



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia

South Africa
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
0
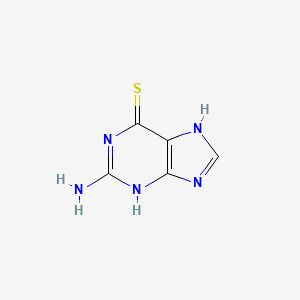

1. 2 Amino 6 Purinethiol
2. 2-amino-6-purinethiol
3. 6 Thioguanine
4. 6-thioguanine
5. Anhydrous, Thioguanine
6. Lanvis
7. Tabloid
8. Thioguanin Gsk
9. Thioguanin-gsk
10. Thioguanine Anhydrous
11. Thioguanine Hemihydrate
12. Thioguanine Monosodium Salt
13. Thioguanine Tabloid
14. Thioguaningsk
15. Tioguanina Wellcome
16. Tioguanine
1. 6-thioguanine
2. 154-42-7
3. Tioguanine
4. 2-amino-6-mercaptopurine
5. 6-mercaptoguanine
6. Tioguanin
7. Tabloid
8. 2-amino-6-purinethiol
9. Lanvis
10. 2-amino 6mp
11. 2-aminopurin-6-thiol
12. 2-aminopurine-6-thiol
13. 2-aminopurine-6(1h)-thione
14. Wellcome U3b
15. 6-mercapto-2-aminopurine
16. 2-amino-9h-purine-6-thiol
17. 6-tg
18. 2-amino-6-merkaptopurin
19. Tioguaninum
20. Guanine, Thio-
21. Tioguanina
22. 6h-purine-6-thione, 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-
23. 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-6h-purine-6-thione
24. Thioguanine Anhydrous
25. Nsc-752
26. Bw 5071
27. Purine-6-thiol, 2-amino-
28. Purine-6(1h)-thione, 2-amino-
29. 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-6h-purine-6-thione
30. Tg
31. Thioguanine, Anhydrous
32. Thg
33. Nsc 752
34. 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-6h-purin-6-thion
35. X 27
36. Tioguanine (inn)
37. Tioguanine [inn]
38. 2-amino-6,7-dihydro-3h-purine-6-thione
39. 2-amino-1,9-dihydropurine-6-thione
40. Chembl727
41. Wix31zpx66
42. 2-amino-3,7-dihydro-6h-purine-6-thione
43. Chebi:9555
44. Nsc752
45. Thioguanine2-amino-6-purinethiol
46. 2-thioguanine
47. 2-amino-1h-purine-6(9h)-thione
48. 2-amino-1,7-dihydropurine-6-thione
49. Nsc-76504
50. Ncgc00094792-01
51. Dsstox_cid_3652
52. 2-amino-6-mp
53. Tioguanine Hemihydrate
54. Dsstox_rid_77129
55. Dsstox_gsid_23652
56. Tioguaninum [inn-latin]
57. C5h5n5s
58. 2-aminopurin-6-thiol [czech]
59. Guanine, Thio- (van)
60. 2-amino-6-merkaptopurin [czech]
61. 6-tioguanine
62. Tioguanina [inn-spanish]
63. Cas-154-42-7
64. Dx4
65. Smr000857244
66. Lanvis (tn)
67. Ccris 8997
68. 9h-purine-6-thiol, 2-amino-
69. Hsdb 2504
70. Sr-05000002077
71. Einecs 205-827-2
72. Thioguanine [usan:usp]
73. 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-6h-purin-6-thion [czech]
74. Unii-wix31zpx66
75. Thioquanine
76. Ai3-26078
77. 6-thioguano-sine
78. 6-tg/thioguanine
79. Mfcd00233553
80. 1330266-29-9
81. Spectrum_000235
82. Thioguanine [mi]
83. Spectrum2_000695
84. Spectrum3_000577
85. Spectrum4_000926
86. Spectrum5_001455
87. Purine Antimetabolite: Antimetabolite: Inhibits Nucleic Acid Replication
88. Thioguanine [hsdb]
89. 2-amino-6-mercapto-purin
90. 6-thioguanine, >=98%
91. Schembl3701
92. Schembl5898
93. Nciopen2_004153
94. Tioguanine [who-dd]
95. Bspbio_001994
96. Kbiogr_001452
97. Kbiogr_002476
98. Kbioss_000715
99. Kbioss_002483
100. Mls001333131
101. Mls001333132
102. Mls006010896
103. Divk1c_000428
104. Spectrum1500573
105. Spbio_000849
106. 154-42-7
107. 6-thioguanine
108. 2-amino-6-mercapto-9h-purine
109. Gtpl6845
110. Thioguanine (tn) (glaxosmith)
111. Dtxsid6023652
112. Hms501f10
113. Kbio1_000428
114. Kbio2_000715
115. Kbio2_002476
116. Kbio2_003283
117. Kbio2_005044
118. Kbio2_005851
119. Kbio2_007612
120. Kbio3_001494
121. Kbio3_002954
122. Cmap_000061
123. Ninds_000428
124. Bcpe000001
125. Hms1921e09
126. Hms2092m11
127. Hms2235f05
128. Hms3865g13
129. Pharmakon1600-01500573
130. Albb-023493
131. Bcp27718
132. Zinc6382803
133. Tox21_111035
134. Tox21_113184
135. Tox21_202401
136. Tox21_300275
137. Bdbm50200099
138. Ccg-39890
139. Nsc757348
140. S1774
141. Akos003389499
142. Akos015901298
143. Tox21_111035_1
144. 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-purine-6-thione
145. 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-purine-6-thione
146. Ac-8421
147. Bcp9000197
148. Ccg-213953
149. Ccg-266338
150. Cs-1497
151. Db00352
152. Nsc-757348
153. Ps-5007
154. Wln: T56 Bnm Fym Inj Fus Hz
155. Idi1_000428
156. Smp2_000326
157. Ncgc00094792-02
158. Ncgc00094792-03
159. Ncgc00094792-05
160. Ncgc00094792-06
161. Ncgc00094792-17
162. Ncgc00188976-01
163. Ncgc00188976-02
164. Ncgc00254082-01
165. Ncgc00259950-01
166. Ncgc00263442-01
167. Ncgc00263442-02
168. Ncgc00263442-05
169. Ac-23020
170. Bt166463
171. Hy-13765
172. Nci60_041643
173. Smr004701808
174. Sbi-0051533.p003
175. Ft-0611217
176. T0212
177. 2-amino-1,7-dihydro-6h-purine-6-thione #
178. C07648
179. D08603
180. T71841
181. Ab00174074_06
182. Ab00918694_06
183. Ab01273926-01
184. Ab01273926-02
185. Ab01273926_03
186. 154t427
187. A809532
188. Q385347
189. Sr-05000002077-1
190. Sr-05000002077-5
191. W-108030
192. W-205813
193. Z2768769146
194. 6-thioguanine;6-tg;2-amino-6-mercaptopurine;2-amino-6-purinethiol
195. Thioguanine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
196. Thioguanine;6-tg; 2-amino-6-mercaptopurine; 2-amino-6-purinethiol
197. 6-thioguanine, Hybri-max(tm), 50 X, Gamma-irradiated, Lyophilized Powder, Bioxtra, Suitable For Hybridoma
| Molecular Weight | 167.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N5S |
| XLogP3 | -0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 167.02656635 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 167.02656635 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 111 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 225 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Thioguanine |
| PubMed Health | Thioguanine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | TABLOID brand Thioguanine was synthesized and developed by Hitchings, Elion, and associates at the Wellcome Research Laboratories. It is one of a large series of purine analogues which interfere with nucleic acid biosynthesis, and has been found acti... |
| Active Ingredient | Thioguanine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 40mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aspen Global |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Thioguanine |
| PubMed Health | Thioguanine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | TABLOID brand Thioguanine was synthesized and developed by Hitchings, Elion, and associates at the Wellcome Research Laboratories. It is one of a large series of purine analogues which interfere with nucleic acid biosynthesis, and has been found acti... |
| Active Ingredient | Thioguanine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 40mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aspen Global |
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
CLINICALLY, THIOGUANINE HAS BEEN USED IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE LEUKEMIA AND, IN COMBINATION WITH CYTARABINE, IS ONE OF THE MOST EFFECTIVE AGENTS FOR INDUCTION OF REMISSIONS IN ACUTE GRANULOCYTIC LEUKEMIA; IT HAS NOT BEEN USEFUL IN THE TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH SOLID TUMORS. THIS CMPD HAS BEEN USED AS AN IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE AGENT, PARTICULARLY IN PATIENTS WITH NEPHROSIS AND WITH COLLAGEN-VASCULAR DISORDERS. TOXIC MANIFESTATIONS INCLUDE BONE MARROW DEPRESSION AND GI EFFECTS, ALTHOUGH THE LATTER MAY BE LESS PRONOUNCED THAN WITH MERCAPTOPURINE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1236
SHORT TERM TREATMENT WITH DOXORUBICIN, CYTARABINE, & 6-THIOGUANINE WAS GIVEN TO 90 PATIENTS WITH ACUTE MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA. FIFTY PATIENTS RECEIVED HIGH DOSES (REGIMEN 1) & 41 RECEIVED VERY HIGH DOSES (REGIMEN 2). REMISSION RATE WAS SIGNIFICANTLY HIGHER WITH REGIMEN 1 THAN WITH REGIMEN 2. DURATION OF REMISSION WAS, HOWEVER, SIGNIFICANTLY LONGER WITH REGIMEN 2.
BELL R ET AL; BR MED J 284 (APR 24): 221-24 (1982)
IN ADVANCED COLORECTAL ADENOCARCINOMA, TWO DIFFERENT SCHEDULES OF COMBINATION METHYL-CCNU, 6-THIOGUANINE, & 5-FLUOROURACIL EXHIBITED SIMILAR EFFICACIES, WITH A COMBINED COMPLETE & PARTIAL REMISSION RATE OF 17% & A MEDIAN SURVIVAL OF 53+ WK. SIGNIFICANT SYMPTOMATIC BENEFIT WAS SEEN IN 52% OF PATIENTS. TOXICITY WAS PREDOMINATELY HEMOPOIETIC & GI.
PMID:7231364 ARONEY RS ET AL; MED PEDIATR ONCOL 9 (2): 181-6 (1981)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for THIOGUANINE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Risk-benefit should be considered when the following medical problems exist: Bone marrow depression; chickenpox, existing or recent (including recent exposure; herpes zoster (risk of severe generalized disease); gout, history of; urate renal stones, history of (risk of hyperuricemia); hepatic function impairment (reduced biotransformation; lower dosage is recommended); infection; renal function impairment (reduced elimination; lower dosage is recommended); or sensitivity to thioguanine. Caution should be used also in patients who have had cytotoxic drug therapy and radiation therapy within 4 to 6 weeks.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 2653
Because normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by thioguanine therapy, concurrent use with alive virus vaccine may potentiate the replication of the vaccine virus, may increase the side/adverse effects of the vaccine virus, and/or may decrease the patient's antibody response to the vaccine; immunization of these patients should be undertaken only with extreme caution after careful review of the patient's hematologic status and only with the knowledge and consent of the physician managing the thioguanine therapy. The interval between discontinuation of medication that cause immunosuppression and restoration of the patient's ability to respond to the vaccine depends on the intensity and type of immunosuppression-causing medication used, the underlying disease, and other factors; estimates vary from 3 months to 1 year. Patients with leukemia in remission should not receive live virus vaccine until at least 3 months after their last chemotherapy. Immunization with oral poliovirus vaccine should also be postponed in persons in close contact with the patient, especially family members.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 2653
Because normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by thioguanine therapy, the patient's antibody response to the vaccine may be decreased. The interval between discontinuation of medications that cause immunosuppression and restoration of the patient's ability to respond to the vaccine depends on the intensity and type of immunosuppression-causing medication used, the underlying disease, and other factors; estimates vary from 3 months to 1 year.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 2653
TOXIC MANIFESTATIONS INCL BONE MARROW DEPRESSION & GI EFFECTS ... .
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1236
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for THIOGUANINE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For remission induction and remission consolidation treatment of acute nonlymphocytic leukemias.
FDA Label
Thioguanine is an antineoplastic anti-metabolite used in the treatment of several forms of leukemia including acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Anti-metabolites masquerade as purine or pyrimidine - which become the building blocks of DNA. They prevent these substances becoming incorporated in to DNA during the "S" phase (of the cell cycle), stopping normal development and division. Thioguanine was first synthesized and entered into clinical trial more than 30 years ago. It is a 6-thiopurine analogue of the naturally occurring purine bases hypoxanthine and guanine. Intracellular activation results in incorporation into DNA as a false purine base. An additional cytotoxic effect is related to its incorporation into RNA. Thioguanine is cross-resistant with mercaptopurine. Cytotoxicity is cell cycle phase-specific (S-phase).
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic
Antimetabolites that are useful in cancer chemotherapy. (See all compounds classified as Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01B - Antimetabolites
L01BB - Purine analogues
L01BB03 - Tioguanine
Absorption
Absorption of an oral dose is incomplete and variable, averaging approximately 30% of the administered dose (range: 14% to 46%)
Incompletely and variably (about 30%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
USP Convention. USPDI-Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 14th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1994. (Plus Updates)., p. 2652
THIOGUANINE IS INCOMPLETELY ABSORBED WHEN GIVEN ORALLY, AVERAGING ABOUT 30% OF AN ADMIN DOSE. ... THE ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE OF THE PARENT DRUG IS 1.5 HR, BUT PEAK PLASMA LEVELS OF METABOLITES ARE REACHED IN 6-8 HR. BETWEEN 24% & 46% IS EXCRETED IN THE URINE AS METABOLITES WITHIN 24 HR. ... THIS DRUG IS CLEARED RAPIDLY FROM PLASMA AFTER IV ADMINISTRATION; MORE THAN 80% EXCRETED WITHIN 24 HR. ALTHOUGH THIOGUANINE.../SRP: HAS LIMITED ACCESS ACROSS/ THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER IN ANIMALS AFTER LARGE DOSES, VERY LITTLE ENTERS THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF HUMANS AFTER THE USUAL CLINICAL DOSES ARE EMPLOYED.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 2046
THE METABOLISM AND PHARMACOKINETICS OF 6-THIOGUANINE WERE STUDIED IN DOGS AFTER IV ADMIN OF 5 MG/KG (35)S-THIOGUANINE (TG). THIOGUANINE WAS RAPIDLY & EXTENSIVELY DEGRADED. METABOLITES WERE NOT FOUND IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID IN SIGNIFICANT CONCENTRATIONS.
PMID:7307231 LOO TL ET AL; CANCER CHEMOTHER PHARMACOL 6 (2): 131-6 (1981)
Hepatic. First converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP). TGMP is further converted to the di- and tri-phosphates, thioguanosine diphosphate (TGDP) and thioguanosine triphosphate (TGTP) by the same enzymes that metabolize guanine nucleotides.
... WHEN THIOGUANINE IS ADMIN TO MAN, THE S-METHYLATION PRODUCT, 2-AMINO-6-METHYLTHIOPURINE, RATHER THAN FREE THIOGUANINE APPEARS IN URINE; INORGANIC SULFATE IS ALSO A MAJOR URINARY METABOLITE. LESSER AMT OF 6-THIOURIC ACID ARE FORMED, SUGGESTING THAT DEAMINATION CATALYZED BY THE ENZYME GUANASE DOES NOT HAVE A MAJOR ROLE IN THE METABOLIC INACTIVATION OF THIOGUANINE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1236
THE PHARMACOKINETICS OF RADIOLABELED 6-THIOGUANINE (TG) WERE COMPARED WITH THAT OF BETA-2'-DEOXYTHIOGUANOSINE (BETA-TGDR) AFTER IV ADMIN. URINARY EXCRETION OF THE RADIOLABEL WAS 75% OF THE DOSE 24 HR AFTER ADMIN. BOTH THIOPURINES WERE RAPIDLY & EXTENSIVELY DEGRADED & EXCRETED AS 6-THIOXANTHINE, INORGANIC SULFATE, S-METHYL-6-THIOXANTHINE, & 6-THIOURIC ACID IN ADDITION TO OTHER PRODUCTS. SMALL AMOUNTS OF UNCHANGED DRUG WERE ALSO EXCRETED. STUDIES SUGGEST THAT BETA-TGDR IS A LATENT FORM OF TG. SINCE RESISTANCE TO ANTILEUKEMIC AGENT 6-THIOGUANINE INEVITABLY DEVELOPS IN ANIMAL TUMORS, THIS NEW AGENT BETA-TGDR IS OF POTENTIAL CLINICAL USE.
LU K ET AL; PHARMACOKINETICS AND METABOLISM OF BETA-2'-DEOXYTHIOGUANOSINE AND 6-THIOGUANINE IN MAN; CANCER CHEMOTHER PHARMACOL 8 (1): 119-23 (1982)
When the compound was given in singles doses of 65 to 300 mg/m^2, the median plasma half-disappearance time was 80 minutes (range 25-240 minutes)
Thioguanine competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and is itself converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP), which reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses. TGMP interferes with the synthesis of guanine nucleotides by its inhibition of purine biosynthesis by pseudofeedback inhibition of glutamine-5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase, the first enzyme unique to the de novo pathway of purine ribonucleotide synthesis. TGMP also inhibits the conversion of inosinic acid (IMP) to xanthylic acid (XMP) by competition for the enzyme IMP dehydrogenase. Thioguanine nucleotides are incorporated into both the DNA and the RNA by phosphodiester linkages, and some studies have shown that incorporation of such false bases contributes to the cytotoxicity of thioguanine. Its tumor inhibitory properties may be due to one or more of its effects on feedback inhibition of de novo purine synthesis; inhibition of purine nucleotide interconversions; or incorporation into the DNA and RNA. The overall result of its action is a sequential blockade of the utilization and synthesis of the purine nucleotides.
THIOGUANINE, THE 6-THIO ANALOGUE OF GUANINE, IS A PRODRUG THAT IS CONVERTED TO 6-THIOGUANINE-RIBOSE-PHOSPHATE, AN ACTIVE METABOLITE. ... 6-THIOGUANINE-RIBOSE-PHOSPHATE IS A FEEDBACK INHIBITOR OF THE INITIAL (AMIDOTRANSFERASE) STEP IN PURINE BIOSYNTHESIS. THIS METABOLITE ALSO BLOCKS CONVERSIONS OF INOSINIC ACID TO GUANYLIC ACID & OF GUANYLIC ACID TO GDP. THIOGUANINE ALSO IS CONVERTED TO THE DEOXYNUCLEOTIDE TRIPHOSPHATE, WHICH CAN BE INCORPORATED INTO TUMOR CELL DNA. ALTHOUGH SOME INVESTIGATORS BELIEVE THAT THIS IS THE MAJOR MECHANISM OF CYTOTOXICITY, THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF THE VARIOUS SITES OF ACTION HAS NOT BEEN DETERMINED. ... THIOGUANINE IS CELL-CYCLE SPECIFIC FOR THE S PHASE.
American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 2046
APPARENTLY, THE METABOLISM OF 6-THIOGUANINE TO 6-THIOGUANOSINE IN SARCOMA 180 & 180/TG CELLS IS MEDIATED BY PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE & NEWLY SYNTHESIZED 6-THIOGUANOSINE IS READILY EFFLUXED INTO THE CELLULAR ENVIRONMENT. THE FORMATION OF 6-THIOGUANINE, BY PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE, MAY BE IMPORTANT TO THE EXPRESSION OF CELLULAR SENSITIVITY TO 6-THIOGUANINE, IN THAT IT DECR THE AVAIL OF 6-THIOGUANINE FOR DIRECT CONVERSION BY HYPOXANTHINE-GUANINE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE TO THE NUCLEOTIDE LEVEL, A PHENOMENON CRITICAL TO THE EXPRESSION OF THE ANTINEOPLASTIC ACTIVITY OF THE 6-THIOPURINES.
PMID:7459851 LEE SH, SARTORELLI AC; CANCER RES 41 (3): 1086-90 (1981)
PHENYL SUBSTITUTION AT C-8 OF 2-AMINO-6-MERCAPTOPURINE ABOLISHED THE IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE ACTIVITY. THEREFORE, A NONSUBSTITUTED 8 POSITION OF 2-AMINO-6-MERCAPTOPURINE IS ESSENTIAL FOR IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE ACTION.
PMID:6031686 FU SC J ET AL; J MED CHEM 10 (1): 109-10 (1967)
SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING LYMPHOCYTES (IN CELL DIVISION IN CULTURES WITHOUT ADDITION OF PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ, PHA) GO THROUGH VARIOUS PHASES OF 1ST DIVISION WITH THE SAME KINETICS AS PHA-STIMULATED CELLS. IN SAMPLES FROM 10 REFERENTS, THE FREQUENCY OF SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING LYMPHOCYTES VARIED FROM 8.9X10-5 TO 9.5X10-3 AS INDICATED WITH AUTORADIOGRAPHY ON CELLS IN (S + G2) PHASE DETERMINED BY FLOW SORTING. IN PHA-STIMULATED SAMPLES FROM THE SAME PERSONS THE FREQUENCY OF 6-THIOGUANINE (TG)-RESISTANT VARIANTS WAS BETWEEN 4X10-7 & 2.6X10-6, WHICH INDICATES THAT MOST OF THE SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING CELLS WERE TG-SENSITIVE.
PMID:6690915 AMNEUS H ET AL; MUTAT RES 139 (1): 41-4 (1984)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for THIOGUANINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.




