated in patients only in a hospital where serum sodium can be monitored closely. Too rapid correction of hyponatremia (e.g., >12 mEq/L/24 hours) can cause osmotic demyelination resulting in dysarthria, mutism, dysphagia, lethargy, affective changes, spastic quadriparesis, seizures, coma and death. In susceptible patients, including those with severe malnutrition, alcoholism or advanced liver disease, slower rates of correction may be advisable.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
Tolvaptan therapy should be initiated or reinitiated only in a hospital setting, where serum sodium concentrations and therapeutic response can be monitored closely. Too rapid a correction of hyponatremia (e.g., increases in serum sodium concentration exceeding 12 mEq/L over 24 hours) may cause osmotic demyelination syndrome, resulting in dysarthria, mutism, dysphagia, lethargy, affective changes, spastic quadriparesis, seizures, coma, or death. Slower rates of correction may be advisable in susceptible patients, including those with severe malnutrition, alcoholism, or advanced liver disease. Patients with syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) or very low baseline serum sodium concentrations may be at increased risk for too rapid a correction of serum sodium concentration. Fluid restriction during the first 24 hours of tolvaptan therapy may increase the risk of overly rapid correction of serum sodium concentration and generally should be avoided.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 2854
Samsca can cause serious and potentially fatal liver injury. In a placebo-controlled and open label extension study of chronically administered tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, cases of serious liver injury attributed to tolvaptan were observed. An increased incidence of ALT greater than three times the upper limit of normal was associated with tolvaptan (42/958 or 4.4%) compared to placebo (5/484 or 1.0%). Cases of serious liver injury were generally observed starting 3 months after initiation of tolvaptan although elevations of ALT occurred prior to 3 months. Patients with symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice should discontinue treatment with Samsca. Limit duration of therapy with Samsca to 30 days. Avoid use in patients with underlying liver disease, including cirrhosis, because the ability to recover from liver injury may be impaired
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has determined that the drug Samsca (tolvaptan) should not be used for longer than 30 days and should not be used in patients with underlying liver disease because it can cause liver injury, potentially requiring liver transplant or death. Samsca is used to treat low sodium levels in the blood. An increased risk of liver injury was observed in recent large clinical trials evaluating Samsca for a new use in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
US FDA; FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Limits Duration and Usage of Samsca (Tolvaptan) Due to Possible Liver Injury Leading to Organ Transplant or Death (April 30, 2013). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm350062.htm
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Tolvaptan (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Jinarc is indicated to slow the progression of cyst development and renal insufficiency of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) in adults with CKD stage 1 to 3 at initiation of treatment with evidence of rapidly progressing disease.
Treatment of adult patients with hyponatraemia secondary to syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic-hormone secretion (SIADH).
Treatment of dilutional hyponatraemia, Treatment of polycystic kidney disease
Antidiuretic Hormone Receptor Antagonists
Endogenous compounds and drugs that inhibit or block the activity of ANTIDUIRETIC HORMONE RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Antidiuretic Hormone Receptor Antagonists.)
C03XA01
C03XA01
C03XA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03X - Other diuretics
C03XA - Vasopressin antagonists
C03XA01 - Tolvaptan
In a study in patients with creatinine clearances ranging from 10-124 mL/min administered a single dose of 60 mg tolvaptan, AUC and Cmax of plasma tolvaptan were less than doubled in patients with severe renal impairment relative to the controls. The peak increase in serum sodium was 5-6 mEq/L, regardless of renal function, but the onset and offset of tolvaptan's effect on serum sodium were slower in patients with severe renal impairment.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
In healthy subjects the pharmacokinetics of tolvaptan after single doses of up to 480 mg and multiple doses up to 300 mg once daily have been examined. Area under the curve (AUC) increases proportionally with dose. After administration of doses > or = 60 mg, however, Cmax increases less than proportionally with dose. The pharmacokinetic properties of tolvaptan are stereospecific, with a steady-state ratio of the S-(-) to the R-(+) enantiomer of about 3. The absolute bioavailability of tolvaptan is unknown. At least 40% of the dose is absorbed as tolvaptan or metabolites. Peak concentrations of tolvaptan are observed between 2 and 4 hours post-dose. Food does not impact the bioavailability of tolvaptan. In vitro data indicate that tolvaptan is a substrate and inhibitor of P-gp. Tolvaptan is highly plasma protein bound (99%) and distributed into an apparent volume of distribution of about 3 L/kg. Tolvaptan is eliminated entirely by non-renal routes and mainly, if not exclusively, metabolized by CYP 3A. After oral dosing, clearance is about 4 mL/min/kg and the terminal phase half-life is about 12 hours. The accumulation factor of tolvaptan with the once-daily regimen is 1.3 and the trough concentrations amount to > or = 16% of the peak concentrations, suggesting a dominant half-life somewhat shorter than 12 hours. There is marked inter-subject variation in peak and average exposure to tolvaptan with a percent coefficient of variation ranging between 30 and 60%.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
In patients with hyponatremia of any origin the clearance of tolvaptan is reduced to about 2 mL/min/kg. Moderate or severe hepatic impairment or congestive heart failure decrease the clearance and increase the volume of distribution of tolvaptan, but the respective changes are not clinically relevant. Exposure and response to tolvaptan in subjects with creatinine clearance ranging between 79 and 10 mL/min and patients with normal renal function are not different.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
In healthy subjects receiving a single dose of Samsca 60 mg, the onset of the aquaretic and sodium increasing effects occurs within 2 to 4 hours post-dose. A peak effect of about a 6 mEq increase in serum sodium and about 9 mL/min increase in urine excretion rate is observed between 4 and 8 hours post-dose; thus, the pharmacological activity lags behind the plasma concentrations of tolvaptan. About 60% of the peak effect on serum sodium is sustained at 24 hours post-dose, but the urinary excretion rate is no longer elevated by this time. Doses above 60 mg tolvaptan do not increase aquaresis or serum sodium further. The effects of tolvaptan in the recommended dose range of 15 to 60 mg once daily appear to be limited to aquaresis and the resulting increase in sodium concentration.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Tolvaptan (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Repeated dosing of female rats reduced systemic exposure to tolvaptan. Analysis of the serum samples for metabolites DM-4103 and DM-4107 revealed increases in the concentrations of these metabolites following repeated dosing, and explained the reduction in serum tolvaptan concentrations. Furthermore, tolvaptan was shown to induce hepatic drug-metabolising enzymes (cytochrome b5 content and aminopyrine N-demethylase activity) in female rats after 7 days dosing at 300 mg/kg/day. Tolvaptan was both a substrate for, and inhibitor of, MDR1-mediated transport.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Samsca (Tolvaptan) p.12 (2009). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000980/WC500048715.pdf
Tolvaptan is extensively metabolized in all species investigated. In vitro studies with rat liver supernatant produced a number of metabolites of tolvaptan. Hydroxylation of the benzazepine ring produced metabolites DM-4110, DM-4111 and DM-4119. Cleavage of the bond between the 1 and 2 positions of the benzazepine ring produced metabolites DM-4103, DM-4104, DM-4105 and DM- 4107. Oxidation of the hydroxyl group at the 5 position in the benzazepine ring produced MOP-21826.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Samsca (Tolvaptan) p.11 (2009). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000980/WC500048715.pdf
Tolvaptan is mainly, if not exclusively, metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A; the drug also is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A and a substrate and inhibitor of the P-glycoprotein transport system. Compared with tolvaptan, metabolites of the drug have little or no antagonist activity for human V2 receptors.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 2856
Tolvaptan is metabolized extensively in humans by the CYP3A4/5 system with seven metabolites (DM-4103, DM-4104, DM-4105, DM-4107, DM-4110, DM-4111, DM-4119) detected in the plasma, urine, and faeces of all subjects in a 14C mass balance study. After administration of (14)C-tolvaptan, 13 metabolites were identified in human plasma. Tolvaptan and identified metabolites accounted for about 70% of administered radioactivity. The predominant metabolite, with >50% of the total dose using the mass balance approach was DM-4103. The terminal elimination half-life of DM-4103 is approximatley 183 hours and after multiple dosing DM-4103 shows accumulation by day 28, but this appears pharmacologically inactive in the concentrations achieved using clinically relevant doses. Only 3% of the radioactivity was due to unchanged tolvaptan in the plasma.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Samsca (Tolvaptan) p.17 (2009). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000980/WC500048715.pdf
After IV administration, a half-life was estimated to be 3.5 hours, but it is suggested that this value most likely represents a distribution half-life and not a true elimination half-life.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Samsca (Tolvaptan) p.17 (2009). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000980/WC500048715.pdf
The terminal phase half-life is about 12 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566
Although tolvaptan is poorly soluble in water, following single dose of 30-480 mg, it is absorbed rapidly with a median time to peak plasma concentrations of about 2 hours (range of 1-12 hours) in healthy subjects. The mean (SD) of elimination half life is 7.8 (4.9) hours.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Samsca (Tolvaptan) p.17 (2009). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000980/WC500048715.pdf
Tolvaptan is a vasopressin antagonist that blocks the binding of arginine vasopressin (AVP) at the V2 receptors of the distal portions of the nephron. Animal pharmacology studies indicated that tolvaptan should increase excretion of water without increasing excretion of electrolytes (aquaresis) and thus offer a means of correcting serum sodium concentration by inducing excretion of water without loss of serum electrolytes. Tolvaptan is about 29 times more selective for V2 receptors than for V1a receptors with virtually no binding to V1b receptors.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Samsca (Tolvaptan) p.18 (2009). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000980/WC500048715.pdf
Tolvaptan is a selective vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist with an affinity for the V2-receptor that is 1.8 times that of native arginine vasopressin (AVP). Tolvaptan affinity for the V2-receptor is 29 times greater than for the V1a-receptor. When taken orally, 15 to 60 mg doses of tolvaptan antagonize the effect of vasopressin and cause an increase in urine water excretion that results in an increase in free water clearance (aquaresis), a decrease in urine osmolality, and a resulting increase in serum sodium concentrations. Urinary excretion of sodium and potassium and plasma potassium concentrations are not significantly changed. Tolvaptan metabolites have no or weak antagonist activity for human V2-receptors compared with tolvaptan. Plasma concentrations of native AVP may increase (avg. 2-9 pg/mL) with tolvaptan administration.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Samsca (Tolvaptan) Tablet (Revised: February 2014). Available from, as of June 5, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5526617c-c7b9-4556-886d-729bbabbc566






