



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia

South Africa
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
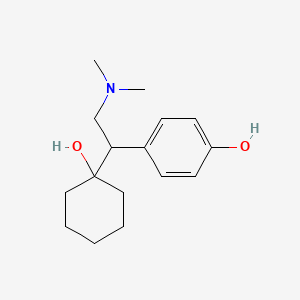

1. 2-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)-2-((4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl)dimethylammonium 3-carboxypropanoate Monohydrate
2. 4-(2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl)phenol
3. 45,233, Wy
4. 45233, Wy
5. Desvenlafaxine Succinate
6. Monohydrate, O-desmethylvenlafaxine Succinate
7. O Desmethylvenlafaxine
8. O Desmethylvenlafaxine Succinate
9. O Desmethylvenlafaxine Succinate Monohydrate
10. O-desmethylvenlafaxine
11. O-desmethylvenlafaxine Succinate
12. O-desmethylvenlafaxine Succinate Monohydrate
13. Pristiq
14. Succinate Monohydrate, O-desmethylvenlafaxine
15. Succinate, Desvenlafaxine
16. Succinate, O-desmethylvenlafaxine
17. Wy 45,233
18. Wy 45233
19. Wy-45,233
20. Wy-45233
21. Wy45,233
22. Wy45233
1. 93413-62-8
2. O-desmethylvenlafaxine
3. 4-(2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl)phenol
4. 4-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol
5. O-desmethyl Venlafaxine
6. Dvs 233
7. Newven
8. D-veniz
9. D,l-o-desmethylvenlafaxine
10. Mdd-xr
11. Desvenlafaxine (inn)
12. Desvenlafaxine [inn]
13. D,l-o-desmethyl Venlafaxine
14. Ng99554anw
15. Chebi:83527
16. 93413-62-8 (free Base)
17. 1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]cyclohexanol
18. Phenol, 4-(2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl)-
19. Phenol, 4-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]-
20. Desvenlafaxine [inn:ban]
21. Khedezla
22. Odv
23. Venlafaxine O-desmethyl
24. Unii-ng99554anw
25. O-desvenlafaxine
26. Hsdb 7993
27. Khedezla (tn)
28. O-desmethylvenlafaxine (odv)
29. O-desmethyl-venlafaxine
30. Desvenlafaxine [mi]
31. Ec 700-516-2
32. Chembl1118
33. Schembl34864
34. Mls006010042
35. Desvenlafaxine [vandf]
36. O-desmethylvenlafaxine Solution
37. (s)-desmethyl Venlafaxine D6
38. Gtpl7158
39. Desvenlafaxine [usp-rs]
40. Desvenlafaxine [who-dd]
41. 4-[2-dimethylamino-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol
42. R-(-)-o-desmethyl-venlafaxine
43. S-(+)-o-desmethyl-venlafaxine
44. Bdbm86748
45. Dtxsid40869118
46. Hms3652k16
47. Hms3885f05
48. Amy15413
49. Bcp28517
50. D,l-o-desmethyl Venlafaxine-[d6]
51. Hy-b0602
52. Desvenlafaxine [orange Book]
53. Mfcd00871934
54. Pdsp1_001804
55. Pdsp2_001787
56. S4113
57. Desvenlafaxine [usp Monograph]
58. Akos015896311
59. Ccg-267081
60. Db06700
61. Ds-1282
62. Sb17444
63. Nsc_6918664
64. Ncgc00345883-04
65. Ncgc00345883-07
66. Smr004701214
67. O-desmethylvenlafaxine, Analytical Standard
68. Cas_386750-22-7
69. D5598
70. Ft-0654519
71. Ft-0666245
72. Ft-0666246
73. Sw219514-2
74. O-desmethylvenlafaxine 0.1 Mg/ml In Methanol
75. D07793
76. Ab01563022_01
77. 413d628
78. A844583
79. Q2419445
80. Venlafaxine O-desmethyl 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
81. 4-[2-dimethyamino-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol
82. 1-[2-dimethylamino-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]cyclohexanol
83. 4-(2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)-ethyl)phenol
84. 4-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-oxidanylcyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol
85. 4-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol #
86. (rs)-1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]cyclohexanol
87. O-desmethylvenlafaxine Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Certified Reference Material
88. O-desmethylvenlafaxine Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
1. O-desmethylvenlafaxine
| Molecular Weight | 263.37 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H25NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 263.188529040 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 263.188529040 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 43.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 266 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Desvenlafaxine |
| PubMed Health | Desvenlafaxine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidepressant |
| Drug Label | KHEDEZLA Extended-release Tablets for oral administration contains desvenlafaxine, a structurally novel SNRI for the treatment of MDD. Desvenlafaxine (O-desmethylvenlafaxine) is the major active metabolite of the antidepressant venlafaxine, a medicat... |
| Active Ingredient | Desvenlafaxine; Desvenlafaxine fumarate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; 100mg; eq 50mg base; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alembic Pharms; Sun Pharma Global |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Desvenlafaxine |
| PubMed Health | Desvenlafaxine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antidepressant |
| Drug Label | KHEDEZLA Extended-release Tablets for oral administration contains desvenlafaxine, a structurally novel SNRI for the treatment of MDD. Desvenlafaxine (O-desmethylvenlafaxine) is the major active metabolite of the antidepressant venlafaxine, a medicat... |
| Active Ingredient | Desvenlafaxine; Desvenlafaxine fumarate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; 100mg; eq 50mg base; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alembic Pharms; Sun Pharma Global |
Antidepressive Agents; Neurotransmitter Uptake Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2011)
Used to treat major depressive, generalized anxiety, social anxiety and panic disorders /Desvenlafaxine succinate monohydrate/
FDA; RxList. The Internet Drug Index. Top 200 Drugs - US Only. Available from, as of Oct 31, 2011: https://www.rxlist.com/script/main/hp.asp
Like some other selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), desvenlafaxine succinate has been studied for the management of vasomotor symptoms in postmenopausal women. /NOT included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 2352
Desvenlafaxine succinate is used in the treatment of major depressive disorder in adults. /Included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 2352
Recent reviews have questioned whether the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) desvenlafaxine succinate offers any practical clinical advantages over existing SNRIs. The following case is one instance where it appears that this SNRI offers unique safety and benefit. Presented is a case report of a patient with Gilbert's syndrome, longstanding social phobia, and more recent depressive disorder not otherwise specified, who was found to have elevated liver transaminases when prescribed both duloxetine and venlafaxine. The patient subsequently responded to desvenlafaxine but without liver abnormalities. In this patient with Gilbert's Syndrome, desvenlafaxine's lack of metabolism through the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 pathway may explain the avoidance of these abnormalities and thus suggests a possible therapeutic role for this SNRI in similarly susceptible patients.
PMID:20394185 Feinberg SS et al; CNS Spectr. 2010 Jan;15(1):53-5 (2010)
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies. These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients over age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressant use in patients aged 65 and older. In patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy, monitor closely for worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Advise families and caregivers of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Pristiq is not approved for use in pediatric patients.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (Updated: March 2015). Available from, as of April 23, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=0f43610c-f290-46ea-d186-4f998ed99fce
In patients with moderate or severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) the clearance of Pristiq was decreased, thus prolonging the elimination half-life of the drug. As a result, there were potentially clinically significant increases in exposures to Pristiq. Dosage adjustment (50 mg every other day) is necessary in patients with severe renal impairment or ESRD. The doses should not be escalated in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment or ESRD.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
Sustained increases in blood pressure have been reported. In controlled studies, sustained hypertension occurred in 0.7-2.3% of patients receiving desvenlafaxine dosages from 50-400 mg daily, with a suggestion of a higher incidence (2.3%) in those receiving 400 mg of the drug daily. In addition, some cases of elevated blood pressure requiring immediate treatment have been reported with desvenlafaxine. Sustained blood pressure increases could have adverse consequences in patients receiving the drug. Therefore, the manufacturer recommends that preexisting hypertension be controlled before initiating desvenlafaxine therapy and that regular blood pressure monitoring be performed in patients receiving the drug. Desvenlafaxine should be used cautiously in patients with preexisting hypertension or other underlying conditions that may be compromised by increases in blood pressure. Dosage reduction or drug discontinuance should be considered in patients who experience a sustained increase in blood pressure during therapy.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 2353
Treatment with selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRIs), including desvenlafaxine, may result in hyponatremia.In many cases, hyponatremia appears to be due to the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Cases with serum sodium concentrations lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Geriatric individuals and patients receiving diuretics or who are otherwise volume depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls; more severe and/or acute cases have been associated with hallucinations, syncope, seizures, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. Initiate appropriate medical intervention and consider drug discontinuance in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 2353
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Desvenlafaxine (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Desvenlafaxine is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder in adults.
FDA Label
Desvenlafaxine is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It lacks significant activity on muscarinic-cholinergic, H1-histaminergic, or α1-adrenergic receptors in vitro. Desvenlafaxine does not appear to exert activity against calcium, chloride, potassium and sodium ion channels and also lacks monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory activity. It was also shown to lack significant activity again the cardiac potassium channel, hERG, in vitro. Compared to other SNRIs, desvenlafaxine undergoes simple metabolism, has a low risk of drug-drug interactions and does not have to be extensively titrated to reach a therapeutic dose.
Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors
Drugs that selectively block or suppress the plasma membrane transport of SEROTONIN and NORADRENALINE into axon terminals and are used as ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors.)
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
N06AX23
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
N06AX23
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06A - Antidepressants
N06AX - Other antidepressants
N06AX23 - Desvenlafaxine
Absorption
Oral bioavailability is approximately 80% and is unaffected by food. Peak plasma concentration is reached in 7.5 hours.
Route of Elimination
Desvenlafaxine is mainly excreted in the urine. 45% of the dose is unchanged in the urine, 19% is excreted as a glucuronide metabolite, and <5% is excreted as N,O-didesmethylvenlafaxine. No dosage adjustment is necessary for gender, ethnicity, food, or combination with other psychotropics.
Volume of Distribution
3.4L/kg.
The plasma protein binding of desvenlafaxine is low (30%) and is independent of drug concentration. The desvenlafaxine volume of distribution at steady-state following intravenous administration is 3.4 L/kg, indicating distribution into nonvascular compartments.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
The absolute oral bioavailability of Pristiq after oral administration is about 80%. Mean time to peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) is about 7.5 hours after oral administration.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
Approximately 45% of desvenlafaxine is excreted unchanged in urine at 72 hours after oral administration. Approximately 19% of the administered dose is excreted as the glucuronide metabolite and < 5% as the oxidative metabolite (N,O-didesmethylvenlafaxine) in urine
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
Desvenlafaxine is excreted into human milk.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 2354
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Desvenlafaxine (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Desvenlafaxine also undergoes oxidative N-demethylation via cytochrome P450 3A4 to a minor extent. CYP2D6 is not involved with the metabolism of desvenlafaxine.
Desvenlafaxine is primarily metabolized by conjugation (mediated by UGT isoforms) and, to a minor extent, through oxidative metabolism. CYP3A4 is the cytochrome P450 isozyme mediating the oxidative metabolism (N-demethylation) of desvenlafaxine. The CYP2D6 metabolic pathway is not involved, and after administration of 100 mg, the pharmacokinetics of desvenlafaxine was similar in subjects with CYP2D6 poor and extensive metabolizer phenotype. ... Approximately 19% of the administered dose is excreted as the glucuronide metabolite and < 5% as the oxidative metabolite (N,O-didesmethylvenlafaxine) in urine
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
The mean terminal half life is 11.1 hours and may be prolonged in patients with renal and/or moderate to severe hepatic impairment.
The mean half life changed from approximately 10 hours in healthy subjects and subjects with mild hepatic impairment to 13 and 14 hours in moderate and severe hepatic impairment, respectively.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
The mean terminal half-life, is approximately 11 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PRISTIQ (desvenlafaxine succinate) tablet, extended release (January 2011). Available from, as of October 25, 2011: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=Desvenlafaxine
Desvenlafaxine, the active metabolite of venlafaxine, is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Desvenlafaxine inhibits neurotransmitter reuptake in serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine transporters. Desvenlafaxine inhibits serotonin transporters with 10 times the affinity of norepinephrine transporters, and dopamine transporters with the lowest affinity. In vitro, desvenlafaxine has no inhibition of monoamine oxidase, and almost no affinity for muscarinic, cholinergic, H1-histaminergic, and alpha1-adrenergic receptors.
The exact mechanism of antidepressant action of desvenlafaxine has not been fully elucidated but appears to be associated with the drug's potentiation of serotonergic and noradrenergic activity in the CNS. Like venlafaxine and duloxetine, desvenlafaxine is a potent inhibitor of neuronal serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake; however, inhibition of dopamine reuptake at concentrations that inhibit serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake appears unlikely in most patients. The drug does not inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) and has not demonstrated significant affinity for muscarinic cholinergic, H1-histaminergic, alpha1-adrenergic, dopaminergic, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, and opiate receptors in vitro.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 2355








