



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
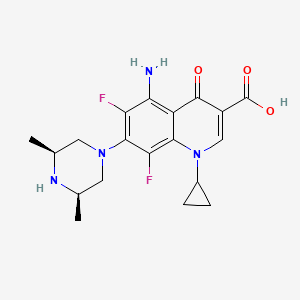

1. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(cis-3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)- 6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
2. At 4140
3. At-4140
4. Ci 978
5. Ci-978
6. Pd 131501
7. Pd-131501
8. Zagam
1. 110871-86-8
2. Zagam
3. At-4140
4. Ci-978
5. Spara
6. Ci 978
7. Spfx
8. Pd 131501
9. Pd-131501
10. At 4140
11. 111542-93-9
12. Chebi:9212
13. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-((3s,5r)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
14. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(cis-3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
15. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3r,5s)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
16. Q90aga787l
17. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3r,5s)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]-6,8-difluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
18. Cis-5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid
19. Esparfloxacino
20. Sparfloxacine
21. Sparfloxacinum
22. Nsc-759641
23. Mfcd00869619
24. Dsstox_cid_3590
25. Dsstox_rid_77097
26. Dsstox_gsid_23590
27. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-, Cis-
28. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-((3r,5s)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
29. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3s,5r)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
30. Sparfloxacine [inn-french]
31. Sparfloxacinum [inn-latin]
32. Drg-0143
33. Esparfloxacino [inn-spanish]
34. Parox
35. Cas-110871-86-8
36. Zagam (tn)
37. Cp 103826
38. Sr-05000001521
39. Brn 3658018
40. Unii-q90aga787l
41. Sparfloxacin & Ru 40555
42. Pd 1315-1
43. Sparfloxacin (jan/usan/inn)
44. Liposome-encapsulated Sparfloxacin
45. Sparfloxacin,(s)
46. Ncgc00159333-02
47. Sparfloxacin [usan:inn:ban:jan]
48. Sparfloxacinhydrochloride
49. Pd131501
50. Rp-64206
51. Cp-103826
52. Sparfloxacin [mi]
53. Sparfloxacin [inn]
54. Sparfloxacin [jan]
55. Chembl850
56. Epitope Id:119065
57. Sparfloxacin [usan]
58. Sparfloxacin [vandf]
59. Schembl41311
60. Sparfloxacin [mart.]
61. Mls000759417
62. Sparfloxacin [who-dd]
63. Dtxsid9023590
64. Gtpl10860
65. Ci978
66. Hms2090n19
67. Hms3715j13
68. Sparfloxacin [orange Book]
69. Zinc538362
70. Bcp23886
71. Hy-b0308
72. Rkl10082
73. Sparfloxacin, >=98.0% (hplc)
74. Tox21_111580
75. At4140
76. Bbl010957
77. Bdbm50366822
78. S1884
79. Stk802067
80. Akos005622503
81. Tox21_111580_1
82. Ccg-221166
83. Db01208
84. Ks-5009
85. Nsc 759641
86. Sparfloxacin 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
87. Ncgc00166294-01
88. Ncgc00166294-02
89. Ncgc00166294-03
90. 3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-6,8-difluoro-7-(3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-, Cis-
91. Ac-11574
92. Smr000466312
93. S0896
94. Sw199632-2
95. C07662
96. D00590
97. S-6990
98. Ab00639950-02
99. Ab00639950_03
100. Sparfloxacin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
101. 871s868
102. A802376
103. A894831
104. Q976559
105. Sr-01000759357
106. Sparfloxacin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
107. Sr-01000759357-2
108. Sr-05000001521-1
109. Sr-05000001521-2
110. Brd-k07612980-001-07-9
111. 4-bromo-1-(tert-butyl)-3-methyl-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxylicacid
112. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-6,8-difluoro-7-(cis-3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
113. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(cis-3,5-dimethyl)-6,8- Difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic Acid & Ru 40555
114. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(cis-3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
115. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3r,5s)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
116. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3s,5r)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]-6,8-difluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid
117. 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-[(3s,5r)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-4-ium-1-yl]-6,8-difluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylate
118. At-4140 Pound>>ci-978 Pound>>ci 978 Pound>>ci978 Pound>>at 4140 Pound>>at4140 Pound>>pd 131501 Pound>>pd131501 Pound>>pd-131501
| Molecular Weight | 392.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H22F2N4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 392.16599690 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 392.16599690 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 98.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 691 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of adults with the following infections caused by susceptible strains microorganisms: community-acquired pneumonia (caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, or Streptococcus pneumoniae) and acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, or Streptococcus pneumoniae).
FDA Label
Sparfloxacin is a synthetic fluoroquinolone broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent in the same class as ofloxacin and norfloxacin. Sparfloxacin has in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. Sparfloxacin exerts its antibacterial activity by inhibiting DNA gyrase, a bacterial topoisomerase. DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme which controls DNA topology and assists in DNA replication, repair, deactivation, and transcription. Quinolones differ in chemical structure and mode of action from (beta)-lactam antibiotics. Quinolones may, therefore, be active against bacteria resistant to (beta)-lactam antibiotics. Although cross-resistance has been observed between sparfloxacin and other fluoroquinolones, some microorganisms resistant to other fluoroquinolones may be susceptible to sparfloxacin. In vitro tests show that the combination of sparfloxacin and rifampin is antagonistic against Staphylococcus aureus.
Antitubercular Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of tuberculosis. They are divided into two main classes: "first-line" agents, those with the greatest efficacy and acceptable degrees of toxicity used successfully in the great majority of cases; and "second-line" drugs used in drug-resistant cases or those in which some other patient-related condition has compromised the effectiveness of primary therapy. (See all compounds classified as Antitubercular Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA09 - Sparfloxacin
Absorption
Well absorbed following oral administration with an absolute oral bioavailability of 92%. Unaffected by administration with milk or food, however concurrent administration of antacids containing magnesium hydroxide and aluminum hydroxide reduces the oral bioavailability of sparfloxacin by as much as 50%.
Hepatic. Metabolized primarily by phase II glucuronidation to form a glucuronide conjugate. Metabolism does not utilize or interfere with the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.
Mean terminal elimination half-life of 20 hours (range 16-30 hours). Prolonged in patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min).
The bactericidal action of sparfloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination.


