



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
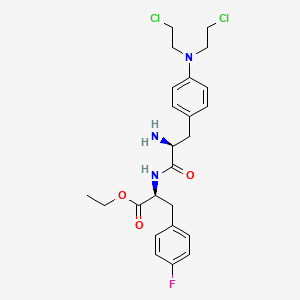

1. Melflufen
2. Melphalan-flufenamide
3. Pepaxto
1. Melflufen
2. Prodrug J 1
3. Prodrug J-1
4. J 1 (prodrug)
5. J-1 (prodrug)
6. 380449-51-4
7. 380449-51-4 (free Base)
8. F70c5k4786
9. J-1
10. L-phenylalanine, 4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)-l-phenylalanyl-4-fluoro-, Ethyl Ester
11. Ethyl (2s)-2-((2s)-2-amino-3-(4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)phenyl)propanamido)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoate
12. J1
13. Mff
14. Ethyl (2s)-2-[[(2s)-2-amino-3-[4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl]propanoyl]amino]-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoate
15. Ethyl (s)-2-((s)-2-amino-3-(4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)phenyl)propanamido)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoate
16. Melphalan Flufenamide [inn]
17. Unii-f70c5k4786
18. Chembl4303060
19. Schembl18239898
20. Gtpl11605
21. Dtxsid40191461
22. Glxc-25713
23. Melphalan Flufenamide (usan/inn)
24. Melphalan Flufenamide [usan:inn]
25. Who 9493
26. Melphalan Flufenamide [usan]
27. Melphalan Flufenamide [who-dd]
28. J 1
29. Hy-105019
30. Cs-0024709
31. D11865
32. Q27277739
| Molecular Weight | 498.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H30Cl2FN3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Exact Mass | 497.1648254 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 497.1648254 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 84.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 579 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Melphalan flufenamide is indicated in combination with [dexamethasone] to treat adults with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received 4 therapies and are refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor, immunomodulatory agent, and anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody. The FDA has withdrawn the drug from the market for this indication following phase 3 trial data showing decreased overall survival.
Pepaxti is indicated, in combination with dexamethasone, for the treatment of adult patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least three prior lines of therapies, whose disease is refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor, one immunomodulatory agent, and one anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, and who have demonstrated disease progression on or after the last therapy. For patients with a prior autologous stem cell transplantation, the time to progression should be at least 3 years from transplantation (see section 4. 4).
Melphalan flufenamide is an alkylating agent indicated to treat relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma in Melphalan flufenamide has a long duration of action as it is given every 28 days. Patients should be counselled regarding risks of thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, anemia, infections, secondary malignancies, embryo-fetal toxicity.
L01AA10
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01A - Alkylating agents
L01AA - Nitrogen mustard analogues
L01AA10 - Melphalan flufenamide
Absorption
For a 40 mg intravenous infusion, the active metabolite reaches a Cmax of 432 ng/mL, with a Tmax of 4-15 minutes, and an AUC of 3143 h\*g/mL.
Route of Elimination
Data regarding the route of elimination of melphalan flufenamide are not readily available. Free melphalan undergoes rapid and spontaneous decomposition, complicating studies on the route of elimination. However, it is expected to be mainly renally excreted.
Volume of Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of melphalan flufenamide is 35 L and of melphalan is 76 L.
Clearance
The mean clearance of melphalan flufenamide is 692 L/h and of melphalan is 23 L/h.
Melphalan flufenamide is metabolised to desethyl-melphalan and melphalan. Melphalan is spontaneously hydrolyzed to monohydroxy-melphalan and dihydroxy-melphalan.
The mean elimination half life of melphalan flufenamide is 2.1 minutes and of melphalan is 70 minutes.
Melphalan flufenamide is a more lipophilic prodrug of melphalan, which allows it to be more readily uptaken by cells. It is likely taken up into malignant cells by passive diffusion, where it is hydrolyzed by aminopeptidase N. The expression of aminopeptidases, along with other hydrolytic enzymes, is upregulated in many malignant cells, making the hydrolysis reaction to melphalan more favourable in a malignant cell. Increased concentrations of free melphalan in malignant cells leads to rapid irreversible DNA damage and apoptosis, reducing the potential for the development of resistance. Free melphalan is an nitrogen mustard derivative alkylating agent. Melphalan attaches alkyl groups to the N-7 position of guanine and N-3 position of adenine, leading to the formation of monoadducts, and DNA fragmenting when repair enzymes attempt to correct the error. It can also cause DNA cross-linking from the N-7 position of one guanine to the N-7 position of another, preventing DNA strands from separating for synthesis or transcription. Finally, melphalan can induce a number of different mutations. While melphalan induces phosphorylation of the DNA damage marker -H2AX in melphalan sensitive cells at 6 hours, melphalan flufenamide induces -H2AX at 2 hours. Melphalan flufenamide is also able to induce -H2AX in melphalan-resistant cells.


