



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
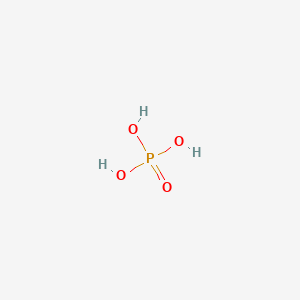

1. Concise Etchant
2. Condact
3. K-etchant
4. Orthophosphoric Acid
5. Uni-etch
1. 7664-38-2
2. Orthophosphoric Acid
3. O-phosphoric Acid
4. Wc-reiniger
5. Acidum Phosphoricum
6. Sonac
7. Phosphorsaeure
8. Evits
9. Acide Phosphorique
10. Phosphoricum Acidum
11. Polyphosphoric Acid
12. Acido Fosforico
13. Phosphorsaeureloesungen
14. Fema No. 2900
15. Oleth-4 Phosphate
16. Superphosphoric Acid
17. Fosforzuuroplossingen
18. Ortho-phosphoric Acid
19. Vococid
20. Amberphos 54
21. Polyphosphoric Acids
22. Phosphate, Dihydrogen
23. Poly(phosphoric Acid)
24. Phosphoric Acid [nf]
25. Trihydroxidooxidophosphorus
26. Nsc-80804
27. H3po4
28. E4ga8884nn
29. Ins No.338
30. Chebi:26078
31. Ins-338
32. Mfcd00011340
33. 62046-92-8
34. Y-11a06
35. Phosphoric Acid (nf)
36. Ncgc00091005-01
37. E 338
38. E-338
39. Dsstox_cid_4263
40. Dsstox_rid_77346
41. Dsstox_gsid_24263
42. 9044-08-0
43. White Phosphoric Acid
44. Caswell No. 662
45. Phosphoric Acid 75%
46. Phosphoric Acid, Ortho-
47. Acido Fosforico [italian]
48. Acide Phosphorique [french]
49. Fosforzuuroplossingen [dutch]
50. Cas-7664-38-2
51. Ccris 2949
52. Phosphorsaeureloesungen [german]
53. Phosphoric Acid 85%
54. Hsdb 1187
55. Phosphoric Acid Solution
56. Phosphoric Acid, Acs Reagent, >=85 Wt. % In H2o
57. Einecs 231-633-2
58. Nsc 80804
59. Un1805
60. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 076001
61. Unii-e4ga8884nn
62. Phospholeum
63. Phosphoric Cid
64. Ortho-phosphate
65. Phosphor-ic Acid
66. Polyphosphorc Acds
67. Nfb Orthophosphate
68. 2hp
69. Orthophosphate(3-)
70. Ortho Phosphoric Acid
71. Phosphate Ion(3-)
72. Tetraoxophosphoric Acid
73. Phosphate Anion(3-)
74. Phosphate (po43-)
75. Phosphoric Acid, 75%
76. Phosphoric Acid, 85%
77. Condensed Phosphoric Acid
78. Orthophosphate (po43-)
79. Phosphoric Acid Ion(3-)
80. Phosphate Ion (po43-)
81. Ec 231-633-2
82. Chembl1187
83. Phosphoric Acid, 10% V/v
84. Phosphoric Acid [ii]
85. Phosphoric Acid [mi]
86. Phosphoric Acid [fcc]
87. D-mannan, Dihydrogen Phosphate
88. Phosphoric Acid [fhfi]
89. Phosphoric Acid [hsdb]
90. Phosphoric Acid [inci]
91. Phosphoric Acid [vandf]
92. Dtxsid5024263
93. Phosphoric Acid [mart.]
94. Phosphoric Acid, Ar, >=88%
95. Phosphoric Acid, Technical Grade
96. [po(oh)3]
97. Bdbm14671
98. Chebi:52641
99. H3 P O4
100. Phosphoric Acid [usp-rs]
101. Phosphoric Acid [who-dd]
102. Trihydrogen Tetraoxophosphate(3-)
103. Phosphoric Acid Solution, 1.0 M
104. Phosphoric Acid, Ar, 88-93%
105. Phosphoric Acid, Lr, 88-93%
106. Phosphoric Acid (fragrance Grade)
107. Phosphoric Acid 85% Reagent Acs
108. Phosphoricum Acidum [hpus]
109. Nsc80804
110. Phosphoric Acid, 85%, Acs Grade
111. Phosphoric Acid, Puriss., >=99%
112. Phosphoric Acid, 85%, Hplc Grade
113. Tox21_111053
114. Tox21_202285
115. Tox21_303246
116. Phosphoric Acid, Acs Reagent, 85%
117. Phosphoric Acid [orange Book]
118. Phosphoric Acid, For Hplc, >=85%
119. Akos028109726
120. Db09394
121. Ncgc00091005-02
122. Ncgc00257071-01
123. Ncgc00259834-01
124. 68891-72-5
125. E338
126. Isooctanol, Reaction Products With Phosphorus Oxide (p2o5) And Polyethylene Glycol Monotridecyl Ether
127. Phosphoric Acid [un1805] [corrosive]
128. Phosphoric Acid, Bioultra, >=85% (t)
129. P1745
130. Phosphoric Acid, Saj First Grade, >=85.0%
131. C00009
132. D05467
133. Orthophosphoric Acid, 85% W/w Aqueous Solution
134. Phosphoric Acid, Jis Special Grade, >=85.0%
135. Q184782
136. Etidronate Disodium Impurity A [ep Impurity]
137. J-523994
138. Q27110336
139. Phosphoric Acid Solution, 85 Wt. % In H2o, Fcc, Fg
140. Phosphoric Acid, P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, 85%
141. Phosphoric Acid, 85% In H2o, 99.99% Trace Metal Basis
142. Zoledronic Acid Monohydrate Impurity F [ep Impurity]
143. 730a9101-d5de-4668-97ca-7b6178b84417
144. Phosphoric Acid, Crystalline, >=99.999% Trace Metals Basis
145. Phosphoric Acid, Puriss. P.a., Crystallized, >=99.0% (t)
146. Pamidronate Disodium Pentahydrate Impurity B [ep Impurity]
147. Phosphoric Acid, 85 Wt. % In H2o, 99.99% Trace Metals Basis
148. Phosphoric Acid, Bioreagent, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture, 85%
149. Phosphoric Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
150. Phosphoric Acid, >=85 Wt. % In H2o, >=99.999% Trace Metals Basis
151. Phosphoric Acid, Semiconductor Grade Vlsi Puranal(tm) (honeywell 17644)
152. Phosphoric Acid, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., >=85%
153. Phosphoric Acid, Semiconductor Grade Mos Puranal(tm) (honeywell 17938), >=85%
154. Phosphoric Acid, Semiconductor Grade Puranal(tm) (honeywell 17861), >=85%
155. Phosphate Atomic Spectroscopy Standard Concentrate 1.00 G Po43-, 1.00 G/l, For 1l Standard Solution, Analytical Standard
156. Phosphate Atomic Spectroscopy Standard Concentrate 10.00 G Po43-, 10.00 G/l, For 1 L Standard Solution, Analytical Standard
157. Phosphoric Acid Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 85% In D2o (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 3 Mm X 8 In.
158. Phosphoric Acid Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 85% In D2o (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 4.2 Mm X 8 In. , Wgs-5bl Coaxial Nmr Tube
159. Phosphoric Acid Solution, Nmr Reference Standard, 85% In D2o (99.9 Atom % D), Nmr Tube Size 5 Mm X 8 In.
160. Phosphoric Acid, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Packed In Coated, Shock- And Leak-protected Glass Bottle, >=85% (t)
161. Phosphoric Acid, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Nf, Fcc, 85.0-88.0%
| Molecular Weight | 97.995 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | H3O4P |
| XLogP3 | -2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 97.97689557 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 97.97689557 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 49.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Diluted phosphoric acid national formulary: it has ... been employed in lead poisoning and in other conditions in which it is desired to administer large amount of phosphate and at /the/ same time produce mild acidosis. It has been given in dose of 60 mL daily (5 mL/hr) under carefully controlled conditions.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 1263
Phosphoric acid is used ... to control the pH of the urinary tract in many animals, particularly in mink and cats, to prevent stone formation.
Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 3rd ed., Volumes 1-26. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, 1978-1984., p. 17:108
Medication (Vet): Has been used to treat lead poisoning.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 1266
Acid cleaning: acids such as sulfuric ... phosphoric, sometimes with chromic or hydrofluoric, are used in water solutions and their splash hazard and corrosive action on skin, clothing, and machinery are well recognized. Bubbles of hydrogen rising from bath carry invisible acid mist. ...
Patty, F. (ed.). Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume II: Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Interscience Publishers, 1963., p. 2280
Splash contact of concentrated strong acids, such as ... phosphoric/acid/, ... can prove as, severely and devastatingly injurious to the eye as splashes of strong alkalies.
Grant, W.M. Toxicology of the Eye. 3rd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher, 1986., p. 46
Phosphoric acid is used in dentistry and orthodontics as an etching solution, to clean and roughen the surfaces of teeth where dental appliances or fillings will be placed.
Transport of phosphate from the gut lumen is an active, energy-dependent process that is modified by several factors. ... Vitamin D stimulates phosphate absorption, an effect reported to precede its action on calcium ion transport.
Dental Materials
Materials used in the production of dental bases, restorations, impressions, prostheses, etc. (See all compounds classified as Dental Materials.)
Absorption
Ortho phosphate is absorbed from, and to a limited extent secreted into, the gastrointestinal tract.
Route of Elimination
In adults, about two thirds of the ingested phosphate is absorbed, and that which is absorbed is almost entirely excreted into the urine.
Volume of Distribution
Absorbed phosphoric acid is distributed widely in the body as phosphate. Increased serum phosphate concentrations have been reported rarely after phosphoric acid ingestion
Clearance
Absorbed phosphate is filtered at the glomerulus and partially reabsorbed, with phosphate clearance 80 per cent of creatinine clearance.
The hygroscopic growth of phosphoric acid aerosol (diameter change > 0.5 micrometers) within the human tracheobronchial tree is modeled to investigate changes in deposition characteristics when compared to nonhygroscopic aerosols of identical preinspired size. Phosphoric acid particles are assumed to grow in a stepwise fashion to 99% relative humidity within conducting airways of the lung, having initially reached equilibrium at 90% relative humidity (T= 37 degrees) in the trachea. Deposition efficiencies for growth and no growth are calculated from theoretical equations for inertial impaction, sedimentation, and diffusion. The results show that neglecting the growth of an inhaled phosphoric acid aerosol may result in underestimation of the total deliverable dose by a factor of as much as 600-700%. Significant differences in regional deposition sites for hygroscopic or nonhygroscopic aerosols are predicted. Increased deposition efficiencies imply that measured physical properties (respirable fraction, aerodynamic diameter) of aerosols alone are not sufficient to assess deposition characteristics within the lung; hygroscopic growth must also be considered.
PMID:6884619 Martonen TB, Clark ML; Fundam Appl Toxicol 3 (1): 10-5 (1983)
/Ortho/ phosphate is absorbed from, and to a limited extent secreted into, the gastrointestinal tract. Transport of phosphate from the gut lumen is an active, energy-dependent process that is modified by several factors. ... Vitamin D stimulates phosphate absorption, an effect reported to precede its action on calcium ion transport. In adults, about two thirds of the ingested phosphate is absorbed, and that which is absorbed is almost entirely excreted into the urine. In growing children, phosphate balance is positive. Concentrations of phosphate in plasma are higher in children than in adults. This "hyperphosphatemia" decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and is hypothesized to explain the physiological "anemia" of childhood. /Phosphates/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 1524
The level of inorganic phosphate in the blood is stabilized by exchange with the mineral deposit in the skeleton through the action of parathyroid hormone. This hormone inhibits tubular reabsorption of phosphates by the kidney and brings about demineralization of bone tissue through the action of osteoclasts. The amount of parathyroid hormone that enters the circulation is probably regulated by the calcium level of the blood.
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Phosphoric acid and phosphate salts (WHO Food Additives Series 17). Available from, as of July 28, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
In infants with normal renal function the serum half-life of phosphate following single oral or rectal overdose is 5-11 hours
Phosphate supplementation of the diet of rodents has been shown to lead to reduction in the incidence of dental caries and different phosphates have different powers in reducing the cariogenic potential of the carbohydrates in a diet. Phosphate supplements seem to exert their cariostatic effect on the tooth surface either directly during eating or by excretion in the saliva.
Phosphate supplementation of the diet of rodents has been shown to lead to reduction in the incidence of dental caries and different phosphates have different powers in reducing the cariogenic potential of the carbohydrates in a diet. Phosphate supplements seem to exert their cariostatic effect on the tooth surface either directly during eating or by excretion in the saliva.
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Phosphoric acid and phosphate salts (WHO Food Additives Series 17). Available from, as of July 28, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html






