



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
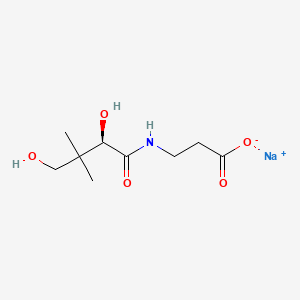

1. 867-81-2
2. Sodium D-pantothenate
3. Sodium (r)-3-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido)propanoate
4. D-pantothenic Acid Sodium
5. D-pantothenic Acid Sodium Salt
6. Pantothenate Sodium
7. Sodium Pantothenic Acid
8. D-pantothenic Acid (sodium)
9. Pantothenic Acid, Monosodium Salt, D-
10. Oes0r93f0c
11. Sodium;3-[[(2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino]propanoate
12. D-pantothenate Sodium
13. Mfcd00002767
14. Unii-oes0r93f0c
15. Pantothenic Acid, Sodium Salt
16. Ccris 1905
17. Hsdb 760
18. Vitamin B5 Sodium
19. Einecs 212-768-6
20. Sodium Pantothenate,(s)
21. Pantothenic Acid Sodium Salt
22. Dsstox_cid_27173
23. Dsstox_rid_82171
24. Dsstox_gsid_47173
25. Panthothenic Acid Sodium Salt
26. Schembl124920
27. Dtxsid4047173
28. Hy-b0430a
29. Hms2093p20
30. Sodium Pantothenate [hsdb]
31. Sodium Pantothenate [inci]
32. Tox21_302487
33. Pantothenate Sodium [who-dd]
34. Sodium N-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-beta-alanine, (r)-
35. Ccg-213530
36. Cs-5150
37. Beta-alanine, N-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Monosodium Salt, (r)-
38. Ncgc00256852-01
39. Cas-867-81-2
40. Pantothenic Acid Sodium Salt [mi]
41. P0013
42. D11519
43. O12072
44. Q-201535
45. Q27285618
46. Beta-alanine, N-((2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Monosodium Salt
47. Beta-alanine, N-((2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Sodium Salt (1:1)
48. .beta.-alanine, N-((2r)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)-, Sodium Salt (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 241.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H16NNaO5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 241.09261689 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 241.09261689 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 244 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Topical application of pantothenate is widely used in clinical practice for wound healing.
Wiederholt T et al; Exper Dermatol 18 (11): 969-78 (2009). Available from, as of March 16, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=19397697
Distribution of pantothenate from plasma into liver was very rapid; during 10 min after iv admin about 80% of dose was cleared from plasma.
PMID:1265350 Taylor T et al; Res Vet Sci 20 (2): 151-4 (1976).
Total blood pantothenic acid levels were higher after oral admin of 21.6 uM/kg pantethine than after calcium pantothenate in rats but no difference in amount of bound pantothenic acid. Max concentrations were observed at 2-4.5 hr after ingestion of both groups.
Ono S et al; J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 20(3) 203 (1974)
Total pantothenic acid excretions after 24 hr oral admin to rats were 29% and 18% after administration of pantethine and calcium pantothenate, respectively. Pantethine was more readily absorbed from GI tract than calcium pantothenate.
Ono S et al; J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 20(3) 203 (1974)
... To test the functional effect of pantothenate on dermal fibroblasts, cells were cultured and in vitro proliferation tests were performed using a standardized scratch test procedure. For all three donors analyzed, a strong stimulatory effect of pantothenate at a concentration of 20 ug/mL on the proliferation of cultivated dermal fibroblasts was observed. To study the molecular mechanisms resulting in the proliferative effect of pantothenate, gene expression was analyzed in dermal fibroblasts cultivated with 20 ug/mL of pantothenate compared with untreated cells using the GeneChip Human Exon 1.0 ST Array. A number of significantly regulated genes were identified including genes coding for interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, Id1, HMOX-1, HspB7, CYP1B1 and MARCH-II. Regulation of these genes was subsequently verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Induction of HMOX-1 expression by pantothenol and pantothenic acid in dermal cells was confirmed on the protein level using immunoblots. Functional studies revealed the enhanced suppression of free radical formation in skin fibroblasts cultured with panthenol. In conclusion, these studies provided new insight in the molecular mechanisms linked to the stimulatory effect of pantothenate and panthenol on the proliferation of dermal fibroblasts. /Calcium pantotenate/
Wiederholt T et al; Exper Dermatol 18 (11): 969-78 (2009). Available from, as of March 16, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=19397697


