



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
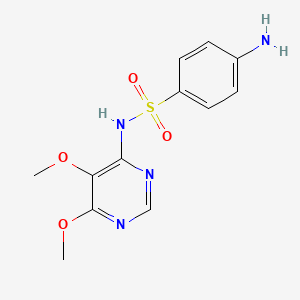

1. Fanasil
2. Ro 4 4393
3. Ro 4-4393
4. Ro 44393
5. Sulformethoxine
6. Sulformetoxine
7. Sulforthomidine
8. Sulphormetoxin
9. Sulphorthodimethoxine
1. 2447-57-6
2. Sulphadoxine
3. Sulforthomidine
4. Sulfadoxin
5. 4-amino-n-(5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
6. Fanasil
7. Sulphormethoxine
8. Sulfadoxinum
9. Sulfadoxina
10. Fanzil
11. Ro 4-4393
12. 4-amino-n-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide
13. 4-sulfanilamido-5,6-dimethoxypyrimidine
14. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-n-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)-
15. Fanasulf
16. N'-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidyl)sulfanilamide
17. 6-(4-aminobenzenesulfonamido)-4,5-dimethoxypyrimidine
18. Sulfadoxine (sulphadoxine)
19. Nsc-759319
20. Ro-4-4393
21. Chebi:9329
22. Solfadossina
23. 4-amino-n-(5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-4-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide
24. Sulfadoxine-d3
25. Ro-44393
26. 88463u4sm5
27. Wr-4073
28. Ncgc00016612-01
29. Orthosulfin
30. J21.373j
31. Cas-2447-57-6
32. Solfadossina [dcit]
33. Dsstox_cid_3608
34. Dsstox_rid_77106
35. Dsstox_gsid_23608
36. Sulfadoxinum [inn-latin]
37. Sulfadoxina [inn-spanish]
38. 4-amino-n-[5,6-bis(methyloxy)pyrimidin-4-yl]benzenesulfonamide
39. Wr 4873
40. Sr-05000001523
41. Einecs 219-504-9
42. N1-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide
43. Brn 0625453
44. Sulfadoxine (jan/usp/inn)
45. Unii-88463u4sm5
46. Sanasil: Sulfadoxine: Sulformetoxin
47. Mfcd00792890
48. N(sup 1)-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide
49. Wr 4073
50. Sulfadoxine [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
51. Sulfadoxine [mi]
52. Prestwick0_001094
53. Prestwick1_001094
54. Prestwick2_001094
55. Prestwick3_001094
56. Sulfadoxine [inn]
57. Sulfadoxine [jan]
58. Sulfadoxine [usan]
59. Sulfadoxine [vandf]
60. Chembl1539
61. Sulfadoxine [mart.]
62. Schembl41069
63. Bspbio_001168
64. Sulfadoxine [usp-rs]
65. Sulfadoxine [who-dd]
66. Sulfadoxine [who-ip]
67. 5-25-13-00306 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
68. Mls002154150
69. Spbio_003054
70. Bpbio1_001286
71. Zinc2094
72. Sulfadoxin, >=95% (tlc)
73. Dtxsid6023608
74. Gtpl10173
75. Sulfadoxine [orange Book]
76. Hms1571k10
77. Hms2090p07
78. Hms2094c19
79. Hms2098k10
80. Hms2230e05
81. Hms3371i15
82. Hms3715k10
83. Pharmakon1600-01506086
84. Sulfadoxine [ep Monograph]
85. Sulfadoxine [usp Monograph]
86. Hy-b0439
87. Sulfadoxinum [who-ip Latin]
88. Tox21_110523
89. Bbl023187
90. Fansidar Component Sulfadoxine
91. Nsc759319
92. S2511
93. Stl356042
94. Akos015897281
95. Sulfadoxin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
96. Tox21_110523_1
97. Ac-8428
98. Ccg-213610
99. Db01299
100. Ks-5334
101. Nsc 759319
102. Sulfadoxine Component Of Fansidar
103. Ncgc00016612-02
104. Ncgc00016612-04
105. Ncgc00016612-05
106. Sulfadoxine 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
107. Smr000857259
108. Sbi-0206941.p001
109. Sulfadoxine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
110. Db-046463
111. Ab00514044
112. Ft-0603610
113. N1-5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinylsulfanilamide
114. 47s576
115. C07630
116. D00580
117. H10765
118. Sulfadoxin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
119. Ab00514044-06
120. Ab00514044_07
121. Ab00514044_08
122. A817328
123. Q411557
124. Sr-05000001523-1
125. Sr-05000001523-3
126. W-107313
127. Brd-k55250441-001-03-1
128. Brd-k55250441-001-06-4
129. Sulfadoxin, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
130. 4-amino-n-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide;
131. 4-azanyl-n-(5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
132. Sulfadoxine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
133. Sulfadoxine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 310.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H14N4O4S |
| XLogP3 | 0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 310.07357611 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 310.07357611 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 125 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 420 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Sulfadoxine is used in combination with pyrimethamine for the treatment or prevention of malaria. It can also be used to treat various infections in livestock as well. Sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine is indicated for the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in those patients in whom chloroquine resistance is suspected.
Sulfadoxine helps inhibit the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase which is an enzyme necessary in the conversion of PABA to folic acid. As folic acid is vital to the synthesis, repair, and methylation of DNA which is vital to cell growth in Plasmodium falciparum. With this vital nutrient lacking, the parasite has difficulty in reproducing.
Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary
Substances capable of killing agents causing urinary tract infections or of preventing them from spreading. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary.)
Anti-Infective Agents
Substances that prevent infectious agents or organisms from spreading or kill infectious agents in order to prevent the spread of infection. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents.)
Antimalarials
Agents used in the treatment of malaria. They are usually classified on the basis of their action against plasmodia at different stages in their life cycle in the human. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p1585) (See all compounds classified as Antimalarials.)
Sulfadoxine is a sulfa drug, often used in combination with pyrimethamine to treat malaria. This medicine may also be used to prevent malaria in people who are living in, or will be traveling to, an area where there is a chance of getting malaria. Sulfadoxine targets Plasmodium dihydropteroate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase. Sulfa drugs or Sulfonamides are antimetabolites. They compete with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for incorporation into folic acid. The action of sulfonamides exploits the difference between mammal cells and other kinds of cells in their folic acid metabolism. All cells require folic acid for growth. Folic acid (as a vitamin) diffuses or is transported into human cells. However, folic acid cannot cross bacterial (and certain protozoan) cell walls by diffusion or active transport. For this reason bacteria must synthesize folic acid from p-aminobenzoic acid.


