



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0

1. 5-hydroxymilbemycin Beta7
2. Cl 301,423
3. Cl 301423
4. Cydectin
5. Milbeknock
6. Milbemectin
7. Milbemycin A3
8. Milbemycin A4
9. Milbemycin Alpha1
10. Milbemycin Alpha10
11. Milbemycin Alpha11
12. Milbemycin Alpha13
13. Milbemycin Alpha14
14. Milbemycin Alpha15
15. Milbemycin Alpha2
16. Milbemycin Alpha3
17. Milbemycin Alpha4
18. Milbemycin Alpha5
19. Milbemycin Alpha6
20. Milbemycin Alpha7
21. Milbemycin Alpha8
22. Milbemycin Alpha9
23. Milbemycin B
24. Milbemycin Beta1
25. Milbemycin Beta12
26. Milbemycin Beta2
27. Milbemycin Beta3
28. Milbemycin D
29. Milbemycins
30. Mixture Of Milbemycins A3 And A4
1. 113507-06-5
2. Proheart 6
3. Ngu5h31yo9
4. Cl 301,423
5. Nsc-760424
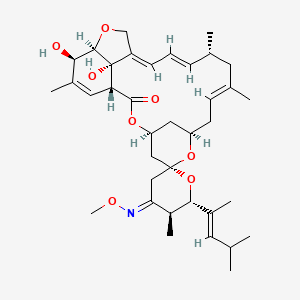
6. (1r,4s,4'e,5's,6r,6's,8r,10e,13r,14e,16e,20r,21r,24s)-21,24-dihydroxy-4'-methoxyimino-5',11,13,22-tetramethyl-6'-[(e)-4-methylpent-2-en-2-yl]spiro[3,7,19-trioxatetracyclo[15.6.1.14,8.020,24]pentacosa-10,14,16,22-tetraene-6,2'-oxane]-2-one
7. Cl-301,423
8. (6r,25s)-5-o-demethyl-28-deoxy-25-((e)-1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl)-6,28-epoxy-23-oxomilbemycin B 23-(e)-(o-methyloxime)
9. Milbemycin B
10. Moxidectina
11. Moxidectine
12. Moxidectinum
13. Moxidectine [inn-french]
14. Moxidectinum [inn-latin]
15. Unii-ngu5h31yo9
16. Moxidectina [inn-spanish]
17. Moxidectin [usan:inn:ban]
18. Moxidectin (tn)
19. (2ae,2'r,4e,4'e,5's,6r,6's,8e,11r,15s,17ar,20r,20ar,20bs)-6'-[(1e)-1,3-dimethylbut-1-enyl]-20,20b-dihydroxy-4'-(methoxyimino)-5',6,8,19-tetramethyl-3',4',5',6,6',7,10,11,14,15,17a,20,20a,20b-tetradeca
20. Hydrospiro[2h,17h-11,15-methanofuro[4,3,2-pq][2,6]benzodioxacyclooctadecine-13,2'-pyran]-17-one
21. Moxidectin [mi]
22. Moxidectin (usp/inn)
23. Moxidectin [inn]
24. Moxidectin [usan]
25. Moxidectin [mart.]
26. Moxidectin [usp-rs]
27. Moxidectin [who-dd]
28. Moxidectin For Veterinary Use
29. Moxidectin [green Book]
30. Chembl2104415
31. Dtxsid5037577
32. Moxidectin [orange Book]
33. Schembl13112872
34. Chebi:183811
35. Moxidectin [usp Monograph]
36. Advocate Component Moxidectin
37. Hy-b0777
38. Mfcd00866560
39. S3713
40. Akos025401990
41. Zinc253476173
42. Ccg-270317
43. Db11431
44. Moxidectin Component Of Advocate
45. Nsc 760424
46. Moxidectin [ema Epar Veterinary]
47. (2ae,4e,5'r,6r,6's,8e,11r,13s,15s,17ar,20r,20ar,20bs)-6'-((e)-1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl)-5',6,6',7,10,11,14,15,17a,20,20a,20b-dodecahydro-20,20b-dihydroxy-5',6,8,19-tetramethylspiro(11,15-methano-2h,13h,17h-furo(4,3,2-pq)(2,6)benzodioxacyclooctadecin-13,2'-(2h)pyran)-4',17(3'h)-dione 4'-(e)-(o-methyloxime)
48. Ac-27773
49. As-17881
50. Moxidectin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
51. Cl-301423
52. M3136
53. D05084
54. Moxidectin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
55. 507m065
56. Moxidectin For Veterinary Use [ep Monograph]
57. Moxidectin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
58. Moxidectin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
59. Moxidectin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
60. Moxidectin For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
61. Milbemycin B, 5-o-demethyl-28-deoxy-25-((1e)-1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl)-6,28-epoxy-23-(methoxyimino)-, (6r,23e,25s)-
62. Milbemycin B, 5-o-demethyl-28-deoxy-25-(1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl)-6,28-epoxy-23-(methoxyimino)-, (6r,23e,25s(e))-
63. Milbemycin B, 5-o-demethyl-28-deoxy-25-(1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl)-6,28-epoxy-23-(methoxyimino)-,(6r,23e,25s(e))-
| Molecular Weight | 639.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C37H53NO8 |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 639.37711765 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 639.37711765 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 116 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 46 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1340 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Moxidectin is indicated for the treatment of river blindness, also called onchocerciasis, in patients aged 12 years and older. River blindness is caused by a parasitic worm _Onchocerca volvulus_ and it is manifested as severe itching, disfiguring skin conditions and visual impairment caused by the worm's larvae. The transmission of _Onchocerca volvulus_ is performed person to person by black flies that breed in fast-flowing rivers in sub-Saharan Africa, Yemen and South and Central America. The larvae released by the adult parasite invade skin and eyes where they can produce the severe disease manifestations.
FDA Label
Moxidectin has been reported to be highly effective against _Onchocerca volvulus_ when compared to ivermectin. When moxidectin was administered in infected individuals, the microfilarial load in the skin was lower even when compared to the current therapy, ivermectin. The levels of microfilarial got reduced to an undetectable level while being safe to be used in mass drug administration.
Anthelmintics
Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of HELMINTHIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Anthelmintics.)
Antinematodal Agents
Substances used in the treatment or control of nematode infestations. They are used also in veterinary practice. (See all compounds classified as Antinematodal Agents.)
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P02 - Anthelmintics
P02C - Antinematodal agents
P02CX - Other antinematodals
P02CX03 - Moxidectin
Absorption
The penetration of moxidectin in the parasite is not restricted as this compound is a very poor substrate of p-glycoprotein, which is vital for the reduction of the uptake of lipophilic compounds from the GI tract and for the increase in biliary, intestinal and renal secretion. After oral administration of moxidectin, the plasma maximal concentration of 70.4 mg/kg was reached after 0.37 day with a reported AUC of 363.6 mcg/day/ml. It is also important to mention that oral bioavailability is enhanced with the co-administration with lipids.
Route of Elimination
When moxidectin is orally administered, 2% of the dose is eliminated unchanged in the feces within 72 hours. Renal elimination is negligible.
Volume of Distribution
Moxidectin presents a larger volume of distribution and mean residence time when compared to ivermectin. The reported volume of distribution is of 1.2 l/kg.
Clearance
The apparent clearance of moxidectin is 3.5 L/hour.
Reports have registered enzymatic modification in humans and in nematodes. In the case of moxidectin, there has been registered C29-30- and C14-mono-hydroxymethyl derivatives mainly by the cytochrome CYP3A and CYP2B. The metabolism of moxidectin is considered to contribute to a small extent to the elimination. Some other metabolites formed are O-demethyl-dihydroxy metabolites. The metabolism of the of moxidectin is not major as the major residue in fat, liver, kidney and muscle is the unchanged moxidectin.
Moxidectin reporter terminal half-life is 20.2 days.
Moxidectin selectively binds to the parasite's GABA-A and glutamate-gated chloride ion channels which are vital for the function of invertebrate nerve and muscle cells. It presents activity against the parasite but it does not kill him. Once moxidectin is bound, there is an increased permeability leading to an influx of chloride ions and flaccid paralysis of the parasite.


