



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
0
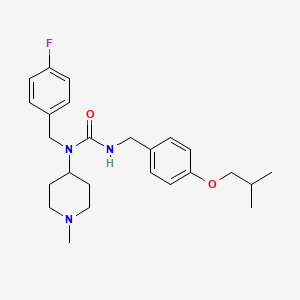

1. Acp 103
2. Acp-103
3. Acp103
4. Bis(1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-(2-methylpropoxy)benzyl)urea) (2r,3r)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
5. N-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-n-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-n'-(4-(2-methylpropyloxy)phenylmethyl)carbamide
6. Nuplazid
7. Pimavanserin Tartrate
8. Urea, N-((4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-n-(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-n'-((4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, (2r,3r)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (2:1)
1. 706779-91-1
2. Acp-103
3. 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-(4-isobutoxybenzyl)-1-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)urea
4. Pimavanserin [inn]
5. Pimavanserin Free Base
6. Jz963p0dik
7. 706779-91-1 (free Base)
8. 1-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-1-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-[[4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]methyl]urea
9. N-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-n-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-n'-(4-(2-methylpropyloxy)phenylmethyl) Carbamide
10. Unii-jz963p0dik
11. N-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-n-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-n'-(4-(2-methylpropyloxy)phenylmethyl)carbamide
12. 706782-28-7
13. Pimanavserin
14. Methyltrimethylacetate
15. Ac-5273
16. Pimavanserin [mi]
17. Pimavanserin(acp-103)
18. Pimavanserin [who-dd]
19. Schembl675165
20. Nuplazid (proposed Trade Name)
21. Gtpl8423
22. Chembl2111101
23. Dtxsid90990906
24. Chebi:133017
25. Bdbm139370
26. Hms3742a03
27. Bcp11618
28. Ex-a4895
29. Mfcd09953792
30. Zinc16159083
31. Akos015902593
32. Cs-3378
33. Db05316
34. Me-0240
35. Sb16963
36. Ncgc00390656-01
37. Ncgc00390656-02
38. Hy-14557
39. B8019
40. Ft-0653701
41. A14434
42. 779p911
43. A836958
44. J-503297
45. Q7194603
46. N-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-n-(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-n'-[[4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]methyl]urea;
47. N-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-n-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-n'-{[4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]methyl}urea
| Molecular Weight | 427.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H34FN3O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 427.26350550 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 427.26350550 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 44.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 523 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Pimavanserin is indicated for the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinsons disease psychosis.
Treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
Pimavanserin's unique actions on serotonin receptors improve symptoms of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease. In clinical studies, 80.5% of individuals treated with pimavanserin reported improvement in symptoms. Pimavanserin does not worsen motor functioning in patients with Parkinson's disease psychosis.
Antiparkinson Agents
Agents used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The most commonly used drugs act on the dopaminergic system in the striatum and basal ganglia or are centrally acting muscarinic antagonists. (See all compounds classified as Antiparkinson Agents.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of SEROTONIN or SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTOR AGONISTS. Included under this heading are antagonists for one or more specific 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonists.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05A - Antipsychotics
N05AX - Other antipsychotics
N05AX17 - Pimavanserin
Absorption
The median Tmax of pimavanserin in clinical studies was 6 hours, regardless of the dose. Bioavailability of an oral tablet of pimavanserin and a solution were almost identical. The major active circulating N-desmethylated metabolite, AC-279, has a median Tmax of 6 hours.
Route of Elimination
About 0.55% of a 34 mg oral dose was excreted unchanged in the urine and 1.53% was eliminated in feces within 10 days. Less than 1% of the administered dose and its active metabolite AC-279 were recovered in urine during clinical studies.
Volume of Distribution
Following administration of a single dose of 34 mg, the average apparent volume of distribution was 2173 L in clinical studies.
Pimavanserin is mainly metabolized CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 hepatic cytochrome enzymes, and to a lesser extent by CYP2J2, CYP2D6, and other cytochrome and flavin-containing monooxygenase enzymes. CYP3A4 metabolizes pimavanserin to its major active metabolite, AC-279.
The average plasma half-lives for pimavanserin and its active metabolite (AC-279) are estimated at 57 hours and 200 hours, respectively.
Parkinson's disease psychosis (PDP) is a imbalance of serotonin and dopamine from disruption of the normal balance between the serotonergic and dopaminergic receptors and neurotransmitters in the brain. The mechanism by which pimavanserin treats hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinsons disease psychosis is not fully established. It is possible that pimavanserin acts via inverse agonist and antagonist activity at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors with limited effects on serotonin 5-HT2C receptors. Pimavanserin is an inverse agonist and antagonist of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors with high binding affinity, demonstrating low binding affinity to serotonin 5-HT2C receptors. In addition, this drug exhibits low affinity binding to sigma 1 receptors. Pimavanserin lacks activity at muscarinic, dopaminergic, adrenergic, and histaminergic receptors, preventing various undesirable effects typically associated with antipsychotics.






