
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
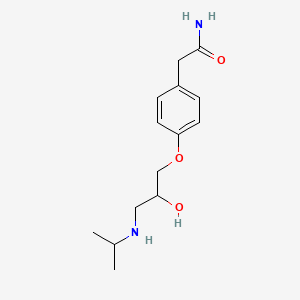

1. Ici 66082
2. Ici-66082
3. Ici66082
4. Tenormin
5. Tenormine
1. 29122-68-7
2. Tenormin
3. Blokium
4. Myocord
5. Normiten
6. Prenormine
7. Tenormine
8. (rs)-atenolol
9. Duraatenolol
10. Betacard
11. Corotenol
12. Tenoblock
13. Atehexal
14. Betablok
15. Cuxanorm
16. Juvental
17. Selobloc
18. Antipressan
19. Atcardil
20. Atenblock
21. Evitocor
22. Farnormin
23. Internolol
24. Normalol
25. Premorine
26. Prenolol
27. Tenoprin
28. Tensimin
29. Vascoten
30. Vericordin
31. Alinor
32. Anselol
33. Atecard
34. Atendol
35. Atenet
36. Atenil
37. Atereal
38. Aterol
39. Hipres
40. Hypoten
41. Ibinolo
42. Lotenal
43. Oraday
44. Serten
45. Stermin
46. Tenidon
47. Tenolol
48. Tredol
49. Uniloc
50. Wesipin
51. Altol
52. Ateni
53. Noten
54. Xaten
55. Seles Beta
56. Apo-atenolol
57. Felo-bits
58. Lo-ten
59. Atenolin
60. Atenomel
61. Blocotenol
62. Cardaxen
63. Cardiopress
64. Jenatenol
65. Panapres
66. Plenacor
67. Servitenol
68. Tenobloc
69. Aircrit
70. Betasyn
71. Ormidol
72. Prinorm
73. Unibloc
74. Loten
75. Atenol Acis
76. Atenol Cophar
77. Atenol Fecofar
78. Atenol Heumann
79. Atenol Nordic
80. Atenol Quesada
81. Atenol Gador
82. Atenol Stada
83. Atenol-mepha
84. Atenol-wolff
85. Atenol Atid
86. Atenol Ct
87. Atenol Tika
88. Atenol Trom
89. Atenol Genericon
90. Betatop Ge
91. Atenol Von Ct
92. Atenol-ratiopharm
93. Atenol Al
94. Atenol Pb
95. Atenol Gnr
96. Atenol Msd
97. Atenol Nm Pharma
98. Scheinpharm Atenol
99. Atenol 1a Pharma
100. Atenololum
101. 2-(4-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)acetamide
102. Tenormine [french]
103. (r,s)-atenolol
104. Atenololum [inn-latin]
105. Ici 66082
106. 2-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]acetamide
107. Tenormin (tn)
108. Ici-66082
109. Novaten
110. 1-p-carbamoylmethylphenoxy-3-isopropylamino-2-propanol
111. Ici 66,082
112. 2-[4-(2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropoxy)phenyl]acetamide
113. 2-(p-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)acetamide
114. 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)benzeneacetamide
115. 2-(4-{2-hydroxy-3-[(propan-2-yl)amino]propoxy}phenyl)acetamide
116. Benzeneacetamide, 4-[2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]-
117. C07ab03
118. Chembl24
119. Duratenol
120. Nsc-757832
121. Benzeneacetamide, 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)-
122. 50vv3vw0ti
123. Mls000069622
124. Chebi:2904
125. Atenolol Bp
126. 60966-51-0
127. Smr000036768
128. Atenol
129. 2-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl}acetamide
130. Acetamide, 2-(p-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)-
131. Teno-basan
132. Neatenol
133. Tensotin
134. Atcard
135. Dl-atenolol
136. Ccris 4196
137. (+/-)-atenolol
138. Hsdb 6526
139. Sr-01000000159
140. Einecs 249-451-7
141. Einecs 262-544-7
142. Mfcd00057645
143. Unii-50vv3vw0ti
144. Brn 2739235
145. 2-(4-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy]phenyl)acetamide
146. Artrenolol
147. 2-(4-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)ethanamide
148. 4-(2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy)benzeneacetamide
149. 2-(4-(2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropoxy)phenyl)acetamid
150. Phenyl)acetamide
151. Atenolol [usan:ban:inn:jan]
152. (y)-atenolol
153. Atenalol (rs)
154. Atenolol,(s)
155. (?)-atenolol
156. Atenolol [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
157. (a+/-)-atenolol
158. Tenoretic (salt/mix)
159. Atenolol (jan/usp)
160. Spectrum_001364
161. Atenolol [hsdb]
162. Atenolol [usan]
163. Atenolol [inn]
164. Atenolol [jan]
165. Atenolol [mi]
166. Atenolol [vandf]
167. Opera_id_1283
168. Spectrum2_001411
169. Spectrum3_001448
170. Spectrum4_000435
171. Spectrum5_001509
172. Atenolol [mart.]
173. Dsstox_cid_2628
174. Atenolol [usp-rs]
175. Atenolol [who-dd]
176. Atenolol [who-ip]
177. A 7655
178. Schembl4362
179. Dsstox_rid_76663
180. Dsstox_gsid_22628
181. Lopac0_000121
182. Oprea1_448775
183. Bspbio_002915
184. Gtpl548
185. Kbiogr_000790
186. Kbioss_001844
187. Mls001066372
188. Mls001074163
189. Mls001304038
190. Divk1c_000057
191. Spectrum1501127
192. Atenolol (jp17/usp/inn)
193. Spbio_001482
194. Atenolol [orange Book]
195. Atenolol [ep Monograph]
196. Atenolol [usp Impurity]
197. Atenolol [usp Monograph]
198. Dtxsid2022628
199. Bdbm25753
200. Hms500c19
201. Kbio1_000057
202. Kbio2_001844
203. Kbio2_004412
204. Kbio2_006980
205. Kbio3_002415
206. Metkimkyrpqlgs-uhfffaoysa-
207. Polycap Component Atenolol
208. Atenololum [who-ip Latin]
209. Ninds_000057
210. S-atenolol-d7 (iso-propyl-d7)
211. 2-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy]-phenyl}acetamide
212. Hms1569l13
213. Hms1921h09
214. Hms2090i19
215. Hms2092d19
216. Hms2233e06
217. Hms3259k08
218. Hms3260i04
219. Hms3266k13
220. Hms3369b14
221. Hms3369d20
222. Hms3369p20
223. Hms3411g21
224. Hms3675g21
225. Hms3886g03
226. Pharmakon1600-01501127
227. ( Inverted Question Mark)-atenolol
228. Tenoretic Component Atenolol
229. Bcp12899
230. Atenolol 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
231. Atenolol, >=98% (tlc), Powder
232. Tox21_302426
233. Tox21_500121
234. 2-[4-({2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propyl}oxy)phenyl]acetamide
235. Atenolol 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
236. Bbl009276
237. Ccg-39010
238. Geo-03413
239. Nsc757832
240. S4817
241. Stk528649
242. Akos005111050
243. Atenolol Component Of Tenoretic
244. Ac-8245
245. Atenolol, Analytical Reference Material
246. Db00335
247. Ks-5341
248. Lp00121
249. Nc00548
250. Nsc 757832
251. Sdccgsbi-0050109.p004
252. Idi1_000057
253. Mrf-0000571
254. Ncgc00015007-06
255. Ncgc00015007-07
256. Ncgc00015007-08
257. Ncgc00015007-09
258. Ncgc00015007-10
259. Ncgc00015007-11
260. Ncgc00015007-13
261. Ncgc00015007-24
262. Ncgc00024566-03
263. Ncgc00024566-04
264. Ncgc00024566-05
265. Ncgc00024566-06
266. Ncgc00024566-07
267. Ncgc00255122-01
268. Ncgc00260806-01
269. Ba166036
270. Hy-17498
271. Sbi-0050109.p003
272. Cas-29122-68-7
273. Db-072177
274. Db-079552
275. Eu-0100121
276. Ft-0662315
277. Ft-0662316
278. Ft-0693045
279. 2-(4-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)
280. Bim-0050109.0001
281. D00235
282. O10469
283. Ab00052208-13
284. Ab00052208-15
285. Ab00052208_16
286. 122a687
287. L000116
288. Q411325
289. Q-200656
290. Sr-01000000159-2
291. Sr-01000000159-4
292. Sr-01000000159-5
293. Sr-01000000159-8
294. Brd-a20239487-001-02-5
295. Brd-a20239487-001-15-7
296. Atenolol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
297. Z1541638518
298. Atenolol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
299. (+)-4-[2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]benzeneacetamide
300. (rs)-4-[2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]benzeneacetamide
301. 2-(p-(hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)acetamide
302. (+/-)-4-(2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy)benzeneacetamide
303. 2-(4-{[(2s)-2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propyl]oxy}phenyl)acetamide
304. Atenolol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
305. 2-(p-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenyl)acetamide (racemate)
306. 2-[4-({(2r)-2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propyl}oxy)phenyl]acetamide
307. Atenolol Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
308. 106020-65-9
| Molecular Weight | 266.34 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H22N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 266.16304257 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 266.16304257 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 84.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 263 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Atenolol |
| PubMed Health | Atenolol |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Atenolol, a synthetic, beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent, may be chemically described as benzeneacetamide, 4 -[2'-hydroxy-3'-[(1- methylethyl) amino] propoxy]-. The molecular formula is C14H22N2O3 and its structural |
| Active Ingredient | Atenolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ipca Labs; Mutual Pharm; Teva; Ipr; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Zydus Pharms Usa; Northstar Hlthcare; Unique Pharm Labs; Sandoz; Mylan; Dava Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tenormin |
| PubMed Health | Atenolol |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | TENORMIN (atenolol), a synthetic, beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent, may be chemically described as benzeneacetamide, 4 -[2'-hydroxy-3'-[(1- methylethyl) amino] propoxy]-. The molecular and structural formulas are: |
| Active Ingredient | Atenolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Atenolol |
| PubMed Health | Atenolol |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Atenolol, a synthetic, beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent, may be chemically described as benzeneacetamide, 4 -[2'-hydroxy-3'-[(1- methylethyl) amino] propoxy]-. The molecular formula is C14H22N2O3 and its structural |
| Active Ingredient | Atenolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ipca Labs; Mutual Pharm; Teva; Ipr; Aurobindo Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Zydus Pharms Usa; Northstar Hlthcare; Unique Pharm Labs; Sandoz; Mylan; Dava Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tenormin |
| PubMed Health | Atenolol |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | TENORMIN (atenolol), a synthetic, beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent, may be chemically described as benzeneacetamide, 4 -[2'-hydroxy-3'-[(1- methylethyl) amino] propoxy]-. The molecular and structural formulas are: |
| Active Ingredient | Atenolol |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Antihypertensive Agents; Sympatholytics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Atenolol has been used with good results alone or in conjunction with a benzodiazepine in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal in a limited number of patients.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1739
Atenolol ... /is/ indicated in the treatment of classic angina pectoris, also referred to as "effort-associated angina". /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 550
Atenolol /is/ used in the treatment of mitral value prolapse syndrome. /NOT included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 551
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ATENOLOL (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Atenolol should be used with caution and in reduced dosage in patients with impaired renal function, especially when creatinine clearance is less than 35 ml/minute per 1.73 sq m. ... Patients receiving atenolol after hemodialysis /should/ be administered the drug under close supervision in a hospital setting, since marked hypotension may occur.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1742
Atenolol is contraindicated in patients with sinus bradycardia, AV block greater than first degree, cardiogenic shock, and overt cardiac failure.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1742
Atenolol should be used with caution in patients undergoing major surgery involving general anesthesia. The necessity of withdrawing beta-adrenergic blocking therapy prior to major surgery is controversial. Severe, protracted hypotension and difficulty in restarting or maintaining a heart beat have occurred during surgery in some patients who have received beta-adrenergic blocking agents.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1742
Abrupt withdrawal of atenolol may exacerbate angina symptoms and/or precipitate myocardial infarction and venticular arrhythmias in patients with coronary artery disease, or may precipitate thyroid storm in patients with thyrotoxicosis. Therefore, patients receiving atenolol (especially those with ischemic heart disease) should be warned not to interrupt or discontinue therapy without consulting their physician.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1741
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ATENOLOL (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
**Indicated** for: 1) Management of hypertension alone and in combination with other antihypertensives. 2) Management of angina pectoris associated with coronary atherosclerosis. 3) Management of acute myocardial infarction in hemodynamically stable patients with a heart rate greater than 50 beats per minutes and a systolic blood pressure above 100 mmHg. **Off-label** uses include: 1) Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction. 2) Management of heart failure. 3) Management of atrial fibrillation. 4) Management of supraventricular tachycardia. 5) Management of ventricular arrythmias such as congenital long-QT and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. 6) Management of symptomatic thyrotoxicosis in combination with [methimazole]. 7) Prophylaxis of migraine headaches. 8) Management of alcohol withdrawal.
FDA Label
Atenolol is a cardio-selective beta-blocker and as such exerts most of its effects on the heart. It acts as an antagonist to sympathetic innervation and prevents increases in heart rate, electrical conductivity, and contractility in the heart due to increased release of norepinephrine from the peripheral nervous system. Together the decreases in contractility and rate produce a reduction in cardiac output resulting in a compensatory increase in peripheral vascular resistance in the short-term. This response later declines to baseline with long-term use of atenolol. More importantly, this reduction in the work demanded of the myocardium also reduces oxygen demand which provides therapeutic benefit by reducing the mismatch of oxygen supply and demand in settings where coronary blood flow is limited, such as in coronary atherosclerosis. Reducing oxygen demand, particularly due to exercise, can reduce the frequency of angina pectoris symptoms and potentially improve survival of the remaining myocardium after myocardial infarction. The decrease in rate of sinoatrial node potentials, electrical conduction, slowing of potentials traveling through the atrioventricular node, and reduced frequency of ectopic potentials due to blockade of adrenergic beta receptors has led to benefit in arrhythmic conditions such as atrial fibrillation by controlling the rate of action potential generation and allowing for more effective coordinated contractions. Since a degree of sympathetic activity is necessary to maintain cardiac function, the reduced contractility induced by atenolol may precipitate or worsen heart failure, especially during volume overload. The effects of atenolol on blood pressure have been established, although it is less effective than alternative beta-blockers, but the mechanism has not yet been characterized. As a 1 selective drug, it does not act via the vasodilation produced by non-selective agents. Despite this there is a sustained reduction in peripheral vascular resistance, and consequently blood pressure, alongside a decrease in cardiac output. It is thought that atenolol's antihypertensive activity may be related to action on the central nervous system (CNS) or it's inhibition of the renin-aldosterone-angiotensin system rather than direct effects on the vasculature. Atenolol produces CNS effects similar to other beta-blockers, but does so to a lesser extent due to reduces ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. It has the potential to produce fatigue, depression, and sleep disturbances such as nightmares or insomnia. The exact mechanisms behind these have not been characterized but their occurrence must be considered as they represent clinically relevant adverse effects. Atenolol exerts some effects on the respiratory system although to a much lesser extent than non-selective beta-blockers. Interaction with 2 receptors in the airways can produce bronchoconstriction by blocking the relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle mediated by the sympathetic nervous system. The same action can interfere with -agonist therapies used in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Unlike some other beta-blocker drugs, atenolol does not have intrinsic sympathomimetic or membrane stabilizing activity nor does it produce changes in glycemic control.
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Sympatholytics
Drugs that inhibit the actions of the sympathetic nervous system by any mechanism. The most common of these are the ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS and drugs that deplete norepinephrine or reduce the release of transmitters from adrenergic postganglionic terminals (see ADRENERGIC AGENTS). Drugs that act in the central nervous system to reduce sympathetic activity (e.g., centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, see ADRENERGIC ALPHA-AGONISTS) are included here. (See all compounds classified as Sympatholytics.)
Adrenergic beta-1 Receptor Antagonists
Drugs that bind to and block the activation of ADRENERGIC BETA-1 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-1 Receptor Antagonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C07AB03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C07AB03
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
C07AB03
S66 | EAWAGTPS | Parent-Transformation Product Pairs from Eawag | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.3754448
C - Cardiovascular system
C07 - Beta blocking agents
C07A - Beta blocking agents
C07AB - Beta blocking agents, selective
C07AB03 - Atenolol
Absorption
Approximately 50% of an oral dose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with the remainder being excreted unchanged in the feces. Administering atenolol with food can decrease the AUC by about 20%. While atenolol can cross the blood-brain barrier, it does so slowly and to a small extent.
Route of Elimination
85% is eliminated by the kidneys following IV administration with 10% appearing in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
Total Vd of 63.8-112.5 L. Atenolol distributes into a central volume of 12.8-17.5 L along with two peripheral compartments with a combined volume of 51-95 L. Distribution takes about 3 hrs for the central compartment, 4 hrs for the shallower peripheral compartment, and 5-6 hrs for the deeper peripheral compartment.
Clearance
Total clearance is estimated at 97.3-176.3 mL/min with a renal clearance of 95-168 mL/min.
In animals, atenolol is well distributed into most tissues and fluids except brain and /cerebrospinal fluid/. Unlike propranolol, only a small portion of atenolol is apparently distributed into the CNS.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
Approximately 5-15% of atenolol is bound to plasma protein.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
Atenolol readily crosses the placenta, and has been detected in cord blood. During continuous administration, fetal serum concentrations of the drug are probably equivalent to those in maternal serum. Atenolol is distributed into milk; peak milk concentrations of the drug are higher than peak serum concentrations after an individual dose, and the area under the milk concentration-time (AUC) is substantially greater than that of the serum AUC in lactating women receiving the drug continuously.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
Atenolol is rapidly but incompletely absorbed from the GI tract. Only about 50-60% of an oral dose of atenolol is absorbed. In healthy adults, peak plasma concentrations of 1-2 ug/ml are achieved 2-4 hours after oral administration of a single 200 mg dose of atenolol. An approximately fourfold interindividual variation in plasma concentrations attained has been reported with a specific oral dose of atenolol. Peak plasma atenolol concentrations are achieved within 5 minutes following direct IV injection of the drug, and decline rapidly during an initial distribution phase; after the first 7 hours, plasma concentrations reportedly decline with an elimination half-life similar to that of orally administered drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ATENOLOL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Minimal metabolism in the liver. The sole non-conjugated metabolite is the product of a hydroxylation reaction at the carbon between the amide and benzene groups. The only other metabolite to be confirmed is a glucuronide conjugate. These metabolites make up 5-8% and 2% of the renally excreted dose with 87-90% appearing as unchanged drug. The hydroxylated metabolite is exerts 1/10th the beta-blocking activity of atenolol.
Minimal hepatic metabolism; removable by hemodialysis; very low lipid solubility.
US Pharmacopeial Convention; US Pharmacopeia Dispensing Information (USP DI); Drug Information for the Health Care Professional 12th ed, V.I p.635 (1992)
Little or no metabolism of atenolol occurs in the liver. Approximately 40-50% of an oral dose of the drug is excreted in urine unchanged. The remainder is excreted unchanged in feces, principally as unabsorbed drug. About 1-12% of atenolol is reportedly removed by hemodialysis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
6-7 hrs.
In patients with normal renal function, atenolol has a plasma half-life (t1/2) of 6-7 hours. Children with normal renal function may exhibit a shorter elimination half-life. In one study in children ages 5-16 (mean: 8.9) with arhythmias and normal renal and hepatic function, the terminal elimination half-life averaged 4.6 hours. Plasma t1/2 of the drug increases to 16-27 hours in patients with creatinine clearances of 15-35 ml/minute per 1.73 sq m and exceeds 27 hours with progressive renal impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
The half-life in the elderly was significantly longer (8.8 + or - 0.9 hr) compared with that in the young (5.8 + or - 1.1 hr) (p < 0.01).
PMID:3358894 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1386352 Scott M et al; Br J Clin Pharmacol 25 (3): 289-96 (1988)
Atenolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker, called such because it selectively binds to the 1-adrenergic receptor as an antagonist up to a reported 26 fold more than 2 receptors. Selective activity at the 1 receptor produces cardioselectivity due to the higher population of this receptor in cardiac tissue. Some binding to 2 and possibly 3 receptors can still occur at therapeutic dosages but the effects mediated by antagonizing these are significantly reduced from those of non-selective agents. 1 and 2 receptors are Gs coupled therefore antagonism of their activation reduces activity of adenylyl cyclase and its downstream signalling via cyclic adenosime monophosphate and protein kinase A (PKA). In cardiomyocytes PKA is thought to mediate activation of L-type calcium channels and ryanodine receptors through their phosphorylation. L-type calcium channels can then provide an initial rise in intracellular calcium and trigger the ryanodine receptors to release calcium stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) and increased contractility. PKA also plays a role in the cessation of contraction by phosphorylating phospholamban which in turn increases the affinity of SR Ca2+ ATPase to increase reuptake of calcium into the SR. It also phophorylates troponin I to reduce affinity of the protein for calcium. Both of these events lead to a reduction in contraction which, when coupled with the initial increase in contraction, allows for faster cycling and consequently higher heart rate with increased contractility. L-type calcium channels are also a major contributor to cardiac depolarization and their activation can increase frequency of action potentials and possibly the incidence of ectopic potentials. Similar inihibitory events occur in the bronchial smooth muscle to mediate relaxation including phosphorylation of myosin light-chain kinase, reducing its affinity for calcium. PKA also inhibits the excitatory Gq coupled pathway by phosphorylating the inositol trisphosphate receptor and phospholipase C resulting in inhibition of intracellular calcium release. Antagonism of this activity by beta-blocker agents like atenolol can thus cause increased bronchoconstriction.
By inhibiting myocardial beta 1-adrenergic receptors, atenolol produces negative chronotropic and inotropic activity. The negative chronotropic action of atenolol on the sinoatrial node results in a decrease in the rate of sinoatrial node discharge and an increase in recovery time, thereby decreasing resting and exercise stimulated heart rate and reflex orthostatic tachycardia by about 25-35%. High doses of the drug may produce sinus arrest, especially in patients with sinoatrial node disease (eg, sick sinus syndrome). Atenolol also slows conduction in the atrioventricular nose. Although stroke index may be increased moderately by about 10%, atenolol usually reduces cardiac output by about 20% probably secondary to its effect on heart rate. The decrease in myocardial contractability and heart rate, as well as the reduction in blood pressure, produced by atenolol generally lead to a reduction in myocardial oxygen consumption which accounts for the effectiveness of the drug in chronic stable angina pectoris; however, atenolol can increase oxygen requirements by increasing left ventricular fiber length and end-diastolic pressure, particularly in patients with cardiac failure.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
Atenolol suppresses plasma renin activity and suppresses the renin aldosterone angiotensin system.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1743
The toxic actions of beta-blockers appear to be related to properties such as membrane depressant activity and possibly due to actions on beta-adrenoceptors distinct from those in the cardiovascular system.
PMID:2565523 Critchley JA, Ungar A; Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp 4 (1): 32-45 (1989)

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
20
PharmaCompass offers a list of Atenolol API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Atenolol manufacturer or Atenolol supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Atenolol manufacturer or Atenolol supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Atenolol API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Atenolol API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Atenolol Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Atenolol Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Atenolol manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Atenolol, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Atenolol manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Atenolol API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Atenolol manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Atenolol supplier is an individual or a company that provides Atenolol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Atenolol finished formulations upon request. The Atenolol suppliers may include Atenolol API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Atenolol DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Atenolol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Atenolol DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Atenolol USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Atenolol DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Atenolol USDMF includes data on Atenolol's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Atenolol USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Atenolol Drug Master File in Japan (Atenolol JDMF) empowers Atenolol API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Atenolol JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Atenolol JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Atenolol Drug Master File in Korea (Atenolol KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Atenolol. The MFDS reviews the Atenolol KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Atenolol KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Atenolol KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Atenolol API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Atenolol CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Atenolol Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Atenolol CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Atenolol EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Atenolol to their clients by showing that a Atenolol CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Atenolol CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Atenolol CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Atenolol CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Atenolol DMF.
A Atenolol CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Atenolol CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Atenolol written confirmation (Atenolol WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Atenolol manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Atenolol active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Atenolol APIs or Atenolol finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Atenolol WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Atenolol as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Atenolol API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Atenolol as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Atenolol and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Atenolol NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Atenolol suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Atenolol Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Atenolol GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Atenolol GMP manufacturer or Atenolol GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Atenolol CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Atenolol's compliance with Atenolol specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Atenolol CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Atenolol CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Atenolol may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Atenolol EP), Atenolol JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Atenolol USP).

