



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
0
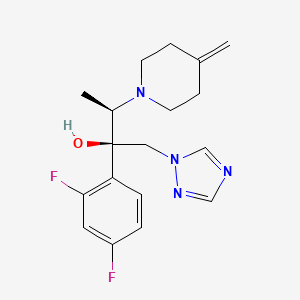

1. Jublia
2. Kp 103
3. Kp-103
4. Kp103
1. 164650-44-6
2. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylenepiperidin-1-yl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
3. Kp-103
4. Jublia
5. Clenafin
6. Kp103
7. Idp-108
8. J82sb7fxwb
9. 164905-19-5
10. Chebi:82718
11. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorofenil)-3-(4-metilenopiperidin-1-il)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazin-1-il)butan-2-ol
12. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylidenepiperidin-1-yl)-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
13. Efinaconazole [inn]
14. Kp 103
15. Unii-j82sb7fxwb
16. Efinaconazole [usan:inn]
17. Efinaconazol
18. Efinaconazolum
19. Clenafin (tn)
20. Jublia (tn)
21. Efinaconazole(kp-103)
22. Efinaconazole; Kp-103
23. Efinaconazole [mi]
24. Efinaconazole [jan]
25. Efinaconazole [usan]
26. Efinaconazole [vandf]
27. Schembl300738
28. Efinaconazole [who-dd]
29. Zinc6251
30. Chembl2103877
31. Efinaconazole (jan/usan/inn)
32. Hsdb 8341
33. Dtxsid40167787
34. Efinaconazole [orange Book]
35. Bcp11665
36. Ex-a2643
37. Mfcd00936406
38. S5025
39. Akos027323571
40. Ccg-268012
41. Cs-3500
42. Db09040
43. Ncgc00390702-01
44. Ncgc00390702-02
45. Ncgc00390702-03
46. Ac-30630
47. As-30126
48. Hy-15660
49. D10021
50. A854585
51. Q21011225
52. (2r, 3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylenepiperidyl)-1-(1,2,4-triazolyl)butan-2-ol
53. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylene-1-piperidinyl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-butanol
54. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylene-1-piperidyl)-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
55. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylenepiperidine-1-yl)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazole-1-yl)butane-2-ol
56. (2r,3r)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylenepiperidino)-1-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol
57. (alphar,betar)-alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-beta-methyl-4-methylene-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1-piperidineethanol
58. 1-piperidineethanol, .alpha.-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-.beta.-methyl-4-methylene-.alpha.-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (r-(r*,r*))-
59. 1-piperidineethanol, .alpha.-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-.beta.-methyl-4-methylene-.alpha.-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-,(.alpha.r,.beta.r)-
60. 1-piperidineethanol, Alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-beta-methyl-4-methylene-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1- Ylmethyl)-, (alphar,betar)-
61. 1-piperidineethanol, Alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-beta-methyl-4-methylene-alpha-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, (alphar,betar)-
| Molecular Weight | 348.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H22F2N4O |
| XLogP3 | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 348.17616766 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 348.17616766 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 54.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 470 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antifungal Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Efinaconazole. Online file (MeSH, 2016). Available from, as of June 24, 2016: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2016/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Jublia (efinaconazole) topical solution, 10% is an azole antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail(s) due to Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Solution (Updated: May 2016). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=922d4d25-c530-11e1-9b21-0800200c9a66
We sought to evaluate the efficacy of efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, in patients with onychomycosis and coexisting tinea pedis. We analyzed 1,655 patients, aged 18 to 70 years, randomized (3:1) to receive efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, or vehicle from two identical multicenter, double-blind, vehicle-controlled 48-week studies evaluating safety and efficacy. The primary end point was complete cure rate (0% clinical involvement of the target toenail and negative potassium hydroxide examination and fungal culture findings) at week 52. Three groups were compared: patients with onychomycosis and coexisting interdigital tinea pedis on-study (treated or left untreated) and those with no coexisting tinea pedis. Treatment with efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, was significantly more effective than vehicle use irrespective of the coexistence of tinea pedis or its treatment. Overall, 352 patients with onychomycosis (21.3%) had coexisting interdigital tinea pedis, with 215 of these patients (61.1%) receiving investigator-approved topical antifungal agents for their tinea pedis in addition to their randomized onychomycosis treatment. At week 52, efinaconazole complete cure rates of 29.4% were reported in patients with onychomycosis when coexisting tinea pedis was treated compared with 16.1% when coexisting tinea pedis was not treated. Both cure rates were significant compared with vehicle (p = 0.003 and 0.045, respectively), and in the latter subgroup, no patients treated with vehicle achieved a complete cure. Treatment of coexisting tinea pedis in patients with onychomycosis enhances the efficacy of once-daily topical treatment with efinaconazole topical solution, 10%.
PMID:26429609 Markinson B, Caldwell B; J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 105 (5): 407-11 (2015)
A number of comorbidities and risk factors complicate the successful management of onychomycosis. Underlying conditions and patient characteristics, such as tinea pedis, age, and obesity, contribute to risk, whereas comorbidities, such as diabetes and psoriasis, can increase susceptibility to the disease. There are limited data on treatment effectiveness in these patients. Here, the authors review post hoc analyses of efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, in mild-to-moderate onychomycosis and present new data in terms of age and obesity. The only post hoc analysis to report significant differences so far is gender, where female patients do much better; however, the reasons are unclear. The authors report significant differences in terms of efficacy in obese patients who do not respond as well as those with normal body mass index (p=0.05) and in patients who have their co-existing tinea pedis treated compared to those in whom co-existing tinea pedis was not treated (p=0.025). Although there is a trend to reduced efficacy in older patients and those with co-existing diabetes, differences were not significant. More research is needed in onychomycosis patients with these important risk factors and comorbidities to fully evaluate the treatment challenges and possible solutions.
PMID:26705439 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4689496 Elewski BE, Tosti A; J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 8 (11): 38-42 (2015)
Onychomycosis is a common fungal infection of the nail unit that results in discoloration, subungual debris, thickening, onycholysis, and often pain and impairment of mobility. Dermatophytomas are characterized by a thick fungal mass within and under the nail plate and are especially resistant to treatment. Here we report a case of a patient with a dermatophytoma who had failed oral terbinafine but was successfully treated with efinaconazole 10% topical solution.
PMID:25942674 Cantrell W et al; J Drugs Dermatol 14 (5): 524-6 (2015)
Adverse effects reported in at least 1% of adults treated with efinaconazole 10% topical solution and more frequently than with topical vehicle solution include application site dermatitis, ingrown toenail, application site vesicles, and application site pain.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016
Prior to treatment of onychomycosis, the diagnosis should be confirmed by direct microscopic examination of scrapings from infected toenails mounted in potassium hydroxide (KOH) or by culture.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016
Efinaconazole 10% solution is for topical use only. The topical solution should not be used orally or intravaginally, and should not be applied to the eyes.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016
Efinaconazole 10% topical solution may cause application site irritation (e.g., redness, swelling, burning, itching, blisters); there is no evidence to date that the solution causes contact sensitization.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Efinaconazole (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Indicated in the treatment of fungal infection of the nail, known as onychomycosis.
FDA Label
Treatment of onychomycosis
mean SD plasma Cmax on Day 28 of treatment: 0.67 0.37 ng/mL. mean SD AUC was 12.15 6.91 ng*h/mL.
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D01 - Antifungals for dermatological use
D01A - Antifungals for topical use
D01AC - Imidazole and triazole derivatives
D01AC19 - Efinaconazole
Administration of Jublia by the topical route leads to low systemic efinaconazole concentrations. Systemic absorption of efinaconazole in 18 patients with severe onychomycosis was determined after application of Jublia once daily for 28 days to patients' 10 toenails and adjacent skin. The concentration of efinaconazole in plasma was determined at multiple time points over the course of 24-hour periods on days 1, 14, and 28. Efinaconazole mean plasma Cmax on Day 28 was 0.67 ng/mL. The mean plasma concentration versus time profile was generally flat over the course of treatment. In onychomycosis patients, the steady state plasma concentration range was 0.1-1.5 ng/mL for efinaconazole and 0.2-7.5 ng/mL for H3 metabolite.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.9 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
/MILK/ Efinaconazole and or its metabolites were excreted in milk from lactating rats. The radioactivity concentration in milk was higher than that in plasma concentration for 24 hours after the administration of 14C-efinaconazole to lactating rats. However, the elimination half-life of the milk radioactivity was about one half of that of the plasma radioactivity, suggesting that efinaconazole or its metabolites was not retained in milk.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.17 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
/MILK/ It is not known whether efinaconazole is excreted in human milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Solution (Updated: May 2016). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=922d4d25-c530-11e1-9b21-0800200c9a66
Efinaconazole penetrates through nails in vitro after Jublia administration, suggesting drug penetrations to the site of fungal infection in the nail and the nail bed, though clinical relevance is unknown. The penetration of Jublia was evaluated in an in vitro investigation after daily application of radiolabelled efinaconazole (10%) to human nails for 28 days at 55.1 uL/sq cm. After 28 days, the cumulative radioactivity in the receptor fluid and in the nail plate, on a percent basis of total administered radioactivity, was 0.03% and 0.16% (3.11 mg eq/g), respectively. The flux rate was relatively constant from Days 18 to 28, mean 1.40 ug eq/sq cm/day, suggesting steady state attainment.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.9 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Efinaconazole (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Efinaconazole is extensively metabolized. It is oxidatively metabolized, cleaved and conjugated to glucuronic acid. The studies have identified 5 metabolites (H1, H2, H3, H4 and H5) of efinaconazole. In rats and minipigs, H3 was the major efinaconazole plasma metabolite, and its levels usually equaled or exceeded those of parent drug. The in vitro and in vivo metabolite profiles in nonclinical species were similar to human with no unique human metabolite(s).
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.17 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
Jublia (efinaconazole) is extensively metabolized through oxidative/reductive processes, with the potential of additional metabolite glucuronidation. Analysis of human plasma confirmed that H3 is the only major efinaconazole metabolite.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.10 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
Efinaconazole metabolites, but not parent drug, were excreted in the bile and urine of rats and dogs which suggests complete metabolism of efinaconazole prior to excretion. Most of the absorbed radioactivity was eliminated during the first 72 hours after dermal and SC dosing in urine and feces.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.17 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
29.9 hours in healthy patients.
In a ... study of healthy volunteers, the plasma half-life of Jublia at day 10 following repeat treatment applications repeated to all 10 toenails was 29.9 hours.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.9 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
Efinaconazole is an azole antifungal. Efinaconazole inhibits fungal lanosterol 14-demethylase involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a constituent of fungal cell membranes.
Efinaconazole is a triazole antifungal agent. Efinaconazole inhibits fungal lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase involved in ergosterol biosynthesis. The accumulation of 14alpha-methyl sterols and subsequent loss of ergosterol in the fungi cell wall may be responsible for the fungistatic and fungicidal activity of efinaconazole. Efinaconazole is shown in vitro to be substantially adsorbed to keratin but keratin binding is weak. Efinaconazole's low keratin affinity is expected to result in increased availability of free drug to the nail infection site.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Jublia (Efinaconazole) Topical Solution, 10% w/w, Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02413388 p.9 (Date of Preparation: October 2, 2013). Available from, as of July 5, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng


