



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
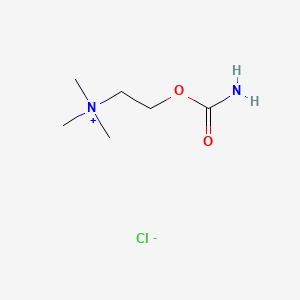

1. Carbachol, Isopto
2. Carbacholine
3. Carbamann
4. Carbamoylcholine
5. Carbamylcholine
6. Carbastat
7. Carbocholine
8. Carboptic
9. Doryl
10. Isopto Carbachol
11. Jestryl
12. Miostat
1. 51-83-2
2. Carbamoylcholine Chloride
3. Miostat
4. Carbamylcholine Chloride
5. Jestryl
6. Carbachol Chloride
7. Carbocholine
8. Doryl
9. Carbacholine Chloride
10. Isopto Carbachol
11. Carbacholin
12. Carbacolina
13. Carbamiotin
14. Carbocholin
15. Carbochol
16. Carcholin
17. Coletyl
18. Vasoperif
19. Carbyl
20. Lentin
21. Moryl
22. Carbacholine
23. Choline Carbamate Chloride
24. Carbacholum
25. Karbachol
26. Rilentol
27. Choline Chlorine Carbamate
28. Choline Chloride, Carbamate
29. Mistura C
30. Doryl (pharmaceutical)
31. Carbaminocholine Chloride
32. P. V. Carbachol
33. (2-carbamoyloxyethyl)trimethylammonium Chloride
34. Carbaminoylcholine Chloride
35. Carbacol
36. Lentine
37. Carbachol Hydrochloride
38. Karbamoylcholin Chlorid
39. (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium Chloride Carbamate
40. Carbamoylcholine-hydrochloride
41. Choline Chloride, Carbamoyl-
42. (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethyl Ammonium Chloride Carbamate
43. Choline, Chloride Carbamate(ester)
44. Carbamoylcholine (chloride)
45. 2-carbamoyloxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium;chloride
46. Carbamic Acid, Ester With Choline Chloride
47. 2-((aminocarbonyl)oxy)-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminium Chloride
48. 2-((aminocarbonyl)oxy)-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminum Chloride
49. Choline Chloride Carbamate
50. Nsc-32865
51. Ethanaminium, 2-((aminocarbonyl)oxy)-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Chloride
52. Chebi:3385
53. 2-(carbamoyloxy)-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminium Chloride
54. 8y164v895y
55. Carbacholinum
56. Carbach
57. Dsstox_cid_2730
58. Dsstox_rid_76703
59. Lentine [french]
60. Dsstox_gsid_22730
61. Karbachol [czech]
62. Carbacolo [dcit]
63. Carbacholum Chloratum
64. Carbacholini Chloridum
65. Chembl14
66. Doryl (van)
67. Carbacholinium Chloratum
68. Carbacolo
69. Carbacol [inn-spanish]
70. Carbacholum [inn-latin]
71. Karbamoylcholin Chlorid [czech]
72. Gamma-carbamoyl Choline Chloride
73. Hsdb 6373
74. Cas-51-83-2
75. Sr-01000075312
76. Ncgc00163219-01
77. (2-carbamoyloxy-ethyl)-trimethyl-ammonium
78. Einecs 200-127-3
79. Nsc 32865
80. Tl 457
81. 2-[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminium Chloride
82. Choline, Chloride, Carbamate
83. Choline, Chloride, Carbamate, Hydrochloride
84. (carbachol)(2-carbamoyloxy-ethyl)-trimethyl-ammonium
85. Unii-8y164v895y
86. 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl Carbamate Chloride
87. Carbachol [usp:inn:ban:jan]
88. Carbachol,(s)
89. Choline, Carbamate
90. Miostat (tn)
91. Mfcd00012011
92. Prestwick_1036
93. Carbachol [inn]
94. Carbachol [jan]
95. Carbachol [mi]
96. Ethanaminium, 2-(aminocarbonyl)oxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Chloride
97. Carbachol [hsdb]
98. Carbachol [vandf]
99. Carbachol [mart.]
100. 2-carbamoyloxyethyl(trimethyl)ammonium Chloride
101. Carbachol [usp-rs]
102. Carbachol [who-dd]
103. Schembl2791
104. Carbachol (jan/usp/inn)
105. Mls002153502
106. Spectrum1500158
107. Carbachol [ep Impurity]
108. Carbachol [orange Book]
109. Carbamoylcholine Chloride, 99%
110. Carbachol [ep Monograph]
111. Dtxsid9022730
112. Hms502e07
113. Carbachol [usp Monograph]
114. Choline, Carbamate, Hydrochloride
115. .gamma.-carbamoyl Choline Chloride
116. Hms1570p21
117. Hms1920i15
118. Hms2091o17
119. Hms2097p21
120. Hms2236l04
121. Hms3260b08
122. Hms3372g03
123. Hms3714p21
124. Pharmakon1600-01500158
125. Hy-b1208
126. Nsc32865
127. Tox21_112029
128. Tox21_500243
129. Ccg-38913
130. Nsc755919
131. Akos015909565
132. Akos025149486
133. Tox21_112029_1
134. Cs-4836
135. Lp00243
136. Nsc-755919
137. Wln: Zvo2k1&1&1 &q &g
138. Ncgc00015237-07
139. Ncgc00093705-01
140. Ncgc00093705-02
141. Ncgc00093705-03
142. Ncgc00093705-04
143. Ncgc00093705-05
144. Ncgc00260928-01
145. Smr000058584
146. B7196
147. C0596
148. Eu-0100243
149. Sw197107-3
150. C 4382
151. C-1770
152. D00524
153. D89274
154. 2-aminocarbonyloxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium Chloride
155. A828807
156. Q419401
157. Sr-01000075312-1
158. Sr-01000075312-3
159. Sr-01000075312-6
160. (2-carbamoyloxy-ethyl)-trimethyl-ammonium(carbachol)
161. Z1551429748
162. 2-(carbamoyloxy)-n,n,n-trimethylethan-1-aminium Chloride
163. Carbachol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
164. Carbamoylcholine Chloride, >=98% (titration), Crystalline
165. Carbachol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
166. Carbachol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
167. Ethanaminium, 2-((aminocarbonyl)oxy)-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Chloride (1:1)
| Molecular Weight | 182.65 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H15ClN2O2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 182.0822054 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 182.0822054 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 117 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Miostat |
| PubMed Health | Carbachol |
| Drug Classes | Antiglaucoma, Direct Acting Miotic |
| Drug Label | MIOSTAT (carbachol intraocular solution, USP) is a sterile balanced salt solution of carbachol for intraocular injection. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:Established name:CarbacholChemical name:Ethanaminium, 2-[(amino... |
| Active Ingredient | Carbachol |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Intraocular |
| Strength | 0.01% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Miostat |
| PubMed Health | Carbachol |
| Drug Classes | Antiglaucoma, Direct Acting Miotic |
| Drug Label | MIOSTAT (carbachol intraocular solution, USP) is a sterile balanced salt solution of carbachol for intraocular injection. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:Established name:CarbacholChemical name:Ethanaminium, 2-[(amino... |
| Active Ingredient | Carbachol |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Intraocular |
| Strength | 0.01% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alcon |
Analgesics, Non-Narcotic; Cardiotonic Agents; Cholinergic Agonists; Miotics; Muscarinic Agonists; Nicotinic Agonists; Parasympathomimetics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Acetylcholine, 1%, or carbachol, 0.01%, is used in cataract extractions and certain other surgical procedures on the anterior segment when it is desired to produce miosis rapidly; the action of acetylcholine is brief. For the chronic therapy of noncongestive, wide-angle glaucoma, carbachol (0.75 to 3.0%) has been employed.
Gilman, A.G., L.S.Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 7th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1985., p. 105
Carbachol has been used in the treatment of postoperative intestinal atony and postoperative retention of urine, for which it has been given by subcutaneous injection ... or by mouth. It has also been used to stop supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia when all other measures have failed. Carbachol has a miotic action and eye-drops ... have been used to lower intraocular pressure in glaucoma ... Even in comparatively late cases of sun blindness the symptoms could in many instances be alleviated ... by retrobulbar injection of carbachol.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 1038
Pilocarpine (or occasionally carbachol) is used to lower intraocular pressure in the emergency treatment of acute (congestive) angle-closure glaucoma prior to surgery.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1657
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CARBACHOL CHLORIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Topical carbachol shares the toxic potentials of the direct-acting miotics, and the usual precautions of miotic therapy should be observed. The manufacturer states that intraocular carbachol does not produce the adverse effects of topically applied carbachol; bullous keratopathy and postoperative iritis following cataract extraction have been reported in some patients.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1660
Corneal edema may occur if excessive amounts of carbachol are introduced into the anterior chamber or if the drug is used in patients with an already compromised endothelium, eg, Fuchs' dystrophy, corneal transplants, cataract surgery that requires more manipulation than usual.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 1855
It is recommended that carbachol should not be used as eye-drops in patients with a corneal abrasion as there may be excessive absorption. The sensitivity of asthmatic patients to carbachol bronchoconstriction was increased when inhalation of carbachol was preceded by maximum respiratory maneurvers.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 1038
Drugs of this class should be admin only by the oral or subcutaneous route for systemic effects; they are also used locally in the eye. If they are given intravenously or intramuscularly, their relative selectivity of action no longer holds, and the incidence and severity of toxic side effects are greatly increased. /Choline esters/
Gilman, A.G., L.S.Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 7th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1985., p. 104
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CARBACHOL CHLORIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Miotics
Agents causing contraction of the pupil of the eye. Some sources use the term miotics only for the parasympathomimetics but any drug used to induce miosis is included here. (See all compounds classified as Miotics.)
Analgesics, Non-Narcotic
A subclass of analgesic agents that typically do not bind to OPIOID RECEPTORS and are not addictive. Many non-narcotic analgesics are offered as NONPRESCRIPTION DRUGS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics, Non-Narcotic.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
Cholinergic Agonists
Drugs that bind to and activate cholinergic receptors. (See all compounds classified as Cholinergic Agonists.)
N07AB01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N07 - Other nervous system drugs
N07A - Parasympathomimetics
N07AB - Choline esters
N07AB01 - Carbachol
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01E - Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics
S01EB - Parasympathomimetics
S01EB02 - Carbachol
Topical carbachol penetrates intact corneal epithelium very poorly; combination with wetting agent ... greatly improves corneal penetration by the drug. ... Carbachol /is/ ... absorbed through intact skin.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1657
Carbachol, which is an unsubstituted carbamyl ester, is totally resistant to hydrolysis by either acetylcholinesterase or nonspecific cholinesterases; its half-life is thus sufficiently long that it is distributed to areas of low blood flow.
Gilman, A.G., L.S.Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 7th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1985., p. 101
The pharmacologic effects of all miotics are similar; they differ primarily in ocular and systemic absorption, duration of action and degree of effects. Acetylcholine, an endogenous mediator of nerve impulses, stimulates cholinergic receptors, resulting in muscarinic and nicotinic effects. The action of acetylcholine is transient. ... Pilocarpine, carbachol, and methacholine also directly stimulate cholinergic receptors; however, these drugs have a more prolonged duration of action (several hours) than does acetylcholine. There is some evidence that carbachol also has a weak anticholinesterase effect ... .
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1657
Miotics reduce intraocular pressure in normal and glaucomatous eyes. The mechanism of action of the drugs in lowering intraocular pressure has not been precisely determined. In patients with open-angle (chronic simple, noncongestive) glaucoma, the drugs facilitate aqueous humor outflow, apparently by causing contraction of the ciliary muscle and widening of the trabecular meshwork. ... Miotics decrease activity of extraocular muscles of convergence. ... Systemically absorbed miotics produce parasympathomimetic effects on various body systems. /Miotics/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 92. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1992 (Plus Supplements 1992)., p. 1656
/Carbachol acts/ ... with selectivity on the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract ... Carbachol /also/ retains substantial nicotinic activity, particularly on autonomic ganglia. It is likely that both its peripheral and its ganglionic actions are due, in part, to the release of endogenous acetylcholine from the terminals of cholinergic fibers.
Gilman, A.G., L.S.Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 7th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1985., p. 101
The choline esters /carbachol & bethanechol/ increase ureteral peristalsis, contract the detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder, increase the maximal voluntary voiding pressure, and decrease the capacity of the bladder. In addition, the trigone and external sphincter are relaxed. In animals with experimental lesions of the spinal cord or sacral roots, these drugs bring about satisfactory evacuation of the neurogenic bladder.
Gilman, A.G., L.S.Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 7th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1985., p. 103
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CARBACHOL CHLORIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.


