



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
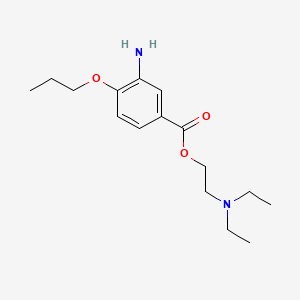

1. 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 3-amino-4-propoxybenzoate
2. 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 3-amino-4-propoxybenzoate Monohydrochloride
3. Ak-taine
4. Alcaine
5. Benzoic Acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester
6. Benzoic Acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester, Monohydrochloride*benzoic Acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester, Monohydrochloride
7. Chibro-kerakain
8. Kracaine
9. Kainair
10. Minims Proxymetacaine Hydrochloride
11. Ocu-caine
12. Ophthaine
13. Ophthetic
14. Parcaine
15. Proparacaine Hcl
16. Proparacaine Hydrochloride
17. Proparakain-pos
18. Proxymetacaine
19. Proxymetacaine Hydrochloride
20. Proxymetacaine Monohydrochloride
21. Proxymethacaine
1. Proxymetacaine
2. 499-67-2
3. 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 3-amino-4-propoxybenzoate
4. Ophthaine
5. Proximetacainum
6. Paracaine
7. Alcaine
8. Prossimetacaina [dcit]
9. Ophthetic
10. Kainair
11. Proxymetacainum [inn-latin]
12. Proximetacaina [inn-spanish]
13. 3-amino-4-propoxybenzoic Acid 2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester
14. Benzoic Acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester
15. Chebi:8485
16. Proxymetacaine (inn)
17. B4ob0jhi1x
18. Prossimetacaina
19. Proximetacaina
20. Proxymetacainum
21. Proxymetacaine [inn]
22. Proxymetacaine [inn:ban]
23. Beta-(diethylamino)ethyl 4-n-propoxybenzoate
24. Ncgc00016991-03
25. Einecs 207-884-9
26. Unii-b4ob0jhi1x
27. Brn 2745891
28. Benzoic Acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester, Hydrochloride
29. Prestwick0_000959
30. Prestwick1_000959
31. Prestwick2_000959
32. Prestwick3_000959
33. Proparacaine [mi]
34. Chembl1196
35. Proparacaine [vandf]
36. Schembl23334
37. Bspbio_000958
38. Mls006011856
39. Spbio_003107
40. Bpbio1_001054
41. Gtpl7283
42. Proxymetacaine [who-dd]
43. Dtxsid30198146
44. Hms3604h05
45. 2,5-dibromopyridine-3-boronicacid
46. Albb-025705
47. Bcp22476
48. Zinc1530762
49. Bbl003355
50. Bdbm50225500
51. Stk520616
52. Akos005457804
53. Db00807
54. Cas-1452000
55. Mrf-0000607
56. Ncgc00016991-01
57. Ncgc00016991-02
58. Ncgc00016991-06
59. Ncgc00016991-13
60. Ac-13440
61. Smr000857219
62. Sbi-0206900.p001
63. Ab00444123
64. Ft-0658833
65. Ft-0674059
66. .beta.-(diethylamino)ethyl 4-n-propoxybenzoate
67. A24938
68. C07383
69. D08448
70. Ab00444123_07
71. Ab00444123_08
72. Q600867
73. J-017667
74. Brd-k79116891-003-03-7
75. 3-amino-4-propoxy-,2-(diethylamino)ethyl Ester Benzoic Acid
76. 3-amino-4-propoxy-benzoic Acid 2-diethylamino-ethyl Ester, Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 294.39 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H26N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 294.19434270 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 294.19434270 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 64.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 295 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used as a local (ophthalmic) anesthetic.
FDA Label
Proparacaine stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses thereby effecting local anesthetic action. More specifically, proparacaine appears to bind or antagonize the function of voltage gated sodium channels.
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01H - Local anesthetics
S01HA - Local anesthetics
S01HA04 - Proxymetacaine
Plasma
The exact mechanism whereby proparacaine and other local anesthetics influence the permeability of the cell membrane is unknown; however, several studies indicate that local anesthetics may limit sodium ion permeability through the lipid layer of the nerve cell membrane. Proparacaine may alter epithelial sodium channels through interaction with channel protein residues. This limitation prevents the fundamental change necessary for the generation of the action potential.


