



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
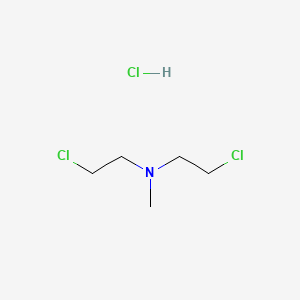

1. Bis(2-chloroethyl)methylamine
2. Caryolysine
3. Chlorethazine
4. Chlormethine
5. Cloramin
6. Embichin
7. Hydrochloride N-oxide, Mechlorethamine
8. Hydrochloride, Mechlorethamine
9. Mechlorethamine
10. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride N Oxide
11. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride N-oxide
12. Mechlorethamine N Oxide
13. Mechlorethamine N-oxide
14. Mechlorethamine Oxide
15. Methylchlorethamine
16. Mitomen
17. Mustargen
18. Mustine
19. N-oxide, Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride
20. N-oxide, Nitrogen Mustard
21. Nitrogen Mustard
22. Nitrogen Mustard N Oxide
23. Nitrogen Mustard N-oxide
24. Nitrogranulogen
25. Nitromin
26. Nsc 10107
27. Nsc 762
28. Nsc-10107
29. Nsc-762
30. Nsc10107
31. Nsc762
1. 55-86-7
2. Chlormethine Hydrochloride
3. Mechlorethamine Hcl
4. Nitrogen Mustard Hydrochloride
5. Chlorethamine
6. 2-chloro-n-(2-chloroethyl)-n-methylethanamine Hydrochloride
7. Hn2 Hydrochloride
8. Chlormethinum
9. Stickstofflost
10. Chloramin
11. Mustine Hydrochloride
12. Bis(2-chloroethyl)methylamine Hydrochloride
13. Azotoyperite
14. Dichloren
15. Embikhine
16. Mitoxine
17. Dimitan
18. Erasol
19. Nitol
20. Dema
21. Nitol Takeda
22. Erasol-ido
23. Chlormethine Hcl
24. Caryolysine
25. Mustin Hydrochloride
26. Embichin
27. Nitrogranulogen Hydrochloride
28. N-mustard
29. Mechlorethamine Chloridrate
30. N-methylbis(2-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
31. Stickstofflost-ebewe
32. 2,2'-dichloro-n-methyldiethylamine Hydrochloride
33. Dichloromethyldiethylamine Hydrochloride
34. 1,5-dichloro-3-methyl-3-azapentane Hydrochloride
35. Di(2-chloroethyl)methylamine Hydrochloride
36. Methyldi(2-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
37. Nci-c56382
38. Mba Hydrochloride
39. Methylbis(2-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
40. Ethanamine, 2-chloro-n-(2-chloroethyl)-n-methyl-, Hydrochloride
41. Chlormethine (hydrochloride)
42. Sk 101
43. N-methyl-2,2'-dichlorodiethylamine Hydrochloride
44. Nsc-762
45. Methyldi(beta-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
46. N-methyl-di-2-chloroethylamine Hydrochloride
47. N-lost
48. Methyl-bis(beta-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
49. N-methyl-bis-beta-chlorethylamine Hydrochloride
50. C 6866
51. N,n-bis(2-chloroethyl)methylamine Hydrochloride
52. Nitrogen Mustard (hn-2), Hydrochloride
53. L0mr697hhi
54. Beta,beta'-dichlorodiethyl-n-methylamine Hydrochloride
55. Nsc762
56. 2-chloro-n-(2-chloroethyl)-n-methylethanamine Hydrochlroide
57. Chebi:55368
58. N,n-bis(2-chloraethyl)methylamin-hydrochlorid
59. Bis(2-chloroethyl)-n-methylamine Hydrochloride
60. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [usp]
61. Carolysine
62. Mebichloramine
63. Nitrogranulogen
64. Embechine
65. Valchlor
66. Ncgc00091835-01
67. 2-chloro-n-(2-chloroethyl)-n-methylethanamine;hydrochloride
68. Embiquine
69. Zagreb
70. Pliva
71. Bis-(2-chloroethyl)methylamine Hydrochloride
72. Dsstox_cid_5757
73. Dsstox_rid_77910
74. Dsstox_gsid_25757
75. Kloramin (van)
76. N-mustard [german]
77. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride (usp)
78. Cas-55-86-7
79. Ccris 448
80. Dichloren Hydrochloride
81. Hsdb 7176
82. Einecs 200-246-0
83. Unii-l0mr697hhi
84. Ai3-16195
85. Mustine Hydrochlor
86. Nitol 'takeda'
87. Mustargen (tn)
88. Prestwick_37
89. Valchlor (tn)
90. Erasol Hydrochloride
91. Mfcd00012517
92. Nitrogen Mustard Hcl
93. Embichin Hydrochloride
94. Chloramin Hydrochloride
95. Mustargen Hydrochloride
96. N,n-bis(2-chloraethyl)methylamin-hydrochlorid [german]
97. Caryolysine Hydrochloride
98. Nsc-762 Hydrochloride
99. Chlormethini Hydrochloridum
100. Chloromethine Hydrochloride
101. Mechorethamine Hydrochloride
102. Schembl3855
103. Mls003899210
104. Diethylamine, 2,2'-dichloro-n-methyl, Hydrochloride
105. Chembl1201001
106. Dtxsid8025757
107. Wln: G2n1&2g &gh
108. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride, 98%
109. Hy-b1253
110. Tox21_111170
111. Tox21_200638
112. S4252
113. Akos015915356
114. Tox21_111170_1
115. Ccg-264667
116. Cs-5080
117. Bis(2-chloroethyl)methylammonium Chloride
118. Ncgc00091835-10
119. Ncgc00258192-01
120. Bp-20221
121. Chlormethine Hydrochloride [mart.]
122. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [mi]
123. Smr000059226
124. Chlormethine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
125. Chlormethine Hydrochloride [who-ip]
126. Db-007290
127. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [hsdb]
128. Bis(2-chloroethyl)-methylamine Hydrochloride
129. Bis(2-chloroethyl)methyl Amine Hydrochloride
130. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [vandf]
131. N,n-bis(chloroethyl)methylamine Hydrochloride
132. Sw220100-1
133. Bis (2-chloroethyl)-methylamine Hydrochloride
134. Bis (2-chloroethyl)methyl Amine Hydrochloride
135. Bis-(2-chloroethyl)-methylamine Hydrochloride
136. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
137. N-methylbis (2-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
138. Bis-(2-chloroethyl)-methyl-amine Hydrochloride
139. D04872
140. F11444
141. Methyldi(.beta.-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
142. N-methyl-bis-(2-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
143. N-methylbis(2-chloroethyl)-amine Hydrochloride
144. 2,2'-dichloro-n-methyldiethylamino Hydrochloride
145. Bis(2-chloroethyl)methylamine-[d4] Hydrochloride
146. Bis-(2-chloro-ethyl)-methyl-amine Hydrochloride
147. Diethylamine,2'-dichloro-n-methyl, Hydrochloride
148. Methylbis(.beta.-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride
149. Chlormethini Hydrochloridum [who-ip Latin]
150. Diethylamine,2'-dichloro-n-methyl-, Hydrochloride
151. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [orange Book]
152. Methyl Bis(.beta.-chloroethyl)amine, Hydrochloride
153. N-methylbis(.beta.-chlorethyl)amine Hydrochloride
154. 1,5-dichloro-3-methyl-3-azapentane, Hydrochloride
155. Mechlorethamine Hydrochloride [usp Monograph]
156. N,n-bis(2-chloroethyl)-n-methylamine Hydrochloride
157. W-105542
158. Q27124263
159. .beta.,.beta.'-dichlorodiethyl-n-methylamine Hydrochloride
160. 2-chloro-n-(chloroethyl)-n-methylethanamine Hydrochloride
161. 2-chloro-n-(2 -chloroethyl)-n-methylethanamine Hydrochloride
162. 2-chloro-n-(2-chloroethyl) -n-methylethanamine Hydrochloride
163. 2-chloro-n-(2-chloroethyl)-n-methylethanamine Hydrochloride (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 192.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H12Cl3N |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 191.003532 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 191.003532 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 3.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 43.7 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Alkylating Agents; Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating;
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Antineoplastic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1032
VET: Antineoplastic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1032
MEDICATION (VET): ... MECHLORETHAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE IS REPORTED TO BE USED FOR TREATMENT OF LYMPHOSARCOMA & OF MAST CELL SARCOMA IN DOGS & OF FOWL LEUKOSIS ... /MECHLORETHAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE/
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V9 198 (1975)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for MECHLORETHAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Adverse CNS effects which have occurred following IV administration of mechlorethamine include weakness, headache, drowsiness, vertigo, lightheadedness, convulsions, progressive muscle paralysis, paresthesia, cerebral degeneration, coma, and death. Serious neurotoxicity appears to be a problem only when high doses or intra-arterial and regional perfusion administration techniques are used. Immediate and delayed neurotoxicity, sometimes severe, has been reported in patients receiving higher than recommended doses of the drug in preparation for bone marrow transplantation; neurotoxicity appeared to increase with age and dose administered and occurred more frequently in patients who also received procarbazine or cyclophosphamide.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1069
Adverse dermatologic effects of systemic mechlorethamine therapy occasionally include a maculopapular skin eruption which is apparently idiosyncratic. The maculopapular skin eruption does not necessarily recur with subsequent doses and is not a contraindication to future use of the drug. Erythema multiforme also has been reported. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in patients receiving IV mechlorethamine. ... Herpes zoster, which occurs commonly in patients with lymphoma, may be precipitated by treatment with mechlorethamine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1069
Major and dose-limiting adverse effects of mechlorethamine are nausea and vomiting, which occur in up to 90% of patients who receive the drug and are presumably due to CNS stimulation.Vomiting, which may be severe enough to precipitate vascular accidents in patients with hemorrhagic tendencies, occurs within 0.5-8 hours (usually 1-3 hours) after administration of mechlorethamine. Emesis generally subsides within 8 hours, but nausea may persist 24 hours or longer. ... Other GI effects of mechlorethamine include anorexia, diarrhea, severe hematemesis and dehydration secondary to vomiting, and rarely, peptic ulcers.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1069
Mechlorethamine must be used with extreme caution in patients with leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or anemia caused by infiltration of bone marrow with malignant cells. In these patients, a good response to mechlorethamine therapy with disappearance of tumor from the bone marrow may be associated with improved bone marrow function; however, in the absence of good response or in patients who have received previous treatment with antineoplastic agents, hematopoiesis may be further compromised, resulting in more severe leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and possibly death. Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia appear to be especially sensitive to the hematopoietic effects of mechlorethamine and should receive the drug with extreme caution, if at all.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1069
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MECHLORETHAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Alkylating Agents
Highly reactive chemicals that introduce alkyl radicals into biologically active molecules and thereby prevent their proper functioning. Many are used as antineoplastic agents, but most are very toxic, with carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, and immunosuppressant actions. They have also been used as components in poison gases. (See all compounds classified as Alkylating Agents.)
Irritants
Drugs that act locally on cutaneous or mucosal surfaces to produce inflammation; those that cause redness due to hyperemia are rubefacients; those that raise blisters are vesicants and those that penetrate sebaceous glands and cause abscesses are pustulants; tear gases and mustard gases are also irritants. (See all compounds classified as Irritants.)
Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating
A class of drugs that differs from other alkylating agents used clinically in that they are monofunctional and thus unable to cross-link cellular macromolecules. Among their common properties are a requirement for metabolic activation to intermediates with antitumor efficacy and the presence in their chemical structures of N-methyl groups, that after metabolism, can covalently modify cellular DNA. The precise mechanisms by which each of these drugs acts to kill tumor cells are not completely understood. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2026) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating.)
Chemical Warfare Agents
Chemicals that are used to cause the disturbance, disease, or death of humans during WARFARE. (See all compounds classified as Chemical Warfare Agents.)
Following IV injection, the drug undergoes rapid chemical transformation and unchanged mechlorethamine is undetectable in the blood within a few minutes. Less than 0.01% of an IV dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1070
Mice given 35 mg/kg body wt mechlorethamine hydrochloride iv and examined by autoradiography had significant levels of compound in brain, spinal cord, lung and submaxillary glands.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V9 201 (1975)
Mechlorethamine is incompletely absorbed following intracavitary administration, probably because of rapid deactivation by body fluids.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1804
Following its in vivo admin, mechlorethamine or its hydrochloride is probably converted into ethyleneimmonium ion which reacts with guanine residues in /either the same or/ adjacent strands of DNA as well as with SH groups.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V9 201 (1975)
Mechlorethamine, as an alkylating agent, interferes with DNA replication and transcription of RNA and ultimately results in the disruption of nucleic acid function. Mechlorethamine also possesses weak immunosuppressive activity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1070
Mechlorethamine, as an alkylating agent, interferes with DNA replication and transcription of RNA, and ultimately results in the disruption of nucleic acid function.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 694




