



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
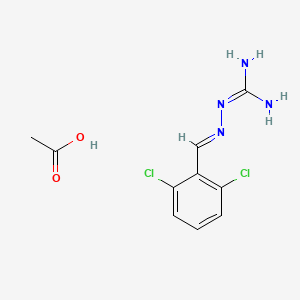

1. 2,6 Dichlorobenzylideneaminoguanidine
2. 2,6-dichlorobenzylideneaminoguanidine
3. Acetate Wyeth-ayerst, Guanabenz
4. Acetate, Guanabenz
5. Br 750
6. Br-750
7. Br750
8. Guanabenz
9. Guanabenz Acetate Wyeth-ayerst
10. Guanabenz Monoacetate
11. Monoacetate, Guanabenz
12. Wy 8678
13. Wy-8678
14. Wy8678
15. Wyeth Ayerst Of Guanabenz Acetate
16. Wyeth-ayerst Of Guanabenz Acetate
17. Wytensin
1. 23256-50-0
2. Wytensin
3. Wy-8678 Acetate
4. Guanabenz (acetate)
5. Guanabenz Acetate Salt
6. Guanabenz Monoacetate
7. Mls000028717
8. Guanabenz (wy-8678) Acetate
9. 443o19gk1a
10. Mfcd00153801
11. ((2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)amino)guanidine Monoacetate
12. Nsc-757044
13. Smr000058454
14. Acetic Acid;2-[(e)-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylideneamino]guanidine
15. Acetic Acid;2-[(z)-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylideneamino]guanidine
16. 60329-04-6
17. 1-[(e)-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylidene]amino]guanidine; Acetic Acid
18. Hydrazinecarboximidamide, 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene)-, Monoacetate
19. Wy 8678 Acetate
20. Hydrazinecarboximidamide, 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene]-, Acetate (1:1)
21. ((2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)amino)guanidine Acetate
22. Sr-01000075268
23. Unii-443o19gk1a
24. Hsdb 6535
25. Wytensin (tn)
26. Prestwick_957
27. Einecs 245-534-7
28. Guanabenz Acetate [usan:usp:jan]
29. Br 750
30. [(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)amino]guanidine Acetate
31. Opera_id_1242
32. Schembl40594
33. Mls001076311
34. Mls001333215
35. Mls001333216
36. Guanabenz Acetate Salt, Powder
37. Chebi:5554
38. Guanabenz Acetate [jan]
39. Chembl1200560
40. Guanabenz Acetate (jp17/usp)
41. Guanabenz Acetate [hsdb]
42. Guanabenz Acetate [usan]
43. Guanabenz Acetate [vandf]
44. Guanabenz Acetate [mart.]
45. Guanabenz Monoacetate [mi]
46. Hms1568c14
47. Hms2095c14
48. Hms3261j04
49. Hms3411d06
50. Hms3675d06
51. Hms3712c14
52. Hms3885i22
53. Guanabenz Acetate [usp-rs]
54. Guanabenz Acetate [who-dd]
55. Hy-b0566
56. Tox21_500601
57. S4065
58. Akos024458680
59. Ccg-220096
60. Ccg-221905
61. Guanabenz Acetate [orange Book]
62. Nsc 757044
63. Guanabenz Acetate [usp Monograph]
64. Ncgc00093977-01
65. Ncgc00261286-01
66. Ac-32690
67. As-12195
68. Guanabenz Acetate - Cas 23256-50-0
69. Eu-0100601
70. G-110
71. A13635
72. D00605
73. A914521
74. A924690
75. J-502674
76. Sr-01000075268-1
77. Sr-01000075268-3
78. Sr-01000075268-5
79. 3-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene)carbazamidine Monoacetate
80. 2-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carboximidamide Acetate
81. Guanidine, ((2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)amino)-, Monoacetate
82. Hydrazinecarboxamidine,2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene)-,acetate
83. N-(2,6-dichlorobenzylidene)-n'-amidinohydrazine Monoacetate
84. Guanabenz Acetate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
85. Hydrazinecarboximidamide, 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene]-, Acetate
86. 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene)hydrazinecarboximidamide Monoacetate
| Molecular Weight | 291.13 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H12Cl2N4O2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 290.0337310 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 290.0337310 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 259 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Guanabenz acetate |
| Active Ingredient | Guanabenz acetate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ani Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Guanabenz acetate |
| Active Ingredient | Guanabenz acetate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 4mg base; eq 8mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ani Pharms |
Adrenergic alpha-Agonists; Antihypertensive Agents; Sympatholytics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Guanabenz is used in the management of hypertension. The efficacy of guanabenz in hypertensive patients is similar to that of other adrenergic inhibitors such as clonidine, methyldopa, or beta-adrenergic blocking agents (eg, pindolol, propranolol).
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1823
Guanabenz may be particularly useful in hypertensive patients whose baseline catecholamine concentrations are markedly elevated and whose hypertension is characterized by increased sympathetic activity. The drug may also be useful in the treatment of hypertension that is predominantly of the systolic form, commonly occurring in patients 60 years of age and older. Because guanabenz does not appear to induce sodium retention, the drug is useful in patients who develop secondary renal or cardiac induced sodium retention during therapy with clonidine or methyldopa. Guanabenz has been used in diabetic hypertensive patients with no adverse effect on control or therapy of diabetes; the drug has also been effective in hypertensive patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, including asthma, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema. As with other hypotensive agents, treatment with guanabenz is not curative; after withdrawal of the drug, blood pressure returns to pretreatment levels or greater.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1823
Guanabenz has been used alone or in combination with naltrexone in the management of opiate withdrawal in patients physically dependent on opiates and undergoing detoxification. Guanabenz has also been used as an analgesic in a limited number of patients with chronic pain; use of the drug permitted a reduction in opiate dosage or discontinuance of opiate therapy in these patients, but additional study is necessary. /Use is not currently included in the labeling approved by the FDA/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1823
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for GUANABENZ ACETATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Because of the risk of rebound or "overshoot" hypertension, patients receiving guanabenz should be warned of the danger of missing doses or stopping the drug without consulting their physician. When guanabenz therapy must be interrupted for surgery, the drug should be discontinued slowly over several days, if possible, to avoid precipitating the withdrawal syndrome. If necessary, parenteral hypotensive therapy should be administered throughout the period that oral medication cannot be given; oral guanabenz should be resumed as soon as possible.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1825
Guanabenz should be used with caution and blood pressure monitored carefully in patients with hepatic and/or renal impairment, since the pharmacokinetics of the drug may be altered in such patients. The drug also should be used with caution in patients with severe coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, and/or cerebrovascular disease. Guanabenz should also be used with caution in geriatric patients since they may be more sensitive to the hypotensive and sedative effects of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1825
Because of the potential sedative effect of guanabenz, patients should be warned that the drug may impair their ability to perform hazardous activities requiring mental alertness or physical coordination (eg, operating machinery, driving a motor vehicle). Additive CNS depression may occur when guanabenz is administered concomitantly with other CNS depressants including alcohol, phenothiazines, barbiturates, or benzodiazepines, and patients should be warned that their tolerance for CNS depressants may be decreased.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1825
Although guanabenz has been used in the management of hypertension in a limited number of children 12 yr of age and older, further study on the use of the drug in these patients is necessary. Safety and efficacy of guanabenz in children younger than 12 yr of age have not been established; therefore, the manufacturer does not recommend use of the drug in these children.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1825
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for GUANABENZ ACETATE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Compounds that bind to and activate ADRENERGIC ALPHA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists.)
Guanabenz undergoes extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism. Its elimination half-life is 7-14 hr, and its renal clearance is 0.09-0.131 l/min. Less than 2% is excreted unchanged in the urine. About 80% of a dose is excreted in urine in the first 24 hr.
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 291
Following oral administration, at least 70-80% of a dose of guanabenz acetate is absorbed. The effect of food on the absorption of guanabenz acetate has not been determined. Following oral administration of the drug in fasting individuals, peak plasma guanabenz concentrations usually occur within 2-5 hr. Following a single 16 mg oral dose, peak plasma guanabenz concentrations average 2.4-2.7 ng/ml (range: 1.2-5.2 ng/ml) in fasting healthy individuals and 7.8 ng/ml (range: 3-16 ng/ml) in fasting individuals with hepatic impairment (chronic alcohol-induced liver disease). ... Such alterations in these patients may result from enhanced oral bioavailability (secondary to portosystemic shunting and/or decreased intrinsic clearance) and decreased hepatic clearance of guanabenz.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1827
The hypotensive effect of guanabenz acetate begins within 1 hr after oral administration and peaks within 2-7 hr. The duration of hypotensive effect is variable; the manufacturer states that the hypotensive effect is substantially diminished within 6-8 hr and that blood pressure returns to baseline values within 12 hr; however, the hypotensive effect of a single dose can persist for 12 or more hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1827
Information on the distribution of guanabenz is limited. Following iv administration in rats, guanabenz is rapidly and extensively distributed into the CNS; brain concentrations of the drug are 3-70 times higher than concurrent plasma concentrations. In humans, guanabenz appears to be extensively distributed. The apparent steady state volume of distribution of guanabenz averages approximately 93 and 147 l/kg after 16 and 32 mg oral doses, respectively. The apparent volume of distribution of guanabenz appears to be substantially decreased in patients with hepatic impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1827
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for GUANABENZ ACETATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Guanabenz is extensively metabolized. The site(s) of guanabenz metabolism has not been determined, but the drug probably undergoes extensive firstpass metabolism. Guanabenz is metabolized principally by hydroxylation to form (E)-p-hydroxyguanabenz (4-hydroxyguanabenz), which is largely conjugated with glucuronic acid. A small fraction of guanabenz is cleaved at the benzal carbon to form 2,6-dichlorobenzyl alcohol, which is apparently completely conjugated. A small fraction of guanabenz also apparently undergoes N-glucuronidation. Other minor metabolites include (Z)-guanabenz and possibly (Z)-p-hydroxyguanabenz (Z-isomer of 4-hydroxyguanabenz); these metabolites are apparently almost completely conjugated. Numerous other, unidentified metabolites are also formed. The (Z)-isomer of guanabenz appears to have about 25% of the hypotensive activity of the unchanged drug following oral administration. Animal studies indicate that (E)-p-hydroxyguanabenz is inactive following oral administration but produces a slight hypotensive effect following intraperitoneal administration of large doses. Other metabolites of guanabenz are inactive.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1827
About 10% of an oral dose of guanabenz is excreted in urine as (E)-p-hydroxyguanabenz, 25% as the glucuronide conjugate of (E)-p-hydroxyguanabenz, 1% as unchanged guanabenz, 5% as guanabenz conjugates, 1% as (Z)-guanabenz, 1% as (Z)guanabenz conjugates, less than 1% possibly as (Z)-p-hydroxyguanabenz, 2% as (Z)-p-hydroxyguanabenz conjugates, 2% as 2,6-dichlorobenzyl alcohol conjugates, and the remainder as unidentified metabolites and their conjugates.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1827
The elimination half-life of guanabenz following single oral doses of the drug in healthy adults has been variably reported to average 4-14 hr (range: 3.5-21 hr); In one well-designed study, the elimination half-life averaged 12-14 hr. In patients with hepatic impairment, the half-life of the drug is only slightly prolonged. The elimination half-life of guanabenz also may be prolonged in patients with renal impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1827
Guanabenz is a central alpha 2-adrenoreceptor agonist. Its antihypertensive action appears to result from a decrease in sympathetic outflow from the brain to the peripheral circulatory system following stimulation of central alpha 2-adrenoreceptors. Peripherally it has a presynaptic alpha-receptor stimulant action and a guanethidinelike neuron-blocking action. There does not appear to be a physical dependence liability of the morphine type.
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 291
The affinity of guanabenz for the alpha2-adrenergic receptor is greater than that for the alpha1-adrenergic receptor. The central effects of the drug in the lower brain stem result in reduced peripheral sympathetic activity and a reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Following iv or oral administration of guanabenz in animals, an initial hypertensive response to the drug occurs and is caused by direct peripheral alpha2-adrenergic stimulated vasoconstriction; however, oral guanabenz usually does not produce an initial increase in blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Guanabenz induced bradycardia appears to result principally from central alpha2-agonist effects, although a peripheral alpha2-agonist effect on the heart may also be involved. In animals, guanabenz induced bradycardia results from inhibition of sympathetic nervous system activity and activation of cholinergic nervous system activity. Although guanabenz is not a true adrenergic blocking agent, the drug produces some postganglionic alpha (similar to guanethidine) and beta-adrenergic blockade and decreases the response to peripheral sympathetic nerve stimulation in animals. Cardiac output, left ventricular ejection fraction, and left ventricular stroke volume remain unchanged during long term therapy with the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1826


