


API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
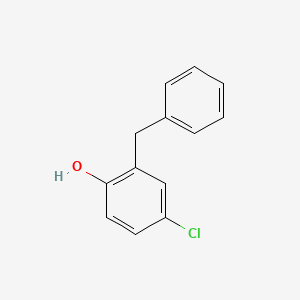

1. Chlorofene
2. Chlorophene
3. Clorofene
4. Clorophene
5. Clorophene Potassium Salt
6. Clorophene Sodium Salt
7. O-benzyl-p-chlorophenol
8. Ortho-benzyl-para-chlorophenol
9. Orthosan
1. 120-32-1
2. Clorophene
3. Clorofene
4. Chlorophene
5. O-benzyl-p-chlorophenol
6. 4-chloro-2-benzylphenol
7. Santophen 1
8. 5-chloro-2-hydroxydiphenylmethane
9. Phenol, 4-chloro-2-(phenylmethyl)-
10. Neosabenyl
11. Septiphene
12. Bio-clave
13. Santophen I Germicide
14. P-chloro-o-benzylphenol
15. Santophen I
16. Santophen 1 Flake
17. Clorophene [usan]
18. Santophen 1 Solution
19. Ketolin H
20. Orthobenzylparachlorophenol
21. Orthobenzyl-p-chlorophenol
22. 2-benzyl-4-chloro-phenol
23. 4-chloro-2-(phenylmethyl)phenol
24. 4-chloro-.alpha.-phenyl-o-cresol
25. Nci-c61201
26. Clorofene [inn]
27. Nsc-59989
28. Phenol, 4-chloro-2-benzyl-
29. Nsc 59989;santophen
30. O-cresol, 4-chloro-.alpha.-phenyl-
31. 7560bb0bo3
32. Nsc59989
33. Clorophene (usan)
34. Ncgc00091532-02
35. Ncgc00091532-04
36. Dsstox_cid_154
37. Ketolin-h
38. Dsstox_rid_75406
39. Dsstox_gsid_20154
40. O-benzylchlorophenol
41. Ortho-benzyl-para-chlorophenol
42. Caswell No. 083
43. Clorofenum
44. Sentiphene
45. Clorofeno
46. Clorofenum [inn-latin]
47. Clorofeno [inn-spanish]
48. Cas-120-32-1
49. Ccris 6205
50. 4-chloro-alpha-phenyl-o-cresol
51. Hsdb 5179
52. O-cresol, 4-chloro-alpha-phenyl-
53. 4-chloro-alpha-phenyl-ortho-cresol
54. Einecs 204-385-8
55. Nsc 59989
56. 4-chloro-2-benzyl Phenol
57. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 062201
58. Brn 1959194
59. Clorophen
60. Unii-7560bb0bo3
61. Ai3-08523
62. Preventol Bp
63. Nipacide Bcp
64. Benzyl Chloro Phenol
65. Mfcd00020140
66. Santophen 1 (tn)
67. Clorophene [mi]
68. Clorophene [hsdb]
69. Chlorophene [inci]
70. Wln: Qr Dg B1r
71. Clorofene [who-dd]
72. Clorophene [mart.]
73. Schembl78119
74. 4-06-00-04636 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
75. Mls002454423
76. Chembl1328919
77. Dtxsid5020154
78. 2-benzyl-4-chlorophenol, 95%
79. Nckmmsifqupkck-uhfffaoysa-
80. 2-hydroxy-5-chlorodiphenylmethane
81. Hms3041d07
82. Zinc136177
83. 4-chloranyl-2-(phenylmethyl)phenol
84. Tox21_111146
85. Tox21_202985
86. Tox21_400046
87. Akos001434264
88. Tox21_111146_1
89. Ncgc00091532-01
90. Ncgc00091532-03
91. Ncgc00091532-05
92. Ncgc00091532-06
93. Ncgc00260530-01
94. Ac-10752
95. Bs-20052
96. Smr000777843
97. Db-041547
98. B0812
99. Cs-0066335
100. Ft-0611303
101. D03564
102. D88696
103. A804486
104. W-108479
105. Q22829551
106. Z271137930
| Molecular Weight | 218.68 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H11ClO |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 218.0498427 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 218.0498427 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 20.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 189 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC:Probable oral lethal dose (human) 0.5-5 g/kg, between 1 oz and 1 pint for 70 kg person (150 lbs).
Gosselin, R.E., R.P. Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984., p. II-193
Anti-Infective Agents, Local
Substances used on humans and other animals that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. They are distinguished from DISINFECTANTS, which are used on inanimate objects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Local.)
Chlorophene was applied to the intrascapular region of male Fischer-344 rats at a total dose of 10 mg/kg in dermal studies. Three days after exposure to Chlorophene, 59% of the dose was excreted in the urine and feces. Chlorophene was distributed, as a percent of the total dose, to large intestinal contents (1.58%), small intestinal contents (0.55%), the skin (0.23%), and the skin site (32.33%). Chlorophene was incompletely absorbed through the skin.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
Rats /were/ dosed with 10 mg/kg chlorophene /iv/ and three rats each were sacrificed at various time points from 15 min to 72 hr. After iv exposure, 88% of the dose was excreted by 72 hr. After 15 min of treatment, about 30% of the chlorophene dose administered was present in the intestinal contents. Radioactivity was greatest in the kidneys and liver at this same time point and remained the greatest after 72 hr. The relative percent of unmetabolized chlorophene increased with time in the blood and liver over 72 hr. However, in the kidneys, it decreased with time. The skin had significant chlorophene radioactivity, 7.92% of the total dose administered after 15 min, but little remained after 24 hr.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
/Investigators/ dosed rats orally with 10, 100, or 1000 mg/kg chlorophene. The relative concentration of chlorophene excreted in the urine and feces was dose dependent. At the low and high dose, feces were the major route of excretion, whereas at the intermediate dose, urinary excretion predominated. However, more than 92% of the radioactive chlorophene was excreted within 3 days by rats in all dose groups. Rats injected with 5, 10, or 25 mg/kg chlorophene in the femoral vein had a dose-related decrease in biliary excretion.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
Male Sprague-Dawley rats /were administered/ (3/dose level) a single dose of 69 or 206 mg/kg [14C]-chlorophene. The kidneys and liver had the highest radiochemical concentrations of chlorophene and its metabolites. The combined concentrations of these two organs accounted for 0.16% and 0.13% of the 69 and 206 mg/kg doses, respectively. Approximately 0.23% and 0.18% of the dose was associated with the body fat at the low and high dose, respectively.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for O-BENZYL-P-CHLOROPHENOL (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
After iv treatment with 10 mg/kg chlorophene, the major metabolite formed was the glucuronic acid conjugate of the parent compound. The metabolite gradually decreased over a 6-hr period after treatment. The oxidative metabolite increased from 0.5% to 6% of the glucuronide acid conjugates in bile over 6 hr.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
In vitro metabolism studies found that about 95% of chlorophene was metabolized by liver supernatant in the presence of NADPH, uridine diphosphoglucuronic acid (UDPGA), and glutathione (GSH). Metabolism varied from 14% to 51% as the parent compound was exposed to various combinations of the cofactors, microsomes, and organ extracts.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
/Investigators/ isolated the metabolites of [14C]-chlorophene in urine and feces over a 5-day period. A significant percentage of the radioactive dose was present in the urine and feces from 12 to 24 hr. The majority of metabolites were present as either glucuronide or sulfate ester conjugates in the urine during this time period. Two additional metabolites were also identified, one in which the benzyl aromatic ring had a hydroxyl and a methoxyl substituent (22.9% and 17.6% of the low and high dose, respectively) and the second in which the benzyl aromatic ring had a hydroxyl substituent (12.7% and 29.4% of the low and high dose, respectively). These same metabolites were identified in feces but at a lower concentration. Chlorophene was also identified in the urine as 5.3% and 14.1% of the low and high dose, respectively. However, a larger percentage of [14C]-chlorophene was identified in feces, 21.4% and 22.4% of the low and high dose, respectively.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
Undiluted chlorophene (2 mL/kg) applied to the skin of rabbits lowered the percent of inorganic sulfates. However, the amount of glucuronate excreted was not affected. Application of 0.2 g/kg chlorophene in cottonseed oil and castor oil soap caused a slight increase in the output of glucuronates, but did not affect excretion of sulfates. The dilutions (1:100 and 1:300) produced no change in the excretion of glucuronates or sulfates.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for O-BENZYL-P-CHLOROPHENOL (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Male rats given an oral dose of 69 mg/kg or 206 mg/kg (14)C labeled o-benzyl-p-chlorophenol. ... Excretion of o-benzyl-p-chlorophenol was biphasic with an initial rapid alpha phase with a half life of 8 to 9 hr and slightly slower beta phase estimated to have a half life of 52 to 140 hr. ...
PMID:3712489 Ridley WP et al; J Toxicol Environ Health 18 (2): 267-83 (1986)
After iv injections of 10 mg/kg, ... feces, or feces and urine combined /were collected/, /investigators/ describe the elimination phase as a single-component model with a half-life of 14 hr.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review; International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 1): 1-27 (2004)


