



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
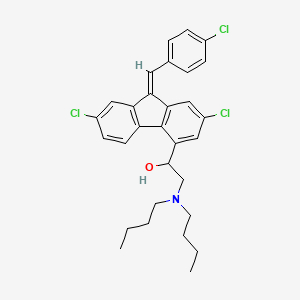

1. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-
2. Benflumetol
3. Benflumetol, (+)-isomer
4. Benflumetol, (+-)-isomer
5. Benflumetol, (-)-isomer
1. Benflumetol
2. 82186-77-4
3. Dl-benflumelol
4. Lumefantrine, (+)-
5. Lumefantrine, (-)-
6. Benflumelol
7. (z)-2-(dibutylamino)-1-(2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl)ethanol
8. D-benflumelol
9. L-benflumelol
10. 2-(dibutylamino)-1-[(9z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylidene]fluoren-4-yl]ethanol
11. Gnf-pf-1971
12. Cpg-56695
13. Zuv4b00d9p
14. (+-)-2,7-dichloro-9-((z)-p-chlorobenzylidene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)fluorene-4-methanol
15. 01np22j3sv
16. 120583-70-2
17. 120583-71-3
18. Chebi:156095
19. F38r0jr742
20. 2-(dibutylamino)-1-(2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl)ethanol
21. 2-(dibutylamino)-1-[(9z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylidene]-9h-fluoren-4-yl]ethan-1-ol
22. Hsdb 7210
23. Ncgc00167490-01
24. 2-(dibutylamino)-1-[(9z)-2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl]ethanol
25. 2-dibutylamino-1-[2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chloro-benzylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl]-ethanol
26. Dsstox_cid_26663
27. Dsstox_rid_81805
28. Dsstox_gsid_46663
29. 2-dibutylamino-1-{2,7-dichloro-9-[1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-meth-(z)-ylidene]-9h-fluoren-4-yl}-ethanol
30. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (9z)-(+)-
31. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (9z)-(-)-
32. Cas-82186-77-4
33. Lumefantrinum
34. Lumefruntrine
35. Unii-f38r0jr742
36. Lumefantrine [usan:inn:ban]
37. Mfcd05662268
38. Lumefantrine [mi]
39. Lumefantrine [inn]
40. Lumefantrine [jan]
41. Unii-zuv4b00d9p
42. Lumefantrine [hsdb]
43. Lumefantrine [usan]
44. (+-)-2,7-dichloro-9-((z)-p-chlorobenzylidene)-alpha((dibutylamino)methyl)fluorene-4-methanol
45. Lumefantrine [vandf]
46. Unii-01np22j3sv
47. Benflumetol, Cpg-56695
48. Lumefantrine [mart.]
49. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-
50. Mls003899226
51. Chembl38827
52. Lumefantrine [usp-rs]
53. Lumefantrine [who-dd]
54. Lumefantrine [who-ip]
55. Schembl127331
56. Lumefantrine (jan/usp/inn)
57. Gtpl9969
58. Dtxsid3046663
59. Hms3260f22
60. Lumefantrine [orange Book]
61. Lumefantrine For System Suitability
62. Amy22191
63. Hy-b0803
64. Lumefantrine [usp Monograph]
65. Tox21_112491
66. Tox21_500270
67. Bbl030364
68. Coartem Component Lumefantrine
69. Lumefantrinum [who-ip Latin]
70. S3746
71. Stl373579
72. Akos015918181
73. Tox21_112491_1
74. Ac-4542
75. Ccg-221574
76. Cs-5130
77. Db06708
78. Hs-0098
79. 2-(dibutylamino)-1-[(9z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylene]fluoren-4-yl]ethanol
80. Lumefantrine Component Of Coartem
81. Ncgc00167490-03
82. Ncgc00167490-05
83. Ncgc00260955-01
84. (9z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylene]-alpha-[(dibutylamino)methyl]-9h-fluorene-4-methanol
85. Smr002543514
86. Cs-0368446
87. L0256
88. J3.642.651i
89. D03821
90. 186l774
91. Q904464
92. Lumefantrine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
93. (z)-2-(dibutylamino)-1-(2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl)ethan-1-ol
94. 2-(dibutylamino)-1-[(z)-2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-9h-fluorene-4-yl]ethanol
95. (+/-)-2,7-dichloro-9-((z)-p-chlorobenzylidene)-.alpha.((dibutylamino)methyl)fluorene-4-methanol
96. (+/-)-2,7-dichloro-9-((z)-p-chlorobenzylidene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)fluorene-4-methanol
97. (1rs)-2-(dibutylamino)-1-[(z)-2,7-dichloro-9-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl]ethanol
98. (9z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylene]-alpha-[(dibutylamino)methyl]-9h-fluoren-4-methanol
99. 2-dibutylamino-1-(2,7-dichloro-9-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)meth-(z)-ylidene)-9h-fluoren-4-yl)ethanol
100. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-.alpha.-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (9z)-(+)-
101. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-.alpha.-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (9z)-(-)-
102. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-.alpha.-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-
103. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-.alpha.-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-(+)-
104. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-.alpha.-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-(-)-
105. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-(+)-
106. 9h-fluorene-4-methanol, 2,7-dichloro-9-((4-chlorophenyl)methylene)-alpha-((dibutylamino)methyl)-, (z)-(-)-
| Molecular Weight | 528.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H32Cl3NO |
| XLogP3 | 8.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 527.154948 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 527.154948 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 23.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 671 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antimalarial
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1003
The efficacy and safety of the 6-dose regimen of artemether-lumefantrine were assessed in an open randomized trial in children and adults presenting with acute, uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Thailand between November 1997 and March 1998. 200 patients were enrolled in 2 centers: 150 received artemether-lumefantrine (i.e., a median total dose of 9.6 mg/kg (interquartile range 8.7-10.7) and 57.9 mg/kg of lumefantrine (52.4-64.0)) and 50 the standard combination of artesunate (12 mg/kg over 3 d) and mefloquine (25 mg/kg). All patients had rapid initial clinical and parasitological responses. The 28 day cure rates were high: 97.7% (95% confidence interval (95% CI) 93.5-99.5%) for artemether-lumefantrine and 100% (95% CI 92.5-100%) for artesunate-mefloquine. The 6-dose regimen of artemether-lumefantrine was better tolerated than, and as effective as, artesunate-mefloquine, the current standard treatment in this area of multidrug-resistant P. falciparum malaria. /Artemether-lumefantrine fixed combination/
PMID:11132386 van Vugt M et al; Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 94 (5): 545-8 (2000)
We report here the results of a randomized double blind trial comparing coartemether (CGP56697), a combination of artemether and benflumetol, with pyrimethamine/sulfadoxine (P/S). Two hundred eighty-seven children 1-5 years of age with uncomplicated falciparum malaria were enrolled at two centers in The Gambia between July 1996 and December 1996. Following treatment, children were visited at home every 24 hr until a blood film free of asexual parasites was obtained. Genotyping of parasites was used to distinguish recrudescence from new infections. Three days after the start of treatment, 133 (100%) of the CGP56697-treated children compared with 128 (93.4%) of children treated with P/S had cleared their parasites (P = 0.003). The day 15 cure rate was 93.3% for CGP56697 and 97.7% for P/S (P = 0.13). Within the third and fourth week after initiation of therapy, 20 children treated with CGP56697 and one of the P/S-treated children returned with second malaria episodes (P < 0.0001). Genotyping suggested that the majority (19 of 23 (82.6%)) of these second episodes were due to new infections, supporting the World Health Organization recommendation that longer follow-up is not relevant for the assessment of drug efficacy. At the two-week follow-up, 28.9% of the P/S treated children but none of the CGP56697-treated children carried gametocytes (P < 0.0001). This study showed that CGP56697 is safe in African children with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria, clears parasites more rapidly than P/S, and results in fewer gametocyte carriers. More frequent new infections within the third and fourth week following treatment with CGP56697 than treatment with P/S are likely to be due to the short prophylactic effect of CGP56697. /Artemether-lumefantrine fixed combination/
PMID:9598454 von Seidlein L et al; Am J Trop Med Hyg 58 (5): 638-44 (1998)
Two hundred and sixty patients were enrolled into a randomized, double-blind, parallel group, dose-finding trial. CGP 56697 /artemether and benflumetol in a fixed combination tablet/ was given orally, either as: A, 4 x 4 tablets over 48 hr; B, 4 x 2 tablets over 48 hr or C, 3 x 4 tablets over 24 hr. Each tablet contained artemether 20 mg amd benflumetol 120 mg. The pharmacokinetics were determined using a population-based approach combining full profiles (42 patients) and sparse data (218 patients). Parasite clearance time and 28 day cure rate were correlated with the derived pharmacokinetic parameters. ... Using a population-based approach it was confirmed that the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of benflumetol and artemether differ markedly. Benflumetol AUC is associated with cure and the effect of benflumetol when coadministered with artemether is to prevent recrudescence. The mode of action of benflumetol is consistent with its longer elimination half-life. A short course of low-dose artemether, which is rapidly absorbed and has a short elimination half-life, produced effective parasite clearance. The complementary pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of benflumetol and artemether was the main rationale for developing a fixed-dose combination. While the 4 x 4 dose regimen is very effective in most endemic areas, the poorer absorption (2.5 fold lower than in China) and the more resistant parasites in Thailand require higher doses of this drug. /Artemether-lumefantrine fixed combination/
PMID:9862244 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1873796 Ezzet F et al; Br J Clin Pharmacol 46 (6): 553-61(1998)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for BENFLUMETOL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
An open, randomized comparison of artemether-benflumetol (CGP 56 697; Novartis) with artesunate-mefloquine was conducted in 617 patients with acute uncomplicated multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria on the western border of Thailand. ... Both regimens were well tolerated. Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sleep disorders, and other neurological side effects were between two and four times more common in the artesunate-mefloquine group than in the artemether-benflumetol group (P < 0.001). /Artemether-lumefantrine fixed combination/
PMID:9449273 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC105468 van Vugt M et al; Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42 (1): 135-9 (1998)
Artemether-lumefantrine is a new fixed antimalarial combination effective against multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria. A prospective electrocardiographic study was conducted in 150 patients receiving artemetherlumefantrine and 50 treated with artesunate-mefloquine. There was no evidence for clinically significant changes in the electrocardiographic intervals and in particular no relationship between plasma concentrations of lumefantrine and QTc prolongation. Artemether-lumefantrine does not have significant cardiac effects at therapeutic doses. /Artemether-lumefantrine fixed combination/
PMID:10674679 van Vugt M et al; Am J Trop Med Hyg 61 (6): 964-7 (1999)
Artemether-lumefantrine (A-L), a new fixed-dose oral antimalarial drug, combines the fast onset of action of artemether (an artemisinin derivative) in terms of parasite clearance with the high cure rate of lumefantrine in the treatment of acute uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. The extensive clinical trial database of A-L has allowed a comprehensive evaluation of its tolerability and safety in a total of 1869 patients (including 243 children aged 5-12 years and 368 children aged < 5 years). The most commonly reported and possibly related adverse effects following A-L therapy involved the gastro-intestinal (abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea) and central nervous (headache, dizziness) systems. Pruritus and rash were reported by < 2% of patients. More than 90% of the reported adverse events, many of which overlapped considerably with the clinical symptomatology or evolution of acute malaria, were rated mild to moderate in intensity. /Artemether-lumefantrine fixed combination/
PMID:11127248 Bakshi R et al; Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 94 (4): 419-24 (2000)
Lumefantrine and artemether combination therapy is indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum, including malaria acquired in chloroquine-resistant areas. May also be used to treat uncomplicated malaria when the Plasmodium species has not been identified. Indicated for use in adults and children greater than 5 kg.
Lumefantrine is a blood schizonticide active against erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. It is thought that administration of lumefantrine with artemether results in cooperate antimalarial clearing effects. Artemether has a rapid onset of action and is rapidly cleared from the body. It is thus thought to provide rapid symptomatic relief by reducing the number of malarial parasites. Lumefantrine has a much longer half life and is believed to clear residual parasites.
Antimalarials
Agents used in the treatment of malaria. They are usually classified on the basis of their action against plasmodia at different stages in their life cycle in the human. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p1585) (See all compounds classified as Antimalarials.)
Absorption
Food increases absorption.
The combination of artemether and lumefantrine (benflumetol) is a new and very well tolerated oral antimalarial drug effective even against multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria. ... The lumefantrine component is absorbed variably in malaria, and is eliminated more slowly (half-life of 3 to 6 days). Absorption is very dependent on coadministration with fat, and so improves markedly with recovery from malaria.
PMID:10496300 White NJ et al; Clin Pharmacokinet 37 (2): 105-25 (1999)
The pharmacokinetics of benflumetol as a fixed combination, artemether-benflumetol (CGP 56697), following three regimens (regimen A: four tablets at 0, 8, 24 and 48 hr (320 mg artemether, 1,920 mg benflumetol); regimen B: two tablets at 0, 8, 24 and 48 hr (160 mg artemether, 960 mg benflumetol); regimen C: four tablets at 0, 8 and 24 hr (240 mg artemether, 1,440 mg benflumetol)) were investigated in 39 patients with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria. All patients showed a rapid initial response with a median parasite clearance time of 40, 41 and 39.5 hr and a fever clearance time of 27.8, 32 and 24.5 hr for regimens A, B and C, respectively. In nine patients (two, four and three patients in regimens A, B and C, respectively), however, parasitemia reappeared in the peripheral blood smear between days 9 and 23. The pharmacokinetics of benflumetol were highly variable, with coefficients of variation in pharmacokinetic parameters ranging from 14.9% to 144%. Absorption and elimination of benflumetol were relatively slow. Median Cmax per dose (first dose) was significantly higher in regimen B (6.29 ng/ml/mg dose) than in regimen A (2.6 ng/ml/mg dose) and regimen C (3.06 ng/ml/mg dose). Mean T1/2z in regimen C (2.65 hr) was significantly shorter than in regimen A (4.5 hr) and regimen B (3.89 hr). In patients on regimens A and B who showed a sensitive response, plasma concentrations of benflumetol were significantly higher than in those with treatment failure.
PMID:10669897 Na-Bangchang K et al; Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 19 (2): 41-6 (1999)
...Three combination regimens containing an average adult lumefantrine dose of 1,920 mg over 3 days (four doses) (regimen A) or 2,780 mg over 3 or 5 days (six doses) (regimen B or C, respectively) were given to 266 Thai patients. Detailed observations were obtained for 51 hospitalized adults, and sparse data were collected for 215 patients of all ages in a community setting. The population absorption half-life of lumefantrine was 4.5 hr. The model-based median (5th and 95th percentiles) peak plasma lumefantrine concentrations were 6.2 (0.25 and 14.8) ug/mL after regimen A, 9. 0 (1.1 and 19.8) ug/mL after regimen B, and 8 (1.4 and 17.4) ug/mL after regimen C. During acute malaria, there was marked variability in the fraction of drug absorbed by patients (coefficient of variation, 150%). The fraction increased considerably and variability fell with clinical recovery, largely because food intake was resumed; taking a normal meal close to drug administration increased oral bioavailability by 108% (90% confidence interval, 64 to 164) (P, 0.0001). The higher-dose regimens (B and C) gave 60 and 100% higher areas under the concentration-time curves (AUC), respectively, and thus longer durations for which plasma lumefantrine concentrations exceeded the putative in vivo MIC of 280 ug/mL (median for regimen B, 252 hr; that for regimen C, 298 hr; that for regimen A, 204 hr [P, 0.0001]) and higher cure rates. Lumefantrine oral bioavailability is very dependent on food and is consequently poor in acute malaria but improves markedly with recovery. The high cure rates with the two six-dose regimens resulted from increased AUC and increased time at which lumefantrine concentrations were above the in vivo MIC.
PMID:10681341 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC89749 Ezzet F et al; Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44 (3): 697-704 (2000)
Extensively metabolized in the liver primarily by cytochrome P450 3A4. The major metabolite found in plasma is desbutyl-lumefantrine.
~ 4.5 days
Three combination regimens containing an average adult lumefantrine dose of 1,920 mg over 3 days (four doses) (regimen A) or 2,780 mg over 3 or 5 days (six doses) (regimen B or C, respectively) were given to 266 Thai patients. ... The population absorption half-life of lumefantrine was 4.5 hr.
PMID:10681341 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC89749 Ezzet F et al; Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44 (3): 697-704 (2000)
...Three combination regimens containing an average adult lumefantrine dose of 1,920 mg over 3 days (four doses) (regimen A) or 2,780 mg over 3 or 5 days (six doses) (regimen B or C, respectively) were given to 266 Thai patients. ... The population absorption half-life of lumefantrine was 4.5 hr. ...
PMID:10681341 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC89749 Ezzet F et al; Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44 (3): 697-704 (2000)
The exact mechanism by which lumefantrine exerts its antimalarial effect is unknown. However, available data suggest that lumefantrine inhibits the formation of β-hematin by forming a complex with hemin and inhibits nucleic acid and protein synthesis.






