



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
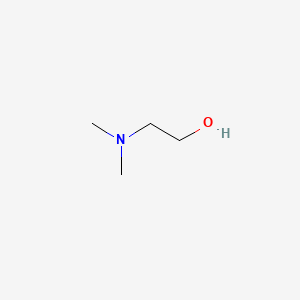

1. 2-(dimethylamino)ethanol
2. N,n-dimethylethanolamine
3. 108-01-0
4. Dimethylaminoethanol
5. Dimethylethanolamine
6. 2-dimethylaminoethanol
7. Norcholine
8. Dmae
9. Dmea
10. Bimanol
11. Liparon
12. N,n-dimethylaminoethanol
13. Varesal
14. Propamine A
15. (2-hydroxyethyl)dimethylamine
16. Ethanol, 2-(dimethylamino)-
17. Kalpur P
18. Dimethylmonoethanolamine
19. Dimethylaminoaethanol
20. N,n-dimethyl-2-aminoethanol
21. Amietol M 21
22. N,n-dimethyl-2-hydroxyethylamine
23. N-dimethylaminoethanol
24. 2-(n,n-dimethylamino)ethanol
25. Dimethyl(hydroxyethyl)amine
26. Texacat Dme
27. Dimethylaethanolamin
28. Dimethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)amine
29. 2-(dimethylamino)-1-ethanol
30. N,n-dimethyl Ethanolamine
31. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)dimethylamine
32. N,n-dimethyl-n-(2-hydroxyethyl)amine
33. 2-(dimethylamino) Ethanol
34. (dimethylamino)ethanol
35. Beta-hydroxyethyldimethylamine
36. 2-dimethylamino-ethanol
37. Beta-dimethylaminoethyl Alcohol
38. 2-(dimethylamino)ethan-1-ol
39. 2-dwumetyloaminoetanolu
40. N-(dimethylamino)ethanol
41. N,n-dimethyl-n-(beta-hydroxyethyl)amine
42. Tegoamin Dmea
43. Nsc 2652
44. Dabco Dmea
45. Deanol [ban]
46. 2-dimethylamino Ethanol
47. N,n-dimethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)amine
48. N,n'-dimethylethanolamine
49. 2-(dimethylamino)-ethanol
50. (ch3)2nch2ch2oh
51. Chembl1135
52. .beta.-(dimethylamino)ethanol
53. 2n6k9dra24
54. .beta.-hydroxyethyldimethylamine
55. .beta.-dimethylaminoethyl Alcohol
56. Chebi:271436
57. Phosphatidyl-n-dimethylethanolamine
58. Nsc-2652
59. Deanol (ban)
60. N,n-dimethylaminoethanol (dmae)
61. Ncgc00159413-02
62. N,n-dimethyl-n-(.beta.-hydroxyethyl)amine
63. Dsstox_cid_505
64. Dsstox_rid_75628
65. Dsstox_gsid_20505
66. Deanol (n,n-dimethylethanolamine)
67. Demanol
68. Demanyl
69. Tonibral
70. Cas-108-01-0
71. Dimethylaethanolamin [german]
72. Dimethylamino Ethanol
73. Dimethylaminoaethanol [german]
74. Ccris 4802
75. 2-dwumetyloaminoetanolu [polish]
76. Hsdb 1329
77. Einecs 203-542-8
78. Un2051
79. Brn 1209235
80. N,n-dimethyl-n-ethanolamine
81. Unii-2n6k9dra24
82. Ai3-09209
83. Dimethylethanoiamine
84. Toyocat -dma
85. Dimethyl Ethanolamine
86. Dimethyl-ethanolamine
87. Mfcd00002846
88. Paresan (salt/mix)
89. Dimethyl Ethanol Amine
90. 2-dimethyamino-ethanol
91. N,n-dimethylethanolamin
92. Biocoline (salt/mix)
93. N,n Dimethylaminoethanol
94. Deanol [who-dd]
95. Deanol [mi]
96. N,n-dimethyl-ethanolamine
97. N,n-dimethylamino Ethanol
98. N,n-dimethylethanol Amine
99. N,n-dimethylethanol-amine
100. Deanol [mart.]
101. 2-hydroxyethyldimethylamine
102. 2-dimethylaminoethanol [un2051] [corrosive]
103. Ec 203-542-8
104. Beta -(dimethylamino)ethanol
105. Dimethyl Mea [inci]
106. Dimethylaminoaethanol(german)
107. Choline Chloride (salt/mix)
108. Luridin Chloride (salt/mix)
109. Beta -hydroxyethyldimethylamine
110. N,n-dimethylethanolamine/dmea
111. Beta -dimethylaminoethyl Alcohol
112. 2-(n,n-dimethyl Amino)ethanol
113. 2-(n,n-dimethylamino) Ethanol
114. Dtxsid2020505
115. N-hydroxyethyl-n,n-dimethylamine
116. 2-(n,n-dimethyl Amino) Ethanol
117. Ni(1/4)oen-dimethylethanolamine
118. Nsc2652
119. Beta -(dimethylamino)ethyl Alcohol
120. 2-hydroxy-n,n-dimethylethanaminium
121. Wln: Q2n1 & 1
122. 2-dimethylaminoethanol, >=99.5%
123. Bcp22017
124. Cs-m3462
125. Zinc1641058
126. .beta.-(dimethylamino)ethyl Alcohol
127. N, N-dimethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)amine
128. Tox21_113163
129. Tox21_201821
130. Tox21_302844
131. Bdbm50060526
132. N,n-dimethyl-beta -hydroxyethylamine
133. Stl282730
134. Dimethylaminopropylamine Reagent Grade
135. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-n,n-dimethylamine
136. Akos000118738
137. N,n-dimethyl-.beta.-hydroxyethylamine
138. Db13352
139. N,n-dimethylethanolamine [hsdb]
140. Un 2051
141. N, N-dimethyl-n-(2-hydroxyethyl)amine
142. Ncgc00159413-03
143. Ncgc00256454-01
144. Ncgc00259370-01
145. Bp-13447
146. N,n-dimethyl-n-(beta -hydroxyethyl)amine
147. Db-002821
148. N, N-dimethyl-n-(beta -hydroxyethyl)amine
149. D0649
150. D07777
151. 2-dimethylaminoethanol [un2051] [corrosive]
152. 2-dimethylaminoethanol, Purum, >=98.0% (gc)
153. Q241049
154. 2-dimethylaminoethanol, Analytical Reference Material
155. 2-dimethylaminoethanol, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
156. W-108727
157. N,n-dimethylethanolamine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
158. 2-dimethylaminoethanol, Purified By Redistillation, >=99.5%
159. N,n-dimethyl-2-hydroxyethylamine, N,n-dimethylethanolamine, Dmea
| Molecular Weight | 89.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H11NO |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 89.084063974 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 89.084063974 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 23.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 28.7 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antidepressive Agents; Anti-Dyskinesia Agents; An antidepressive agent that has also been used in the treatment of movement disorders. The mechanism of action is not well understood.
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (2015 MeSH); Available from, as of February 23, 2015: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/cgi/mesh/2015/MB_cgi?term=Deanol
DMAE has been tested for its efficacy in treating a variety of diseases possibly related to deficiencies of acetylcholine with mixed results. Three reported no benefit from DMAE treatment (tardive dyskinesia; cognitive dysfunction; Alzheimer's disease). Benefits from DMAE treatment were found in other studies evaluating DMAE's ability to increase theta power or concentration. Centrophenoxine showed benefits for patients with organic psychosyndrome.[NTP; Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE)
108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters (November 2002); Available from, as of February 23, 2015: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/dmae_update_110002_508.pdf
No beneficial effects were obtained when deanol was administered to 11 patients with tardive dyskinesia of long duration. Doses of deanol were increased gradually over a period of 9 days until a level of 400 mg 4 times a day was reached; this dose level was then maintained for an additional 9 days. /Former use/
Crane GE; N. Engl. J. Med.; 292: 926 (1975)
Two case reports are presented in which deanol (I) was used unsuccessfully to treat tardive dyskinesia. The first case report involved an 89-yr-old male with a 50 yr history of chronic paranoid schizophrenia and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia. I was administered in doses ranging from 450 to 600 mg daily for 5 months but had to be discontinued due to the development of marked sialism, bronchospasm, and parkinson rigidity. No change in the patient's tardive dyskinesia was noted. A second patient with tardive dyskinesia and a 30 yr history of schizophrenia received up to 800 mg daily of I for 5 months with no improvement noted. /Former use/
Mathew P et al; Am. J. Psychiatry; 133: 1467 (1976)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for 2-DIMETHYLAMINOETHANOL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Principal contraindication to its use is grand mal epilepsy.
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-240
Serious cholinergic side effects were reported in a 37-yr-old woman with tardive dyskinesia who had been taking deanol. Deanol was given for 19 days in increasing doses. After 17 days, while receiving 1.5 g/day, the patient began to experience symptoms.
Nesse R Carroll BJ; Lancet; 2 (3): 50-51(1976)
Deanol (400-6000 mg/day for 1-4 mo) admin to pt with involuntary movement disorders produced mood changes (depression or hypomania) only in those pt with tardive dyskinesia with a past history of psychiatric disorders.
CASEY DE; PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY (BERLIN) 62(2) 187 (1979)
A large number of adverse health effects were associated with DMAE, including cardiovascular, neurological, and/or psychological effects. Specific attribution of adverse effects to DMAE is unlikely, as many of these products also contained Ephedra vulgaris alkaloids and other Ephedra spp.[NTP; Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE)
108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters (November 2002); Available from, as of February 23, 2015: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/dmae_update_110002_508.pdf
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for 2-DIMETHYLAMINOETHANOL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06B - Psychostimulants, agents used for adhd and nootropics
N06BX - Other psychostimulants and nootropics
N06BX04 - Deanol
Daily oral exposures (deanol acetamidobenzoate, DMAE, or Deaner) of chinchilla rabbits or humans produced measurable plasma and cerebrospinal concentrations of the parent compound. The drugs were cleared from the plasma by 36 hours post-treatment.[NTP; Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE)
108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters (November 2002); Available from, as of February 23, 2015: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/dmae_update_110002_508.pdf
Specific methods utilizing combined gas chromatography mass spectrometry were used to measure the metabolism of [(2)H6]deanol and its effects on acetylcholine concentration in vitro and in vivo. In vitro [(2)H6]deanol was rapidly taken up by rat brain synaptosomes, but was neither methylated nor acetylated. [(2)H6]Deanol was a weak competitive inhibitor of the high affinity transport of [(2)H4]choline, thus reducing the synthesis of [(2)H4]acetylcholine. In vivo [(2)H6]deanol was present in the brain after i.p. or p.o. administration, but was not methylated or acetylated. Treatment of rats with [(2)H6]deanol significantly increased the concentration of choline in the plasma and brain but did not alter the concentration of acetylcholine in the brain. Treatment of rats with atropine (to stimulate acetylcholine turnover) or with hemicholinium-3 (to inhibit the high affinity transport of choline) did not reveal any effect of [(2)H6]deanol on acetylcholine synthesis in vivo. However, since [(2)H6]deanol did increase brain choline, it may prove therapeutically useful when the production of choline is reduced or when the utilization of choline for the synthesis of acetylcholine is impaired.
PMID:512912 Jope RS, Jenden DJ; J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 211 (3) :472-9 (1979)
DMAE is absorbed and rapidly transported to the liver where much of it is metabolized. Approximately 280 nmol (25.2 ug) DMAE/gram plasma was observed in male mice about ten minutes after receiving 300 mg (3.30 mmol) DMAE/kg, intraperitoneally. Approximately 2.41, 1.30, and 0.20% of an administered dose of 30 mg/kg (0.13 mmol/kg) (with 100 u Ci) of (14)Cyprodenate was found in the liver, brain, and plasma, respectively, five minutes after intravenous dosing in male rats.[NTP; Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE)
108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters (November 2002); Available from, as of February 23, 2015: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/dmae_update_110002_508.pdf
In male Wistar rats, DMAE was oxidized rapidly to the N-oxide of DMAE, representing the primary urinary metabolite. However, only 13.5 % of the administered dose was eliminated by the 24 hour time point, suggesting that most of the DMAE was routed toward phospholipid biosynthetic pathways. In humans, 33% of an injected 1 g (10 mmol) dose of DMAE was excreted unchanged. It was suggested that the remaining dose might have been demethylated to ethanolamine directed toward normal metabolic pathways.[NTP; Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE)
108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters (November 2002); Available from, as of February 23, 2015: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/dmae_update_110002_508.pdf
Dimethylaminoethanol /prc: postulated to/ undergo endogenous methylation. /From table/
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 171
Specific methods utilizing combined gas chromatography mass spectrometry were used to measure the metabolism of [(2)H6]deanol and its effects on acetylcholine concentration in vitro and in vivo. In vitro [(2)H6]deanol was rapidly taken up by rat brain synaptosomes, but was neither methylated nor acetylated. [(2)H6]Deanol was a weak competitive inhibitor of the high affinity transport of [(2)H4]choline, thus reducing the synthesis of [(2)H4]acetylcholine. In vivo [(2)H6]deanol was present in the brain after i.p. or p.o. administration, but was not methylated or acetylated. Treatment of rats with [(2)H6]deanol significantly increased the concentration of choline in the plasma and brain but did not alter the concentration of acetylcholine in the brain. Treatment of rats with atropine (to stimulate acetylcholine turnover) or with hemicholinium-3 (to inhibit the high affinity transport of choline) did not reveal any effect of [(2)H6]deanol on acetylcholine synthesis in vivo. However, since [(2)H6]deanol did increase brain choline, it may prove therapeutically useful when the production of choline is reduced or when the utilization of choline for the synthesis of acetylcholine is impaired.
PMID:512912 Jope RS, Jenden DJ; J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 211 (3) :472-9 (1979)
Choline (N,N,N-trimethylethanolamine), which is widely distributed in membrane lipids and is a component of sediment biota, has been shown to be utilized anaerobically by mixed prokaryote cultures to produce methane but not by pure cultures of methanogens. Here, we show that five recently isolated Methanococcoides strains from a range of sediments (Aarhus Bay, Denmark; Severn Estuary mudflats at Portishead, United Kingdom; Darwin Mud Volcano, Gulf of Cadiz; Napoli mud volcano, eastern Mediterranean) can directly utilize choline for methanogenesis producing ethanolamine, which is not further metabolized. Di- and monomethylethanolamine are metabolic intermediates that temporarily accumulate. Consistent with this, dimethylethanolamine was shown to be another new growth substrate, but monomethylethanolamine was not. The specific methanogen inhibitor 2-bromoethanesulfonate (BES) inhibited methane production from choline. When choline and trimethylamine are provided together, diauxic growth occurs, with trimethylamine being utilized first, and then after a lag (about 7 days) choline is metabolized. Three type strains of Methanococcoides (M. methylutens, M. burtonii, and M. alaskense), in contrast, did not utilize choline. However, two of them (M. methylutens and M. burtonii) did metabolize dimethylethanolamine. These results extend the known substrates that can be directly utilized by some methanogens, giving them the advantage that they would not be reliant on bacterial syntrophs for their substrate supply.
PMID:23001649 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3497383 Watkins AJ et al; Appl Environ Microbiol. 78 (23): 8298-303 (2012)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for 2-DIMETHYLAMINOETHANOL (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.


