



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
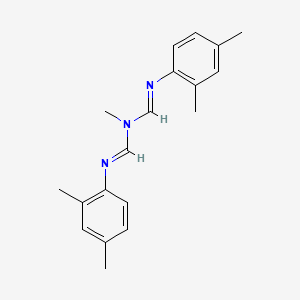

1. Mitaban
2. N-methyl-bis(2,4-xylyiminomethyl) Amine
3. Taktic
4. U 36059
1. 33089-61-1
2. Mitac
3. Taktic
4. Triazid
5. Azaform
6. Mitaban
7. Acarac
8. Baam
9. Azadieno
10. Ectodex
11. Edrizar
12. Amitraz Estrella
13. Fumilat A
14. Amitraze
15. Upjohn U-36059
16. Boots Bts 27419
17. U-36059
18. Bts-27419
19. Certifect
20. Ovasyn
21. Nsc 324552
22. 1,5-di(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-1,3,5-triazapenta-1,4-diene
23. Ent 27967
24. Bts 27,419
25. N-methylbis(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)amine
26. N-methyl-n'-2,4-xylyl-n-(n-2,4-xylylformimidoyl)formamidine
27. N,n-bis(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)methylamine
28. U-36,059
29. N,n-di-(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)methylamine
30. R.d. 27419
31. 2-methyl-1,3-di(2,4-xylylimino)-2-azapropane
32. Nsc-324552
33. N,n'-((methylimino)dimethylidyne)di-2,4-xylidine
34. 2,4-xylidine, N,n'-(methyliminodimethylidyne)bis-
35. N,n'-((methylimino)dimethylidyne)bis(2,4-xylidine)
36. Acadrex
37. Bumetran
38. Istambul
39. Mtiaban
40. Triatix
41. Triatox
42. Maitac
43. Tudy
44. 33iah5017s
45. N,n'-(methyliminodimethylidyne)bis-2,4-xylidine
46. Amitraz 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
47. Methanimidamide, N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-(((2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino)methyl)-n-methyl-
48. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-(((2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino)methyl)-n-methylmethanimidamide
49. Amitraz 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
50. Ncgc00094572-01
51. Bipin
52. Formamidine, N-methyl-n'-2,4-xylyl-n-(n-2,4-xylylformimidoyl)-
53. Dsstox_cid_3871
54. Dsstox_rid_77213
55. Methanimidamide, N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl]-n-methyl-
56. Dsstox_gsid_23871
57. Amitraze [french]
58. U-36-059
59. Mitaban (veterinary)
60. Caswell No. 374a
61. Amitrazum
62. Amitrazum [inn-latin]
63. Oms 1820
64. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-{[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl}-n-methylmethanimidamide
65. N-methyl-bis(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)amine
66. N-methylbis-(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)-amine
67. Cas-33089-61-1
68. Ccris 1552
69. U 36059
70. Hsdb 6939
71. Einecs 251-375-4
72. Bts 27419
73. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 106201
74. Brn 2946590
75. N-methyl-bis(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)amin
76. Unii-33iah5017s
77. Ai3-27967
78. 1,5-bis(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-1,3,5-triazapenta-1,4-diene
79. Amitraz [usan:usp:inn:ban]
80. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-([(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl)-n-methylimidoformamide
81. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[(e)-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)iminomethyl]-n-methylmethanimidamide
82. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-{(e)-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl}-n-methylimidoformamide
83. N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl]-n-methyl-methaniminamide
84. N,4-xylidine]
85. Amitraz (usp/inn)
86. Amitraz [hsdb]
87. Amitraz [usan]
88. Amitraz [inn]
89. Amitraz [mi]
90. Amitraz [mart.]
91. Spectrum2_001243
92. Spectrum3_001944
93. 1,5-di-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-1,3,5-triazapenta-1,4-diene
94. Amitraz [usp-rs]
95. Amitraz, Analytical Standard
96. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)iminomethyl]-n-methylmethanimidamide
97. Schembl37309
98. Amitraz [green Book]
99. Bspbio_003544
100. Ruthenium, Dicyclopentadienyl-
101. Spectrum1505299
102. Spbio_001146
103. Chebi:2665
104. Amitraz [usp Monograph]
105. Chembl1365675
106. Dtxsid5023871
107. Schembl13346111
108. Schembl19312984
109. Kbio3_002829
110. Amy3584
111. Hms1922b10
112. Hms2093o18
113. Hms3885o17
114. Pharmakon1600-01505299
115. Hy-b1111
116. Tox21_111299
117. Tox21_201357
118. Tox21_300930
119. Amitraz 100 Microg/ml In N-hexane
120. Ccg-39116
121. Mfcd00069396
122. Nsc324552
123. Nsc758952
124. S3643
125. Stk368623
126. Zinc18117389
127. Amitraz [ema Epar Veterinary]
128. Promeris Duo Component Amitraz
129. Akos005444180
130. Akos026750163
131. Tox21_111299_1
132. Zinc100025258
133. Zinc100258592
134. Zinc253495784
135. Cs-4710
136. Db11373
137. Ks-5123
138. Nsc-758952
139. 2, N,n'-(methyliminodimethylidyne)bis-
140. Amitraz 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
141. Amitraz Component Of Promeris Duo
142. Ncgc00094572-02
143. Ncgc00094572-03
144. Ncgc00094572-04
145. Ncgc00094572-05
146. Ncgc00094572-06
147. Ncgc00094572-07
148. Ncgc00094572-08
149. Ncgc00094572-11
150. Ncgc00094572-12
151. Ncgc00254832-01
152. Ncgc00258909-01
153. Ac-12471
154. Sbi-0206759.p001
155. Amitraz, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
156. Ft-0629369
157. D02380
158. Ab01563057_01
159. 089a611
160. A821615
161. Q417878
162. Sr-05000001653
163. Sr-05000001653-1
164. Amitraz, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
165. 1,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-1,3,5-triazapenta-1,4-diene
166. Amitraz, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
167. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl]-n-methylmethanimidamide
168. (e)-n'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-((e)-(2,4-dimethylphenylimino)methyl)-n-methylformimidamide
169. Methanimidamide,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl]-n-methyl-
170. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)iminomethyl]-n-methyl-formamidine
171. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-[[(2,4-dimethylphenyl) Imino]methyl]-n-methylmethanimidamide
172. N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-n-{(e)-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl}-n-methylimidoformamide (non-preferred Name)
| Molecular Weight | 293.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N3 |
| XLogP3 | 5.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 293.189197746 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 293.189197746 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 28 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 354 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
MEDICATION (VETERINARY): Amitraz ... is used primarily as an acaricide to control ticks and mites. It is available as a dip for control of canine demodicosis and will also control scabies. An amitraz-impregnated collar is also marketed for the control of ticks on dogs. More recently, an amitraz-containing spot-on product for control of ectoparasites in dogs was developed. It combines the action of amitraz against ticks, mites, and demodectic and sarcoptic mange with that of metaflumizone, a sodium channel blocker, broadening the spectrum of activity by adding efficacy against fleas and lice. Amitraz is not approved for use on cats.
Kahn, C.M (ed.).; The Merck Veterinary Manual 10th Edition. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station NJ. 2010, p. 2360
MEDICATION (VETERINARY): A 2.5-yr-old female llama (Lama glama) ... with skin lesions was presented to the Animal Health Center in Seoul Grand Park Zoo, Korea. Mites of the genus Demodex in the absence of other mites or fungi were identified from the lesions by skin scrapings. ... Treatment with amitraz (0.025%) eliminated the mites and resolved the clinical signs.
PMID:20722277 Eo KY et al; J Zoo Wildl Med. 41 (1): 178-80 (2010)
Treatment and prevention of infestations in dogs by ticks (Ixodes ricinus, Dermacentor reticulatus, Rhipicephalus sanguineus, Ixodes scapularis, Dermacentor variabilis, Haemaphysalis elliptica, Haemaphysalis longicornis, Amblyomma americanum and Amblyomma maculatum) and fleas (Ctenocephalides felis and Ctenocephalides canis). Treatment of infestations by chewing lice (Trichodectes canis). Prevention of environmental flea contamination by inhibiting the development of all flea immature stages. The product can be used as part of a treatment strategy for the control of flea-allergy dermatitis. Elimination of fleas and ticks within 24 hours. One treatment prevents further infestations for five weeks by ticks and for up to five weeks by fleas.
The treatment indirectly reduces the risk of transmission of tick-borne diseases (canine babesiosis, monocytic ehrlichiosis, granulocytic anaplasmosis and borreliosis) from infected ticks for four weeks.
Insect Repellents
Substances causing insects to turn away from them or reject them as food. (See all compounds classified as Insect Repellents.)
Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists
Compounds that bind to and activate ADRENERGIC ALPHA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonists.)
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
Pesticide Synergists
Chemicals that, while not possessing inherent pesticidal activity, nonetheless promote or enhance the effectiveness of other pesticides when combined. (See all compounds classified as Pesticide Synergists.)
QP53AX65
In all species examined, urine was the major route of excretion, accounting for 65-84% of the dose (55-76% within the first 24 hr). ... In both rats and mice, increasing the dose of amitraz from 1 to 100 mg/kg bw increased the excretion of N-methyl- N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine from approximately 5 to 30% of the total excretion.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues Evaluation for Amitraz (33089-61-1) (1998). Available from, as of January 11, 2012: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
In separate studies, groups of two male and two female beagle dogs were dosed orally (4 mg/kg bw by capsule) or dermally (20-21 mg on an area of 400-500 cm sq) with (14)C-amitraz (specific activity, 8.6 mCi/g). Peak blood concentrations of radiolabel were observed during the first 8 hr after oral administration. About 80% of the oral dose was excreted within the first 24 hr and 100% within 72 hr, preferentially in the urine. After dermal treatment, peak blood concentrations occurred within 24-72 hr, and only 25-40% was recovered in urine and feces over a 10-day collection period, demonstrating the poor dermal absorption of amitraz.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues Evaluation for Amitraz (33089-61-1) (1998). Available from, as of January 11, 2012: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
Analysis of urine obtained from volunteers dosed with (14)C-amitraz indicated that the metabolism of amitraz was qualitatively similar to that in the other species. The major metabolites were 4-formamido- meta-toluic acid, 4-acetamido- meta-toluic acid and N-methyl- N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine. In addition, 40-60% of the metabolites excreted in urine were accounted for by a polar fraction containing conjugates of 4-formamido- meta-toluic acid and 4-acetamido- meta-toluic acid. The minor metabolites included 4-amino- meta-toluic acid and form-2',4'-xylidide. Excretion of N-methyl- N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine was dose-dependent. The metabolites identified in the volunteers were 4-formamido- meta-toluic acid plus 4-acetamido- meta-toluic acid (27% of the total radiolabel in urine), N-methyl- N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine (6%), 4-amino- meta-toluic acid (4%), form-2',4'-xylidide (4 %), the product of acid hydrolysis of N-methyl- N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine and form-2',4'-xylidide (1%), and polar material (57%).
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues Evaluation for Amitraz (33089-61-1) (1998). Available from, as of January 11, 2012: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
When (14)C-amitraz was applied to Boophilus microplus, penetration occurred readily. Cleavage to 2,4-dimethylformanilide and N-2,4-dimethylphenyl N'-methylformamidine and large amounts of polar material occurred. 2,4-dimethylaniline adn CO2 were also produced.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides-Update III. Special Scientific Report- Wildlife No. 232. Washington, DC: U.S.Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, 1980., p. 24
... Pear samples were extracted with ethyl acetate and anhydrous sodium sulphate. Amitraz was found to be rapidly decomposed into four related compounds, of which N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)formamidine (DMPF) was the most abundant and persistent. N,N'-bisdimethylphenylformamidine (BDMPF), 2,4-dimethylformamidine (DMF) and 2,4-dimethyl aniline (DMA) were also main metabolites of amitraz.
PMID:18656887 Pico Y et al; J Chromatogr A. 1203 (1): 36-46 (2008)
In separate studies, groups of two male and two female beagle dogs were dosed orally (4 mg/kg bw by capsule) or dermally (20-21 mg on an area of 400-500 cm sq) with (14)C-amitraz (specific activity, 8.6 mCi/g). ... /The/ metabolism of amitraz was essentially the same after oral and dermal administration. 4-Formamido- meta-toluic acid was the predominant residue in both blood and urine. The parent compound and the first hydrolysis products, N-methyl- N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine and form-2',4'-xylidide, were not observed at measurable concentrations in either blood or urine.
WHO/FAO; Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues Evaluation for Amitraz (33089-61-1) (1998). Available from, as of January 11, 2012: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jmpr.html
The hydrolyzed metabolic products of amitraz include 2,4-dimethylaniline, and N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N'-methylformamidine. These metabolites are further metabolized to 2,4-dimethylaniline and ultimately to 4-amino-3-methylbenzoic acid, the principal amitraz metabolite found in the urine and liver.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 1730
Amitraz exhibits monoamine oxidase-inhibiting properties in vitro, but only at high doses does it or its main metabolite (n-2,4 dimethylphenyl-N-methyl-formamide-- BTS27-271) exhibit central; monoamine oxidase-inhibiting properties in animals in vivo. The hydrolyzed metabolic product 2,4-dimethylaniline is a relatively weak methemoglobin formed in dog and presumably man. Topical application of high doses of amitraz in the dog incr plasma glucose and suppresses insulin. Amitraz appears to be a central alpha-adrenoceptor agonist whose action results in diminished peripheral sympathetic tone with a lowering of blood pressure and heart rate. Peripherally, it exhibits both alpha1 and alpha2 adrenoceptor agonist activity resulting in some elevation of blood pressure. The xylene present in amitraz formulations is more likely to induce central nervous system depression.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 1730


