



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
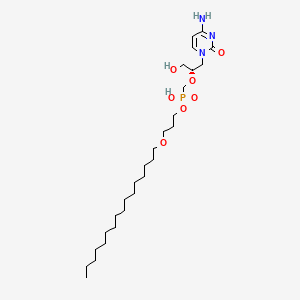

1. Cidofovir Hexadecyloxypropyl Ester
2. Cmx 001
3. Cmx-001
4. Cmx001
5. Hdp-cdv
6. Hexadecyloxypropyl Cidofovir
7. Tembexa
1. 444805-28-1
2. Cmx001
3. Cmx 001
4. Hdp-cidofovir
5. Hexadecyloxypropyl-cidofovir
6. Hdp-cdv
7. Cmx-001
8. Hexadecyloxypropyl Cidofovir
9. Tembexa
10. Brincidofovir [usan]
11. [(2s)-1-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3-hydroxypropan-2-yl]oxymethyl-(3-hexadecoxypropoxy)phosphinic Acid
12. 6794o900ax
13. Brincidofovir (usan)
14. 3-(hexadecyloxy)propyl Hydrogen ((((s)-1-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2h)-yl)-3-hydroxypropan-2-yl)oxy)methyl)phosphonate
15. Phosphonic Acid, P-(((1s)-2-(4-amino-2-oxo-1(2h)-pyrimidinyl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy)methyl)-, Mono(3-(hexadecyloxy)propyl) Ester
16. Cidofovir-hdp
17. Brincidofovir [usan:inn]
18. Hexadecyloxypropyl - Cidofovir
19. Cidofovir Prodrug
20. Unii-6794o900ax
21. Cidofovir Hexadecyloxypropyl Ester
22. Hdp-hpmpc
23. Brincidofovir; Cmx001
24. Hdp-cdvcmx001
25. Brincidofovir [inn]
26. Cmx001;hdp-cdv
27. Brincidofovir (cmx-001)
28. 1-o-hexadecylpropanediol-cdv
29. Schembl139922
30. Brincidofovir [who-dd]
31. Chembl203321
32. Gtpl11556
33. Dtxsid60196190
34. Brincidofovir [orange Book]
35. Bcp08580
36. Ex-a2366
37. Nsc783202
38. Zinc14141521
39. Db12151
40. Nsc-783202
41. Ncgc00686671-01
42. Ac-36043
43. A13326
44. D10547
45. Q15411004
46. C525733000
47. [(1s)-1-[(4-amino-2-oxo-pyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-2-hydroxy-ethoxy]methyl-(3-hexadecoxypropoxy)phosphinic Acid
48. [[(s)-2-(4-amino-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidine-1-yl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl]phosphonic Acid 3-(hexadecyloxy)propyl Ester
49. 3-((2s)-2-{[(3-hexadecyloxypropoxy)(hydroxyphosphoryl)]methoxy}-3-hydroxypropyl)-6-amino-3-hydropyrimidin-2-one
| Molecular Weight | 561.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H52N3O7P |
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 26 |
| Exact Mass | 561.35428800 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 561.35428800 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 144 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 721 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Brincidofovir is indicated for the treatment of human smallpox disease in adult and pediatric patients.
Treatment of adenovirus in immunocompromised patients
Treatment of smallpox
The pharmacologically active agent resulting from brincidofovir metabolism, cidofovir diphosphate, has an exceedingly long duration of action that allows for it to be dosed once weekly. The entirety of a brincidofovir smallpox treatment consists of only two doses, on days 1 and 8, which seemingly reduces the risk of adverse reactions. Regimens involving a longer duration of administration (i.e. more than a single dose on days 1 and 8) have been shown to increase mortality compared to placebo and should therefore be avoided. Brincidofovir is considered a potential human carcinogen and has demonstrated the potential to cause infertility - as such, its use should be restricted to situations in which it is absolutely necessary.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AB - Nucleosides and nucleotides excl. reverse transcriptase inhibitors
J05AB17 - Brincidofovir
Absorption
The oral bioavailability of brincidofovir is 13.4% in its tablet formulation and 16.8% in its suspension formulation. Following oral administration, the Cmax and AUCtau of brincidofovir were 480 ng/mL and 3400 nghr/mL, respectively. The Cmax and AUCtau of the active metabolite, cidofovir diphosphate, were 9.7 pg/106 cells and 1200 pghr/106 cells, respectively. Maximum plasma concentrations (Tmax) of brincidofovir are reached at approximately 3 hours post-administration, while maximal plasma concentrations for cidofovir diphosphate are reached at approximately 47 hours post-administration.
Route of Elimination
Brincidofovir is eliminated as metabolites in both the urine (~51%) and feces (~40%).
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of brincidofovir is 1230 L.
Clearance
The apparent clearance of brincidofovir in healthy adult patients is 44.1 L/h.
Brincidofovir is a pro-drug of [cidofovir] and as such must undergo some basic metabolic reactions to become pharmacologically active. Upon entering the target cell, the phosphodiester bond of brincidofovir is hydrolyzed to generate cidofovir, which is then phosphorylated to generate the active agent: cidofovir diphosphate. The specific enzyme(s) responsible for this reaction have not been elucidated, but _in vitro_ findings suggest sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase plays a major role in the initial hydrolysis of brincidofovir. There are two major inactive metabolites of brincidofovir, CMX103 and CMX064, which are generated via carboxylation of the terminal carbon followed by several cycles of CYP-mediated oxidative reactions and fatty acid oxidation. These reactions are mediated, at least in part, by CYP4F2.
The mean terminal half-lives of brincidofovir and its pharmacologically active metabolite, cidofovir diphosphate, are 19.3 hours and 113 hours, respectively.
Brincidofovir is a pro-drug comprising [cidofovir] conjugated to a lipid molecule - the lipid component mimics an endogenous lipid, lysophosphatidylcholine, which allows the molecule to hijack endogenous lipid uptake pathways to enter infected cells. Following uptake, the lipid molecule is cleaved to generate cidofovir, which is then phosphorylated to generate the active antiviral compound, cidofovir disphosphate. The antiviral effects of cidofovir diphosphate appear to be the result of two distinct mechanisms. Mechanistic studies using recombinant vaccinia DNA polymerase suggest that it inhibits orthopoxvirus DNA polymerase-mediated DNA synthesis. In addition, cidofovir is an acyclic nucleotide analogue of deoxycytidine monophosphate - cidofovir diphosphate can therefore be incorporated into the growing viral DNA chain and consequently slow the rate of viral DNA synthesis.


