
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
VMF
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
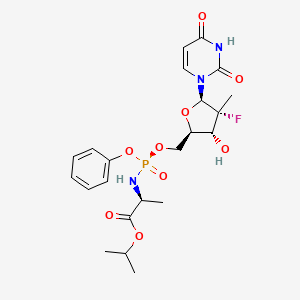

1. 2-((5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyrimidin-1-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethoxy)phenoxyphosphorylamino)propionic Acid Isopropyl Ester
2. 7977, Psi
3. Gs 7977
4. Gs-7977
5. Gs7977
6. Psi 7977
7. Psi-7977
8. Psi7977
9. Sovaldi
1. Psi-7977
2. 1190307-88-0
3. Sovaldi
4. Gs-7977
5. Psi 7977
6. Gs7977
7. Wj6ca3zu8b
8. Propan-2-yl (2s)-2-[[[(2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyloxolan-2-yl]methoxy-phenoxyphosphoryl]amino]propanoate
9. Chebi:85083
10. Gs 7977
11. L-alanine, N-((p(s),2'r)-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-methyl-p-phenyl-5'-uridylyl)-, 1-methylethyl Ester
12. Sofosbuvir [usan]
13. Sofosbuvir [usan:inn]
14. Unii-wj6ca3zu8b
15. Hepcinat
16. Hepcvir
17. Resof
18. Sovihep
19. Hsdb 8226
20. Psi7977
21. Sovaldi (tn)
22. Sofosbuvir [mi]
23. Sofosbuvir [inn]
24. Sofosbuvir [jan]
25. Sofosbuvir (jan/usan)
26. Sofosbuvir [vandf]
27. Sofosbuvir(psi-7977)
28. Sofosbuvir (gs-7977)
29. Sofosbuvir [who-dd]
30. 2-((5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyrimidin-1-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethoxy)phenoxyphosphorylamino)propionic Acid Isopropyl Ester
31. C22h29fn3o9p
32. Gtpl7368
33. Schembl2010114
34. Sofosbuvirpsi7977gs-7977
35. Chembl1259059
36. Sofosbuvir [orange Book]
37. Ammd00019
38. Ex-a389
39. Vosevi Component Sofosbuvir
40. Dtxsid701027632
41. Epclusa Component Sofosbuvir
42. Harvoni Component Sofosbuvir
43. (s)-isopropyl 2-(((s)-(((2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy)phosphoryl)amino)propanoate
44. Isopropyl (2s)-2-[[[(2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyl-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methoxy-phenoxy-phosphoryl]amino]propanoate
45. Mfcd18782704
46. S2794
47. Sofosbuvir Component Of Vosevi
48. Akos024464753
49. Sofosbuvir Component Of Epclusa
50. Sofosbuvir Component Of Harvoni
51. Zinc100074252
52. Am84279
53. Ccg-269909
54. Cs-0554
55. Db08934
56. Gi 7977
57. Gi-7977
58. Sofosbuvir (psi-7977, Gs-7977)
59. Sofosbuvir (psi-7977; Gs-7977)
60. Bs165550
61. Hy-15005
62. Sw219116-1
63. D10366
64. Q2502747
65. (s)-2-{[(1r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyrimidin-1-yl)-4-(r)-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethoxy]phenoxyphosphorylamino}propionic Acid (s)-isopropyl Ester
66. (s)-isopropyl 2-(((s)-(((2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-h
67. (s)-isopropyl 2-((s)-(((2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy)phosphorylamino)propanoate
68. Isopropyl ((s)-(((2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy)phosphoryl)-l-alaninate
69. Isopropyl (2s)-2-{[(s)-{[(2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methoxy}(phenoxy)phosphoryl]amino}propanoate
70. S)-isopropyl 2-((s)-(((2r,3r,4r,5r)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4- Dihydropyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)- (phenoxy)phosphorylamino)propanoate
| Molecular Weight | 529.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H29FN3O9P |
| XLogP3 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 529.16254467 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 529.16254467 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 153 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 913 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Sovaldi is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleotide analog NS5B polymerase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) infection as a component of a combination antiviral treatment regimen. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of December 31, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
The following points should be considered when initiating treatment with Sovaldi: Monotherapy of Sovaldi is not recommended for treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC). Treatment regimen and duration are dependent on both viral genotype and patient population. Treatment response varies based on baseline host and viral factors.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of December 31, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
FDA is warning that serious slowing of the heart rate can occur when the antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone is taken together with either the hepatitis C drug Harvoni (ledipasvir/sofosbuvir) or with Sovaldi (sofosbuvir) taken in combination with another direct acting antiviral for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. FDA is adding information about serious slowing of the heart rate, known as symptomatic bradycardia, to the Harvoni and Sovaldi labels. FDA is recommending that health care professionals should not prescribe either Harvoni or Sovaldi combined with another direct acting antiviral, such as the investigational drug daclatasvir or Olysio (simeprevir), with amiodarone. FDA review of submitted postmarketing adverse event reports found that patients can develop a serious and life-threatening symptomatic bradycardia when either Harvoni or Sovaldi combined with another direct-acting antiviral is taken together with amiodarone. The reports included the death of one patient due to cardiac arrest and three patients requiring placement of a pacemaker to regulate their heart rhythms. The other patients recovered after discontinuing either the hepatitis C drugs or amiodarone, or both. The cause of these events could not be determined. FDA will continue to monitor Harvoni and Sovaldi for risks of serious symptomatic bradycardia and further investigate the reason why the use of amiodarone with these hepatitis C drugs led to the heart-related events.
FDA; Safety Alerts for Human Medical Products; Hepatitis C Treatments Containing Sofosbuvir in Combination With Another Direct Acting Antiviral Drug: Drug Safety Communication - Serious Slowing of Heart Rate When Used With Antiarrhythmic Drug Amiodarone (March 24, 2015). Available from, as of March 24, 2015: https://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm439662.htm?source=govdelivery&utm_medium=email&utm_source=govdelivery
Concomitant use of sofosbuvir with drugs that are potent inducers of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transport system in the intestine (e.g., rifampin, St. John's wort) is not recommended since this may result in substantially decreased sofosbuvir plasma concentrations and could lead to reduced therapeutic effect of sofosbuvir.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 799
Anemia has been reported in patients receiving sofosbuvir in conjunction with ribavirin or in conjunction with peginterferon alfa andribavirin. In clinical trials, anemia was reported in 21% of patients who received 12 weeks of treatment with sofosbuvir, peginterferon alfa, and ribavirin compared with 12% of patients who received 24 weeks of treatment with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin without sofosbuvir. In addition, hemoglobin concentrations less than 10 g/dL were reported in 23% of patients who received 12 weeks of treatment with sofosbuvir, peginterferon alfa, and ribavirin compared with 14% of patients who received 24 weeks of treatment with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin without sofosbuvir.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 799
Adverse effects reported in more than 20% of patients receiving sofosbuvir in conjunction with ribavirin and peginterferon alfa include fatigue, headache, nausea, insomnia, and anemia.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 800
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Sofosbuvir (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Sofosbuvir is used in combination therapy with other antiviral medications to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infected patients with HCV genoptypes 1-6, and to treat HCV and HIV co-infected patients. Depending on the level of cirrhosis or decompensation, combination therapy can also include either ribavirin alone or ribavirin and peg-interferon alfa. When used in combination with [DB09027] as the combination product Harvoni, sofosbuvir has the following indications: treatment of genotypes 1, 4, 5, or 6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis; in combination with [DB00811] for genotype 1 infection with decompensated cirrhosis; or in combination with [DB00811] for the treatment of genotype 1 or 4 infection who are liver transplant recipients without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis. When used in combination with [DB11613] as the combination product Epclusa, sofosbuvir is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis, or in combination with [DB00811] if associated with decompensated cirrhosis. Resistance: Reduced susceptibility to sofosbuvir has been associated with the NS5B substitution mutation S282T.
FDA Label
Sovaldi is indicated in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) in adult and paediatric patients aged 3 years and above (see sections 4. 2, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
For hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype specific activity, see sections 4. 4 and 5. 1.
Sovaldi is indicated in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) in adults and paediatric patients aged 3 years and above (see sections 4. 2, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
For hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype specific activity, see sections 4. 4 and 5. 1.
Sofosbuvir acts against HCV and is categorized as a direct-acting antiviral agent (DAA). At a dose 3 times the recommended dose, sofosbuvir does not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
J05AX15
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AP - Antivirals for treatment of hcv infections
J05AP08 - Sofosbuvir
Absorption
When given orally, sofosbuvir reaches its maximum plasma concentration in about 0.5 to 2 hours with a maximal concentration (Cmax) of 567 ng/mL.
Route of Elimination
Sofosbuvir is eliminated by three routes: urine ( 80%), feces (14%), and respiration (2.5%); however, elimination through the kidneys is the major route.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution for sofosbuvir has yet to be determined.
Clearance
The clearance of sofosbuvir has yet to be determined.
Sofosbuvir is approximately 61-65% bound to human plasma proteins and the binding is independent of drug concentration over the range of 1 ug/mL to 20 ug/mL. Protein binding of GS-331007 was minimal in human plasma. After a single 400 mg dose of (14)C-sofosbuvir in healthy subjects, the blood to plasma ratio of (14)C-radioactivity was approximately 0.7.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
The pharmacokinetic properties of sofosbuvir and the predominant circulating metabolite GS-331007 have been evaluated in healthy adult subjects and in subjects with chronic hepatitis C. Following oral administration of SOVALDI, sofosbuvir was absorbed with a peak plasma concentration observed at approximately 0.5-2 hour post-dose, regardless of dose level. Peak plasma concentration of GS-331007 was observed between 2 to 4 hours post-dose. Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis in subjects with genotype 1 to 6 HCV infection who were coadministered ribavirin (with or without pegylated interferon), geometric mean steady state AUC0-24 was 969 ng*hr/mL for sofosbuvir (N=838), and 6790 ng*hr/mL for GS-331007 (N=1695), respectively. Relative to healthy subjects administered sofosbuvir alone (N = 272), the sofosbuvir AUC0-24 was 60% higher; and GS-331007 AUC0-24 was 39% lower, respectively, in HCV-infected subjects. Sofosbuvir and GS-331007 AUCs are near dose proportional over the dose range of 200 mg to 1200 mg.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
Following a single 400 mg oral dose of (14)C-sofosbuvir, mean total recovery of the dose was greater than 92%, consisting of approximately 80%, 14%, and 2.5% recovered in urine, feces, and expired air, respectively. The majority of the sofosbuvir dose recovered in urine was GS-331007 (78%) while 3.5% was recovered as sofosbuvir. These data indicate that renal clearance is the major elimination pathway for GS-331007.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
Studies in pregnant rats showed that sofosbuvir crossed the placenta. Fetal blood and brain sofosbuvir derived radioactivity was higher than in dams, but fetal liver and kidney had lower levels than corresponding organs in dams. Sofosbuvir-derived radioactivity was also quantifiable in milk from day 2 postpartum rats, but nursing pups did not appear to be extensively exposed to drug-derived radioactivity. Milk to plasma ratios were 0.1 at 1 hour and 0.8 at 24 hours.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Sovaldi; p.21 (November 21, 2013). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002798/WC500160600.pdf
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Sofosbuvir (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In vitro studies in human liver microsomes showed that sofosbuvir was an efficient substrate for Cathepsin A (Cat A) and carboxyl esterase 1 (CES1). Sofosbuvir was cleaved by CatA and CES1 and subsequent activation steps included amino acid removal by histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 (HINT1) and phosphorylation by uridine monophosphate-cytidine monophosphate (UMP-CMP) kinase and nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) kinase. In vitro data indicated that Cat A preferentially hydrolysed sofosbuvir (the S-diastereomer) while CES1 did not exhibit stereoselectivity.
In vitro studies in human liver microsomes showed that sofosbuvir was an efficient substrate for Cathepsin A (Cat A) and carboxyl esterase 1 (CES1). There were no indications of metabolism via urdine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) or flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO). Sofosbuvir was cleaved by CatA and CES1 and subsequent activation steps included amino acid removal by histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 (HINT1) and phosphorylation by uridine monophosphate-cytidine monophosphate (UMP-CMP) kinase and nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) kinase. In vitro data indicated that Cat A preferentially hydrolysed sofosbuvir (the S-diastereomer) while CES1 did not exhibit stereoselectivity. This would be consistent with studies using GS-9851 showing a less efficient metabolism to the triphosphate in the hepatically-derived cell line containing the Clone A replicon and shown to exhibit low CES 1 activity, but high Cat A activity compared with primary human hepatocytes. Following incubation of hepatocytes from rat, dog, monkey and human GS-9851 was converted to the triphosphate GS-461203 in all species, most efficiently in human. Sofosbuvir was also readily converted to the triphosphate in dog liver after oral doses and was the dominant metabolite at all time points assessed with a long half-life of approx. 18 hours. The active metabolite GS-461203 could not be detected in monkey. Further while GS-461203 was detected in rat liver, it could not be measured in liver from mouse.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Sovaldi; p.21-2 (November 21, 2013). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002798/WC500160600.pdf
Sofosbuvir is extensively metabolized in the liver to form the pharmacologically active nucleoside analog triphosphate GS-461203. The metabolic activation pathway involves sequential hydrolysis of the carboxyl ester moiety catalyzed by human cathepsin A (CatA) or carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) and phosphoramidate cleavage by histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 (HINT1) followed by phosphorylation by the pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis pathway. Dephosphorylation results in the formation of nucleoside metabolite GS-331007 that cannot be efficiently rephosphorylated and lacks anti-HCV activity in vitro.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
GS-331007 and GS-566500 were detected in all species with GS-331007 being the major drug related material in all species and all matrices. In plasma, urine and feces of all species administered sofosbuvir the primary metabolite detected was GS-331007 accounting for >80% of total exposure. In rat liver and plasma GS-566500 was also detected. The metabolite profile was overall comparable between non-pregnant, pregnant and postpartum rats and in milk of postpartum rats with GS-331007 and 2 sulfate conjugates of GS-331007 being the major metabolites.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Sovaldi; p.22 (November 21, 2013). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002798/WC500160600.pdf
In dog following a single oral dose of 20 mg/kg of sofosbuvir three metabolites in plasma were identified, GS-331007, GS-566500 and M4 (proposed glucuronidation product of GS-606965), accounting for 93.4%, 1.6% and 0.5%, respectively of total plasma AUC. Parent compound amounted to 4.5%. In dog (and mouse) the majority of a radioactive dose was recovered in urine within 8 to 12 hours.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Sovaldi; p.22 (November 21, 2013). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002798/WC500160600.pdf
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Sofosbuvir (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Sofosbuvir has a terminal half life of 0.4 hours.
The median terminal half-lives of sofosbuvir and GS-331007 were 0.4 and 27 hours, respectively.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: November 2014). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80beab2c-396e-4a37-a4dc-40fdb62859cf
Sofosbuvir is nucleotide analog inhibitor, which specifically inhibits HCV NS5B (non-structural protein 5B) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Following intracellular metabolism to form the pharmacologically active uridine analog triphosphate (GS-461203), sofosbuvir incorporates into HCV RNA by the NS5B polymerase and acts as a chain terminator [synthesis, A7533]. More specifically, Sofosbuvir prevents HCV viral replication by binding to the two Mg2+ ions present in HCV NS5B polymerase's GDD active site motif and preventing further replication of HCV genetic material.
Sofosbuvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent (pan-genotypic polymerase inhibitor) against the hepatitis C virus. HCV RNA replication is mediated by a membrane-associated multiprotein replication complex. The HCV polymerase (NS5B protein) is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). It is the essential initiating and catalytic subunit of this replication complex and is critical for the viral replication cycle. There is no human homolog for HCV NS5B RdRp. Sofosbuvir is a monophosphorylated pyrimidine nucleotide prodrug that undergoes intracellular metabolism to form the pharmacologically active uridine analog triphosphate (GS-461203). GS-461203 competes with natural nucleotides for incorporation (by HCV NS5B) into the nascent RNA strand during replication of the viral genome. GS-461203 differs from endogenous pyrimidine nucleotides in that it has been modified at the 2' position with the addition of a methyl and a fluoro functional group. Incorporation of GS-461203 into nascent RNA strongly reduces the efficiency of further RNA elongation by RdRp, resulting in premature termination of RNA synthesis. The stopping of viral replication leads to a rapid decline of HCV viral load and clearing of HCV levels in the body.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Sovaldi (Sofosbuvir) Tablets, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02418355 p.20 (Date of Preparation: December 4, 2014). Available from, as of March 17, 2015: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Marketed
Registration Country : Norway
Brand Name : Epclusa
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 400mg; 100mg
Packaging :
Approval Date :
Application Number :
Regulatory Info : Marketed
Registration Country : Norway

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Marketed
Registration Country : Norway
Sofosbuvir; Velpatasvir; Voxilaprevir
Brand Name : Vosevi
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 400mg; 100mg; 100mg
Packaging :
Approval Date :
Application Number :
Regulatory Info : Marketed
Registration Country : Norway

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Estonia
Brand Name : Sovaldi
Dosage Form : Film-Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 200mg
Packaging :
Approval Date :
Application Number :
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Estonia

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Estonia
Sofosbuvir; Velpatasvir; Voxilaprevir
Brand Name : Vosevi
Dosage Form : Film-Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 200mg; 50mg; 50mg
Packaging :
Approval Date :
Application Number :
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Estonia

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Authorized
Registration Country : Spain
Brand Name : Epclusa
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 400MG; 100 MG
Packaging :
Approval Date : 14-04-2025
Application Number : 1161116001IP
Regulatory Info : Authorized
Registration Country : Spain

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark
Brand Name : Epclusa
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 200mg; 50mg
Packaging :
Approval Date : 25-08-2020
Application Number : 28106349319
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark
Brand Name : Harvoni
Dosage Form : Coated Granules
Dosage Strength : 33.75mg; 150mg
Packaging :
Approval Date : 03-07-2020
Application Number : 28106286919
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark
Brand Name : Sovaldi
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 200mg
Packaging :
Approval Date : 25-06-2020
Application Number : 28106287219
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark
Brand Name : Sovaldi
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 400mg
Packaging :
Approval Date : 17-01-2014
Application Number : 28105264413
Regulatory Info : Prescription
Registration Country : Denmark

 Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Boost your online visibility by uploading your products, APIs, FDFs, intermediates, excipients, and services for free on PharmaCompass.
Rank higher among suppliers and expand your reach across the internet efficiently and cost-effectively.
Regulatory Info : Approved
Registration Country : Sweden
Brand Name : Sovaldi
Dosage Form : Film Coated Tablet
Dosage Strength : 400mg
Packaging :
Approval Date : 16-01-2014
Application Number : 2.01E+13
Regulatory Info : Approved
Registration Country : Sweden

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
28
PharmaCompass offers a list of Sofosbuvir API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Sofosbuvir manufacturer or Sofosbuvir supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Sofosbuvir manufacturer or Sofosbuvir supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Sofosbuvir API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Sofosbuvir API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Sofosbuvir Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Sofosbuvir Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A sovaldi manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of sovaldi, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates sovaldi manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. sovaldi API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of sovaldi manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A sovaldi supplier is an individual or a company that provides sovaldi active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or sovaldi finished formulations upon request. The sovaldi suppliers may include sovaldi API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of sovaldi suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A sovaldi DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of sovaldi active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of sovaldi DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as sovaldi USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A sovaldi DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. sovaldi USDMF includes data on sovaldi's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The sovaldi USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of sovaldi suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a sovaldi Drug Master File in Korea (sovaldi KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of sovaldi. The MFDS reviews the sovaldi KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the sovaldi KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a sovaldi KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their sovaldi API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of sovaldi suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A sovaldi written confirmation (sovaldi WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a sovaldi manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a sovaldi active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting sovaldi APIs or sovaldi finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a sovaldi WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of sovaldi suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing sovaldi as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for sovaldi API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture sovaldi as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain sovaldi and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a sovaldi NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of sovaldi suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
sovaldi Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of sovaldi GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right sovaldi GMP manufacturer or sovaldi GMP API supplier for your needs.
A sovaldi CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to sovaldi's compliance with sovaldi specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
sovaldi CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each sovaldi CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
sovaldi may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (sovaldi EP), sovaldi JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (sovaldi USP).

