



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
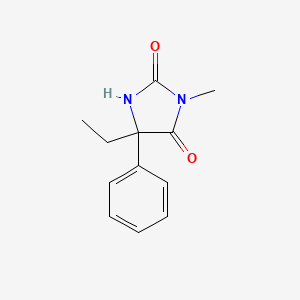

1. 5 Ethyl 3 Methyl 5 Phenylhydantoin
2. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
3. Mefenetoin
4. Mesantoin
5. Methoin
6. Methyl Phenetoin
7. Phenantoin
8. Phenetoin, Methyl
1. Methoin
2. Mesantoin
3. Phenantoin
4. Methylphenetoin
5. 50-12-4
6. Epiazin
7. Methyl Hydantoin
8. Fenantoin
9. Sedantoin
10. Sedantoinal
11. Triantoin
12. Insulton
13. Metydan
14. Sacerno
15. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione
16. Epilan
17. Phenylethylmethylhydantoin
18. Mesontoin
19. (+/-)-mephenytoin
20. Mephentoin
21. Mephenytoinum
22. 3-ethylnirvanol
23. Mephenytoine
24. Mefenitoina
25. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
26. 3-methyl-5,5-phenylethylhydantoin
27. 3-methyl-5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantoin
28. Nsc-34652
29. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-2,4-imidazolidinedione
30. Hydantoin, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-
31. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylimidazolidin-2,4-dione
32. 2,4-imidazolidinedione, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-
33. 5-ethyl-5-fenyl-3-methylhydantoin
34. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-2,4(3h,5h)-imidazoledione
35. L-mephenytoin
36. 3-methyl-5,5-ethylphenylhydantoin
37. 50-12-4 (racemic)
38. Mephenetoinum
39. Mesdontoin
40. R420kw629u
41. Nsc34652
42. Sedantional
43. Gerot-epilan
44. Mefenitoina [inn-spanish]
45. Mephenytoine [inn-french]
46. Mephenytoinum [inn-latin]
47. Mesantoin (tn)
48. (-)-5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
49. Hsdb 3581
50. 5-ethyl-5-fenyl-3-methylhydantoin [czech]
51. Sr-05000001478
52. Mephenytoin (usp/inn)
53. Einecs 200-012-8
54. Nsc 34652
55. Brn 0017282
56. Rac-mephenytoin
57. Unii-r420kw629u
58. (+-)-5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
59. Mephenytoin [usan:usp:inn:ban]
60. 3-methyl-5, 5-ethylphenylhydantoin
61. L-3-methyl-5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantoin
62. Spectrum_001494
63. Mephenytoin [mi]
64. Prestwick0_001108
65. Prestwick1_001108
66. Prestwick2_001108
67. Prestwick3_001108
68. Spectrum4_001094
69. Mephenytoin [inn]
70. (+/-)-5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
71. Ethylmethylhydantoin
72. Mephenytoin [hsdb]
73. Mephenytoin [usan]
74. Chembl861
75. Mephenytoin [vandf]
76. Mephenytoin [mart.]
77. Oprea1_289074
78. Schembl21766
79. Bspbio_001216
80. Kbiogr_001508
81. Kbioss_001974
82. Mephenytoin [who-dd]
83. Mls002154157
84. Divk1c_000937
85. Spbio_003088
86. Bpbio1_001338
87. Chebi:6757
88. Gtpl7223
89. Dtxsid9023257
90. Niosh/mu2276000
91. Hms502o19
92. Kbio1_000937
93. Kbio2_001974
94. Kbio2_004542
95. Kbio2_007110
96. (+/-)-5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-2,4-imidazolidinedione
97. Mephenytoin [orange Book]
98. Ninds_000937
99. 2,4-imidazolidinedione, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-, (+-)-
100. Hms1571m18
101. Hms2089j22
102. Hms2098m18
103. Hms2230e21
104. Hms3369f15
105. Hms3715m18
106. Mephenytoin [usp Impurity]
107. 2, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-
108. Hy-b1184
109. Mephenytoin 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
110. Bdbm50103593
111. Wln: T5mvnv Ehj C1 E2 Er
112. Akos015962176
113. Ccg-213191
114. Cs-4793
115. Db00532
116. Idi1_000937
117. Ncgc00165924-01
118. Ncgc00165924-02
119. (?)-5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
120. Ac-15964
121. As-56694
122. Smr001233457
123. Db-055496
124. Ab00052368
125. Ft-0605165
126. Ft-0605333
127. Ft-0671015
128. Ft-0671016
129. Mu22760000
130. (.+/-.)-5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenylhydantoin
131. Bim-0051837.0001
132. D00375
133. Ab00052368-07
134. Ab00052368_08
135. Hydantoin, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-, (-)-
136. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-2,5h)-imidazoledione
137. 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-imidazolidine-2,4-dione
138. Q1175385
139. Sr-05000001478-1
140. Sr-05000001478-3
141. 2, 4-imidazolidinedione, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-
142. Brd-a83937277-001-03-0
143. 4-ethyl-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-5-one
144. Mephenytoin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
145. 2,4-imidazolidinedione, 5-ethyl-3-methyl-5-phenyl-, (+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 218.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H14N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 218.105527694 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 218.105527694 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 310 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticonvulsants
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Hydantoin anticonvulsants are indicated in the suppression and control of tonic-clonic (grand mal) and simple or complex partial (psychomotor or temporal lobe) seizures. ... Mephenytoin is also used in the treatment of simple partial (focal and Jacksonian) seizures in patients who have not responded to less toxic anticonvulsants. /Hydantoin anticonvulsants; Included in US product labeling./
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 259
Hydantoin anticonvulsants are not indicated in the treatment of absence (petit mal) seizures, or as first-line treatment of febrile, hypoglycemic, or other metabolic seizures. When tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures coexist with absence seizures, combined therapy may be necessary. /Hydantoin anticonvulsants;NOT included in the US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 259
Leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and pancytopenia have occurred. Eosinophilia, monocytosis, and leukocytosis have been described. Simple anemia, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia, and aplastic anemia have occurred but are uncommon.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.2006 (1996)
Maculopapular, morbilliform, scarlatiniform, urticarial, purpuric (associated with thrombocytopenia), and nonspecific skin rashes have been reported. Exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiform (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), and toxic epidermal neurolysis and fatal dermatitides have been described on rare occaisions. Skin pigmentation and rashes associated with a lupus erythematosis syndrome have also been reported.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.2006 (1996)
Drowsiness is dose-related and may be reduced by a reduction in dose. Ataxia, diplopia, nystagmus, dysarthria, fatigue, irritability, choreiform movements, depression, and tremor have been encountered. Nervousness, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and dizziness may occur during the initial stages of therapy. Generally, these symptoms are transient, often disappearing with continued treatment. Mental confusion and psychotic disturbances and increased seizures have been reported but a definite causal relationship with the drug is uncertain.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.2006 (1996)
Hepatitis, jaundice, and nephrosis have been reported but a definite cause and effect relationship between the drug and these effects has not been established. Alopecia, weight gain, edema, photophobia, and conjunctivitis have been encountered. Polyarthropathy, pulmonary fibrosis, lupus erythematosis syndrome, and lymphadenopathy which simulates Hodgkin's disease have also been observed.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.2006 (1996)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MEPHENYTOIN (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of refractory partial epilepsy.
Mephenytoin is an antiepileptic drug which can be useful in the treatment of epilepsy. The primary site of action appears to be the motor cortex where spread of seizure activity is inhibited. Possibly by promoting sodium efflux from neurons, mephenytoin tends to stabilize the threshold against hyperexcitability caused by excessive stimulation or environmental changes capable of reducing membrane sodium gradient. This includes the reduction of posttetanic potentiation at synapses. Loss of posttetanic potentiation prevents cortical seizure foci from detonating adjacent cortical areas. Mephenytoin reduces the maximal activity of brain stem centers responsible for the tonic phase of tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures.
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AB - Hydantoin derivatives
N03AB04 - Mephenytoin
Volume of Distribution
1.4 L/kg
Mephenytoin is absorbed from the GI tract. Following oral administration, the drug has an onset of action of 30 minutes and a duration of action of 24-48 hours. Plasma concentrations required for therapeutic effects are not known; however, total serum concentrations of mephenytoin and its major metabolite of 25-40 ug/mL are reportedly associated with good seizure control without clinical intoxication.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1638
Therapeutic serum concentrations range from 25 to 40 ug/mL (115 to 183 umol/L) for mephenytoin in combination with nirvanol /SRP: its active metabolite/. Time to peak concentration ranges from 45 minutes to 4 hours for mephenytoin and from 16 to 36 hours for nirvanol.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 260
... /A/ single-dose study of mephenytoin (Mesantoin) ... was performed in adult inpatients on stable regimens of other anticonvulsants. Five patients received mephenytoin, 7 mg per kilogram of body weight. Serial blood sampling was performed rigorously. The time to peak concentration (Tmax) for mephenytoin was 1 hour, with a half-life (T 1/2) of 7 hours; the T 1/2 of its metabolite, 5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantion, was 96 hours. ... Saliva accurately represented the unbound fraction for /both/ agents. Mean salivary levels (as percentage of total levels) were 61% for mephenytoin, 73% for its metabolite ... . The implications for therapy are that following mephenytoin administration, the metabolite 5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantoin will provide anticonvulsant effectiveness, with its long half-life producing stable blood levels on simple dose schedules.
PMID:42344 Troupin A et al; Ann Neurol 6 (5): 410-4 (1979)
The rate of hepatic biotransformation is increased in younger children, in pregnant women, in women during menses, and in patients with acute trauma; rate decreases with advancing age. ... Mephenytoin has an active metabolite, nirvanol (5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantoin). /Hydantoin anticonvulsants/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 260
Mephenytoin is N-demethylated by the liver to form a highly toxic compound, 5,5-ethylphenylhydantoin. It is probably that this metabolite at least partly accounts for both the therapeutic and toxic effects of mephenytoin. The N-demethylated /metabolite/ may be excreted in the urine or further metabolized via p-hydroxylation of the phenyl group, conjugated with glucuronic acid, and excreted in the urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1638
Human liver was used in investigations of mephenytoin p-hydroxylase, the enzyme presumably responsible for the genetic polymorphism in mephenytoin metabolism. A gas chromatographic assay method was developed to measure p-hydroxylation and N-demethylation which is the other major metabolic pathway. Both reactions were localized in the microsomal fraction and required NADPH. Inhibition of p-hydroxylation by CO, SKF 525-A, and metyrapone was demonstrated. It was concluded that a form of cytochrome P-450 catalyzes the reaction. The velocity of N-demethylation in human liver did not show saturation even at 500 microM substrate concentration. The p-hydroxylation, however, followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The Km, determined in five different livers, ranged from 59 to 143 microM. The linearity in Eadie-Hofstee plots was consistent with the involvement of a single catalytic site.
PMID:2859161 Jurima M et al; Drug Metab Dispos 13 (2): 151-5 (1985)
A major metabolite of the antiepileptic drug mephenytoin (3-methyl-5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantoin) has been identified in urine after a single oral dose of 100 mg of mephenytoin in man. Using chemical synthesis, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, /investigators/ established its chemical structure as 3-methyl-5-ethyl-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hydantoin (4-OH-M) which is a product of aromatic hydroxylation of mephenytoin in man. Quantitative determinations of 4-OH-M in urine of 10 volunteers showed that 43 +/- 7% (SD) of a single oral dose of 100 mg of mephenytoin were eliminated as the glucuronide of this metabolite. Urinary elimination of the demethylated metabolite, 5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantoin (Nirvanol), was low (1% of the dose per 24 hr) emphasizing the importance of 4-OH-M as the major metabolite after a single oral dose of mephenytoin. Other products of mephenytoin hydroxylation (2-OH-M, E-OH-M, or aliphatically hydroxylated 2-OH-ethyl-M) were not detectable under the conditions selected (less than 1 umol/24 hr).
PMID:6102023 Kupfer A et al; Drug Metab Dispos 8 (1): 1-4 (1980)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for MEPHENYTOIN (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Approximately 7 hours
... /A/ single-dose study of mephenytoin (Mesantoin) ... was performed in adult inpatients on stable regimens of other anticonvulsants. ... The time to peak concentration (Tmax) for mephenytoin was 1 hour, with a half-life (T 1/2) of 7 hours; the T 1/2 of its metabolite, 5-ethyl-5-phenylhydantion, was 96 hours. ...
PMID:42344 Troupin A et al; Ann Neurol 6 (5): 410-4 (1979)
About 7 hours, but for active metabolite, nirvanol, about 95 to 144 hours.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 260
The mechanism of action of mephenytoin is not definitely known, but extensive research strongly suggests that its main mechanism is to block frequency-, use- and voltage-dependent neuronal sodium channels, and therefore limit repetitive firing of action potentials.
The mechanism of action is not completely known, but it is thought to involve stabilization of neuronal membranes at the cell body, axon, and synapse and limitation of the spread of neuronal or seizure activity. ... Hydantoin anticonvulsants have an excitatory effect on the cerebellum, activating inhibitory pathways that extend to the cerebral cortex. This effect may also produce a reduction in seizure activity that is assoc with an increased cerebellar Purkinje cell discharge. /Hydantoin anticonvulsants/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 246


