



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
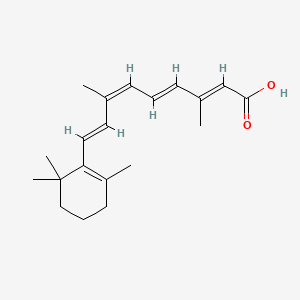

1. 9 Cis Retinoic Acid
2. 9-cis-retinoic Acid
3. 9cra Compound
4. Bal4079
5. Panretin
6. Toctino
1. 9-cis-retinoic Acid
2. Panretin
3. 5300-03-8
4. 9-cis-tretinoin
5. 9-cis Retinoic Acid
6. Panrexin
7. Panretyn
8. Panretin Gel
9. 9(z)-retinoic Acid
10. (9cis)-retinoic Acid
11. Toctino
12. Retinoic Acid, 9-cis-
13. Alitretinoin [usan]
14. Alrt-1057
15. Panretin (tn)
16. Trans-vitamin A Acid
17. Alitretinoin (usan)
18. Alrt1057
19. Agn 192013
20. Bal-4079
21. Lgd-1057
22. Agn-192013
23. Nsc-659772
24. Lg-100057
25. Lgd1057
26. Chembl705
27. 1ua8e65kdz
28. Atragen
29. Effederm
30. Lg100057
31. Retinova
32. (2e,4e,6z,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
33. Chebi:50648
34. Aberela [norway]
35. Avitoin [norway]
36. Tretinoin (tn)
37. Effederm [france]
38. (7e,9z,11e,13e)-retinoic Acid
39. (2e,4e,6z,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
40. A-acido (argentina)
41. 9-cis-ra
42. Retin A (tn)
43. (2e,4e,6z,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
44. (2e,4e,6z,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
45. Trans-retinoate
46. Beta-retinoate
47. 9 Cis Retinoic Acid
48. Alitretinoina
49. Alitretinoine
50. Alitretinoinum
51. Retinoic Acid, Cis-9,trans-13-
52. 9cra
53. (2e,4e,6z,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
54. Tretinoine [inn-french]
55. Tretinoinum [inn-latin]
56. All-trans-b-retinoic Acid
57. Tretinoina [inn-spanish]
58. Tretinoino [inn-spanish]
59. Alrt 1057
60. 9-cis Ra
61. Isotretinoin Retinoic Acid
62. [3h]9-cis-retinoic Acid
63. Tretinoine (french) (einecs)
64. [3h]-9-cis-retinoic Acid
65. 9-cra
66. 9c-ra
67. Acide Retinoique (french) (dsl)
68. 15-apo-beta-caroten-15-oic Acid
69. B-retinoate
70. Bml2-e06
71. Ccris 7098
72. Dtxsid6040404
73. 9-retinoate
74. 9-retinoic Acid
75. Hsdb 7186
76. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (2e,4e,6z,8e)-
77. Mfcd00270072
78. Isotretinoin Retinoate
79. All-trans-b-retinoate
80. Nsc 659772
81. 9-cis- Retinoic Acid
82. Retinoic Acid, 9-cis
83. Ro-04-4079
84. 9-(z)-retinoic Acid
85. Tretinoin (jan/usp)
86. Alpha-acido (argentina)
87. All-trans-beta-retinoate
88. Spectrum5_001935
89. Alitretinoin [mi]
90. Retinoic Acid 9-cis-form
91. Retinoic Acid, (9cis)-
92. Alitretinoin [inn]
93. Unii-1ua8e65kdz
94. Alitretinoin [hsdb]
95. Alpha-vitaminsyre [denmark]
96. Alitretinoin [vandf]
97. Dsstox_cid_20404
98. Dsstox_rid_79490
99. All-trans- Vitamin A1 Acid
100. Dsstox_gsid_40404
101. Schembl18666
102. Alitretinoin [mart.]
103. Bspbio_001495
104. Tretinoin/all-trans Retinoate
105. Tretinoin [usan:ban:inn]
106. Alitretinoin [who-dd]
107. 15-apo-beta-caroten-15-oate
108. Alitretinoin [usan:inn:ban]
109. Gtpl2645
110. Gtpl5383
111. Alitretinoin [ema Epar]
112. Upcmld-dp097:001
113. Upcmld-dp097:002
114. Bdbm31892
115. Alitretinoin [orange Book]
116. Hms1361k17
117. Hms1791k17
118. Hms1989k17
119. Hms3402k17
120. 124510-04-9
121. Amy21903
122. Tox21_302195
123. Lmpr01090022
124. Nsc659772
125. Stk801887
126. Zinc12661824
127. Akos005622553
128. 9-cra. 9-cis-ra. Alrt1057
129. Ccg-208266
130. Db00523
131. Idi1_033965
132. Retinoic Acid 9-cis-form [mi]
133. 9-cis-retinoic Acid, >=98% (hplc)
134. Ncgc00161590-01
135. Ncgc00161590-02
136. Ncgc00161590-03
137. Ncgc00161590-04
138. Ncgc00161590-05
139. Ncgc00161590-06
140. Ncgc00161590-07
141. Ncgc00255697-01
142. As-83566
143. Hy-15128
144. Cas-5300-03-8
145. Tretinoin Impurity D [ep Impurity]
146. Bb 0261656
147. Cs-0003780
148. Isotretinoin Impurity D [ep Impurity]
149. D02815
150. 300r038
151. Sr-05000013784
152. Q3611854
153. Sr-05000013784-1
154. W-200595
155. Brd-k35483542-001-02-3
156. (2e,4e,6z,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl) Nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 300.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O2 |
| XLogP3 | 6.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 300.208930132 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 300.208930132 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 567 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Panretin |
| PubMed Health | Alitretinoin (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Panretin gel 0.1% contains alitretinoin and is intended for topical application only. The chemical name is 9-cis-retinoic acid and the structural formula is as follows:Chemically, alitretinoin is related to vitamin A. It is a yellow powder with a m... |
| Active Ingredient | Alitretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | eq 0.1% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Eisai |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Panretin |
| PubMed Health | Alitretinoin (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Panretin gel 0.1% contains alitretinoin and is intended for topical application only. The chemical name is 9-cis-retinoic acid and the structural formula is as follows:Chemically, alitretinoin is related to vitamin A. It is a yellow powder with a m... |
| Active Ingredient | Alitretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Gel |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | eq 0.1% base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Eisai |
Antineoplastic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Alitretinoin. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Alitretinoin is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Panretin gel is indicated for topical treatment of cutaneous lesions in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma. Panretin gel is not indicated when systemic anti-KS therapy is required (e.g., more than 10 new KS lesions in the prior month, symptomatic lymphedema, symptomatic pulmonary KS, or symptomatic visceral involvement). There is no experience to date using Panretin gel with systemic anti-KS treatment. /Included in US product labeling/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
/EXPL THER/ Lichen amyloidosis (LA) is characterized by the deposition of amyloid that may respond to chronic scratching that may be secondary to atopic dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or interface dermatitis. Despite the development of several therapeutic strategies, including topical steroids, oral antihistamines, cyclosporine, and retinoids, an effective treatment for LA has not been established. A 49-year-old woman who has been treated irregularly for atopic dermatitis for 7 years presented with localized brownish papules on the left forearm and right elbow. They developed 3 months prior and were becoming more prominent despite of treatment with cyclosporine, oral antihistamines, and topical steroids for 5 months prior to presentation. A skin biopsy revealed amyloid deposition in the dermal papillae and the patient was diagnosed with LA associated with atopic dermatitis. A 6-month course of daily oral alitretinoin 30 mg produced marked improvement in the thickness and color of the hyperkeratotic papules without aggravation of the patient's atopic dermatitis. Histologic evaluation showed clearance of amyloid deposition and almost normalization of the epidermal changes. Herein, we report a case of LA treated with alitretinoin and suggest that it could be a potential treatment option for LA, especially in patients with inflammatory skin diseases including atopic dermatitis.
PMID:28906049 Koh WS et al; Dermatol Ther. 2017 Nov;30(6). doi: 10.1111/dth.12537. Epub 2017 Sep 14.
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Alitretinoin (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Retinoids as a class have been associated with photosensitivity. There were no reports of photosensitivity associated with the use of Panretin gel in the clinical studies. Nonetheless, because in vitro data indicate that 9-cis-retinoic acid may have a weak photosensitizing effect, patients should be advised to minimize exposure of treated areas to sunlight and sunlamps during the use of Panretin gel.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
It is not known whether alitretinoin or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions from Panretin gel in nursing infants, mothers should discontinue nursing prior to using the drug.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
Inadequate information is available to assess safety and efficacy in patients age 65 years or older.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Alitretinoin (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For topical treatment of cutaneous lesions in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.
FDA Label
Panretin gel is indicated for the topical treatment of cutaneous lesions in patients with acquired-immune-deficiency-syndrome (AIDS)-related Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) when:
- lesions are not ulcerated or lymphoedematous, and;
- treatment of visceral KS is not required, and;
- lesions are not responding to systemic antiretroviral therapy, and;
- radiotherapy or chemotherapy are not appropriate.
Alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid) is a naturally-occurring endogenous retinoid indicated for topical treatment of cutaneous lesions in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma. Alitretinoin inhibits the growth of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) cells in vitro.
Dermatologic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders or for the routine care of skin. (See all compounds classified as Dermatologic Agents.)
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
L01XX22
D - Dermatologicals
D11 - Other dermatological preparations
D11A - Other dermatological preparations
D11AH - Agents for dermatitis, excluding corticosteroids
D11AH04 - Alitretinoin
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XF - Retinoids for cancer treatment
L01XF02 - Alitretinoin
BACKGROUND: Previous studies have shown that concomitant administration of food may enhance the bioavailability of oral retinoids. AIM: To assess the influence of food on the pharmacokinetics (PK) of alitretinoin after a single oral dose. METHODS: This was a single-dose, open-label, randomized, crossover study, which enrolled 30 healthy men, aged 18-44 years. Subjects received sequential doses of alitretinoin 40 mg either after fasting (treatment A) or 5 min after completion of a standard breakfast (treatment B), with the dosing sequence randomized (A/B or B/A). The washout period between the two doses was 1 week. Plasma concentrations over time were plotted and standard PK variables [area under the curve (AUC) of plasma concentration vs. time, maximum plasma concentration (C(max)), time to maximum plasma concentration (t(max)) and elimination half-life (t(1/2)] were determined. RESULTS: Drug exposure was markedly increased when alitretinoin was taken with food compared with fasting, and there were significant increases in mean C(max) (82.8 vs.25.4 ng/mL, respectively) and AUC (220.2 vs. 55.7 ng/mL/hr). The delaying effect of food on t(max) was less marked (median of 3.0 vs. 2.0 h). Administration with food also increased exposure to drug metabolites. Variability in exposure was markedly reduced if alitretinoin was taken with vs. without food (percentage coefficient of variation 40% vs. 74% for AUC; 49% vs. 85% for C(max)). Alitretinoin was generally well tolerated, with typical retinoid adverse reactions, mostly comprising headache. CONCLUSIONS: Intake of alitretinoin with food substantially increased the bioavailability of alitretinoin, but variability in exposure was reduced. Consequently, oral alitretinoin should be taken with food as outlined in the manufacturer's summary of product characteristics.
PMID:21443600 Schmitt-Hoffmann AH et al; Clin Exp Dermatol 36 (Suppl 2): 18-23 (2011)
BACKGROUND: Alitretinoin, like all retinoids, is teratogenic, and can only be given to women of childbearing potential if pregnancy is excluded and a strict contraceptive programme is followed. AIM: This study was designed to determine whether alitretinoin in the semen of men treated with alitretinoin poses a teratogenic risk to their female partners. METHODS: In total, 24 healthy men aged 18-45 years received alitretinoin 20 mg (n = 12) or 40 mg (n = 12), once daily for 14 days. Subjects in the 40 mg dose group provided ejaculate at baseline, on day 1, before and approximately 4 hr after dosing on day 2, and at follow-up on study day 21 (+/- 2). RESULTS: Alitretinoin and 4-oxo-alitretinoin were detected in 11 of the 12 semen samples. The highest level of alitretinoin in semen was 7.92 ng/mL. Assuming an ejaculate volume of 10 mL, the amount of drug transferred in semen would be about 80 ng, 1/375,000 of a single 30 mg capsule. Complete absorption of 80 ng of alitretinoin from semen, presuming a volume of distribution confined to 5 L of circulating blood in the partner, would lead to an increase in plasma alitretinoin concentration of 0.016 ng/mL, which appears to be negligible compared with measured endogenous plasma levels. Increases in plasma levels of related retinoids are also negligible. CONCLUSIONS: Alitretinoin in the semen of men receiving up to 40 mg of oral alitretinoin per day is unlikely to be associated with teratogenic risk in their female partners. Barrier contraception is therefore not required for men taking alitretinoin.
PMID:21443599 Schmitt-Hoffmann AH et al; Clin Exp Dermatol 36 (Suppl 2): 12-7 (2011)
/MILK/ It is not known whether alitretinoin or its metabolites are excreted in human milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
Limited data indicate that alitretinoin is not substantially absorbed systemically following topical application of the drug.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
Although there are no detectable plasma concentrations of 9-cis-retinoic acid metabolites after topical application of Panretin gel, in vitro studies indicate that the drug is metabolized to 4-hydroxy-9-cis-retinoic acid and 4-oxo-9-cis-retinoic acid by CYP 2C9, 3A4, 1A1, and 1A2 enzymes. In vivo, 4-oxo-9-cis-retinoic acid is the major circulating metabolite following oral administration of 9-cis-retinoic acid.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Panretin (Alitretinoin) Gel (Updated: June 29, 2018). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13c5de6d-d266-4d83-99c4-072ef104e7ff
4-hydroxy-9-cis-retinals is a known human metabolite of 9-cis-retinal.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Alitretinoin binds to and activates all known intracellular retinoid receptor subtypes (RARa, RARb, RARg, RXRa, RXRb and RXRg). Once activated these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control the process of cellular differentiation and proliferation in both normal and neoplastic cells.
Retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and retinoid X receptors (RXRs) mediate the effects of retinoids on gene expression by binding to response elements in retinoid-sensitive genes. RAR- but not RXR-selective retinoids were found in many previous studies to suppress the growth of various cells, implicating RXR-RAR in these effects. ... RXR-selective retinoids inhibited DNA synthesis in squamous carcinoma 1483 cells transfected with RXRalpha but not with RARs. Ligand-induced transcription of the reporter luciferase gene via the activation of RXR-RXR but not RXR-RAR correlated with growth suppression. Studies with RXRalpha deletion mutants indicated that the DNA binding and the ligand binding domains are essential for mediating growth inhibition. A point mutation in the ligand binding domain (L430F) that decreased RXRalpha homodimerization compromised its growth inhibitory function. Further, RXRalpha mutant (F313A), which functions as a constitutively active receptor, inhibited DNA synthesis in the absence of ligand. These results demonstrate that RXR homodimer activation leads to growth inhibition and suggest that transfection of RXRalpha and treatment with RXR-selective retinoids or the transfection of constitutively activated RXRalpha mutant alone may have a therapeutic potential. /Retinoids/
PMID:9756939 Wan H et a; J Biol Chem 273 (41): 26915-22 (1998)
The interaction of retinoid X receptor alpha with 9-cis-retinoic acid was studied ... . Transient kinetic analyses of this interaction suggest a two-step binding mechanism involving a rapid, enthalpically driven pre-equilibrium followed by a slower, entropically driven reaction that may arise from a conformational change within the ligand binding domain of the receptor. The assignment of this kinetic mechanism was supported by agreement between the overall equilibrium constant, Kov, derived from kinetic studies with that determined by equilibrium fluorescence titrations. Although these analyses do not preclude ligand-induced alteration in the oligomerization state of the receptor in solution, the simplest model that can be applied to these data involves the stoichiometric interaction of 9-cis-retinoic acid with retinoid X receptor alpha monomers.
PMID:10346893 Schimerlik MI et al; Biochemistry 38 (21): 6732-40 (1999)


