



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
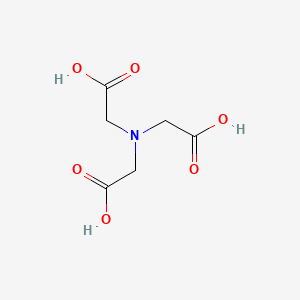

1. Acid, Nitrilotriacetic
2. Aluminum Nitrilotriacetate
3. Dysprosium Nitrilotriacetate
4. Nitrilotriacetate, Aluminum
5. Nitrilotriacetate, Dysprosium
6. Nitrilotriacetate, Trisodium
7. Trisodium Nitrilotriacetate
1. 139-13-9
2. 2,2',2''-nitrilotriacetic Acid
3. Triglycollamic Acid
4. N,n-bis(carboxymethyl)glycine
5. Aminotriacetic Acid
6. Complexon I
7. Nta
8. Nitrilotriacetate
9. Trilon A
10. Glycine, N,n-bis(carboxymethyl)-
11. 2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic Acid
12. Komplexon I
13. Titriplex I
14. Versene Nta Acid
15. Nitrilotriessigsaeure
16. Hampshire Nta Acid
17. Tri(carboxymethyl)amine
18. Nitrilo-2,2',2''-triacetic Acid
19. Acetic Acid, Nitrilotri-
20. Nitrilotriaceticacid
21. 2-(bis(carboxymethyl)amino)acetic Acid
22. Chel 300
23. Nci-c02766
24. Mfcd00004287
25. Nitrilotriacetic Acid (nta)
26. Alpha,alpha',alpha''-trimethylaminetricarboxylic Acid
27. Chebi:44557
28. Ka90006v9d
29. Nsc-2121
30. Nitriloacetate
31. Dsstox_cid_939
32. Dsstox_rid_75878
33. Dsstox_gsid_20939
34. Tris(carboxymethyl)amine
35. Cas-139-13-9
36. Ccris 436
37. Aminotriethanoic Acid
38. N,n-bis(carboxymethyl)glysine
39. Hsdb 2853
40. Kyselina Nitrilotrioctova [czech]
41. Kyselina Nitrilotrioctova
42. Nsc 2121
43. Einecs 205-355-7
44. Brn 1710776
45. Unii-ka90006v9d
46. Ai3-52483
47. H3nta
48. Potassium Cadmium Nitrilotriacetate
49. Einecs 256-488-2
50. Nitrilotriacetic-acid
51. Wln: Qv1n1vq1vq
52. Ec 205-355-7
53. Cambridge Id 5122183
54. Nitrilotriessigsa Currencyure
55. N(ch2-cooh)3
56. Nta (nitrilotriacetic Acid)
57. Schembl20409
58. 4-04-00-02441 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
59. 80751-51-5
60. Mls000069464
61. Bidd:er0361
62. Glycine,n-bis(carboxymethyl)-
63. Nitrilo-2,2''-triacetic Acid
64. Chembl1234848
65. Dtxsid6020939
66. Nsc2121
67. Hms2232k17
68. Nitrilotriacetic Acid [mi]
69. Ccg-2133
70. Str02791
71. Zinc1849692
72. Nitrilotriacetic Acid [hsdb]
73. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, P.a., 99%
74. Tox21_202195
75. Tox21_300156
76. Bbl002469
77. Nitrilo-n,n,n-triacetic Acid
78. Stk387109
79. Akos005441655
80. Nitrilotriacetic Acid [usp-rs]
81. Db03040
82. Hy-w030778
83. Ncgc00091141-01
84. Ncgc00091141-02
85. Ncgc00091141-03
86. Ncgc00091141-04
87. Ncgc00254116-01
88. Ncgc00259744-01
89. Bp-30104
90. Cadmate(1-), (n,n-bis((carboxy-kappao)methyl)glycinato(3-)-kappan,kappao)-, Potassium (1:1), (t-4)-
91. Cadmate(1-), (n,n-bis((carboxy-kappao)methyl)glycinato(3-)-kappan,kappao)-, Potassium, (t-4)-
92. Smr000054748
93. 2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]essigsäure
94. Db-042463
95. Cs-0074802
96. Ft-0631809
97. N0098
98. Nitrilotriacetic Acid Acs Grade 100g
99. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, Sigma Grade, >=99%
100. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, Acs Reagent, >=99.0%
101. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, Bioultra, >=99.0% (t)
102. .alpha.,.alpha.''-trimethylaminetricarboxylic Acid
103. A,a',a''-trimethylaminetricarboxylic Acid
104. Disodium Edetate Impurity A [ep Impurity]
105. Nitrilotriacetic Acid And Its Salts [iarc]
106. Q425340
107. J-007239
108. F1905-6980
109. Sodium Calcium Edetate Impurity A [ep Impurity]
110. Z1889996324
111. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, Acs Reagent, For Complexometry, >=98%
112. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
113. Potassium (n,n-bis(carboxymethyl)glycinato(3-)-n,o,o',o'')cadmate(1-)
114. Nitrilotriacetic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 191.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H9NO6 |
| XLogP3 | -3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 191.04298701 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 191.04298701 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 115 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 187 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Chelating Agents
Chemicals that bind to and remove ions from solutions. Many chelating agents function through the formation of COORDINATION COMPLEXES with METALS. (See all compounds classified as Chelating Agents.)
AFTER ORAL ADMIN OF 180 MG/KG OR 45 MG/KG IV TO RATS, RELATIVELY HIGH CONCN OF NTA WERE FOUND IN LUNGS, INTESTINE, & MUSCLE. PATTERN OF DISTRIBUTION DEPENDED ON ROUTE OF ADMIN. APPROX 99% OF SINGLE ORAL DOSE ELIM IN 24 HR; 96% OF THIS WAS ELIM IN URINE.
CHU I ET AL; BULL ENVIRON CONTAM TOXICOL 19(4) 417 (1978)
NTA-(14)C ADMIN ORALLY TO RATS. 95% WAS EXCRETED IN URINE. LESS THAN 1% ... AS CO2. ABSORPTION OF NTA FROM GI TRACT VARIED: DOG GREATER THAN RAT GREATER THAN RABBIT & MONKEY ... DEPOSITED IN SKELETON. CONCN ... INCR WITH NUMBER OF ADMIN DOSES. MOST ACTIVE AREAS FOR ACCUMULATION ... @ SITES OF VERY ACTIVE BONE FORMATION. ALTHOUGH CONCN /NTA/ DECR RAPIDLY WITH CESSATION OF INTAKE, A SMALL AMT WAS RETAINED IN BONE AFTER EACH DOSE ... .
Menzie, C. M. Metabolism of Pesticides, An Update. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish, Wild-life Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 184, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, l974., p. 279
DOGS ADMIN 10, 20, & 50 MG NITRILOTRIACETIC ACID/KG EXCRETED MATERIAL IDENTIFIED AS CHONDROITIN A SULFATE &/OR CHONDROITIN C SULFATE.
PMID:128847 JAQUES LB, SUE TK; TOXICOL APPL PHARMACOL 34 (3): 521 (1975)
The kidney attains concentrations of NTA greater than that in the plasma in rats with steady state plasma NTA levels. The relatively high kidney concentrations of NTA can be attributed to high concentrations of NTA in small volumes of urine. NTA is not metabolized in mammals and is excreted rapidly by filtration in the kidney ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V8 198 (1989)
A capsule containing 10 mg [1 14C]NTA in gelatin was given orally in fruit juice to each of eight male volunteers who had received no drugs for two weeks before entering the study. Twelve % of the admin radioactivity was excreted in the urine & 77% in the feces as unchanged NTA within 120 h of admin. A peak in the blood concn (6.5 ng/g serum) occurred 12 h after dosing ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V8 202 (1989)
WASHED CELL SUSPENSION OF PSEUDOMONAS SP, ISOLATED FROM SEWAGE EFFLUENT, DEGRADED ALL NTA-NITROGEN TO AMMONIUM PRIOR TO TOTAL CONVERSION OF NTA TO CO2 AND WATER. SMALL AMOUNT OF NITRITE WERE ALSO FORMED. STUDY TENDED TO SUPPORT CONTENTION THAT NTA DEGRADATION PROCEEDED THROUGH AMINODIACETIC ACID AND GLYCINE ... .
Menzie, C. M. Metabolism of Pesticides, An Update. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish, Wild-life Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 184, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, l974., p. 279
In mammalian systems, NTA is not metabolized and is excreted rapidly by filtration in the kidney.
PMID:3899518 Anderson RL et al; Crit Rev Toxicol 15 (1): 1-102 (1985)
A positive synergistic action was produced by nitrilotriacetic acid in combination with soluble chromium(VI) as potassium dichromate in the induction of gene mutations in Salmonella typhimurium and Drosophila melanogaster. The possibility that this action depended on an effect of nitrilotriacetic acid on chromium(VI) reduction by cellular proteins was demonstrated. Gene mutations were detected by the Ames plate incorporation test on strains (TA-100), (TA-92), (TA-104) and (TA-103) of Salmonella typhimurium. In both the Salmonella and Drosophila systems, the nitrilotriacetic acid synergistically increased the mutagenicity of subtoxic doses of chromium(VI) while at higher chromium(VI) dose levels a decline of mutation frequency was noted in the presence of nitrilotriacetic acid, probably as a result of toxicity. Both effects may be referred to enhanced availability of the final genotoxic agent in the presence of nitrilotriacetic acid. The interaction was particularly evident in strains (TA-100) and (TA-104) which carried mutations affecting cell wall permeability and DNA repair. In these strains, the uptake of chromium(VI) and nitrilotriacetic acid was increased and the resulting DNA damage repaired less efficiently or by error prone mechanisms. Nitrilotriacetic acid may facilitate chromate uptake by the anion carriers of the cell membrane. Other mechanisms linked to its chelating action may also be important as suggested by the significant synergistic effect on chromium(VI) mutagenicity produced by ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic acid at very low doses, which do not modify chromium(VI) reduction by Salmonella proteins in cell free conditions.
Gava C et al; Toxicol and Environ Chem 22 (1-4): 27-38 (1989)


