



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
0
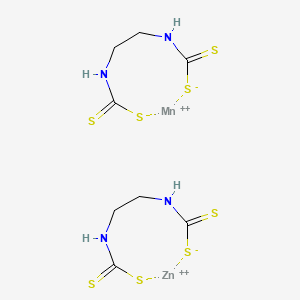

1. Ethylenebisdithiocarbamate Manganese-zinc
2. Mancozeb
1. Mancozeb
2. 8018-01-7
3. 12656-69-8
4. Manganese Zinc Ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate)
5. Mfcd00078616
6. Mancozeb, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
7. 018m017
8. ((1,2-ethanediylbis(carbamodithioato))(2-)) Manganese Mixture With (((1,2-ethanediylbis(carbamodithioato))(2-))zinc
9. 1,3-dithia-5,8-diaza-2?^{2}-manganacyclononane-4,9-dithione;1,3-dithia-5,8-diaza-2?^{2}-zincacyclononane-4,9-dithione
| Molecular Weight | 541.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H12MnN4S8Zn |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 538.749951 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 538.749951 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 181 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 248 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 4 |
Fungicides, Industrial
Chemicals that kill or inhibit the growth of fungi in agricultural applications, on wood, plastics, or other materials, in swimming pools, etc. (See all compounds classified as Fungicides, Industrial.)
Absorption of /mancozeb/ across skin and mucous membranes is probably very limited.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency/Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances. Roberts, J.R., Reigart, J.R. Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings. 6th ed. 2013. EPA Document No. EPA 735K13001, and available in electronic format at: https://www2.epa.gov/pesticide-worker-safety, p. 148
Ethylenethiourea is a decomposition product and metabolite of the ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) group of fungicides. Following administration of single oral doses of (14)C ethylenethiourea to pregnant rats, maternal blood maintained peak radioactivity for 2 hr, and the radioactivity was dispersed uniformly between the RBC and plasma. The level of radioactivity was distributed equally among several maternal tissues but was present in lower amounts in embryos. 24 hr after treatment all tissues examined, except blood, were relatively clear of radioactivity, and 72.8% of the total radioactivity given had been excreted in the urine. Elution patterns of metabolites for Sephadex separation suggested that ethylenethiourea was degraded very little. /Ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) group of fungicides/
PMID:1257912 Ruddick JA et al; Teratology 13 (1): 35 (1976)
Mancozeb appears to be rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, distributed to target organs and excreted almost totally by 96 hr.
Purdue University; National Pesticide Information Retrieval System, Mancozeb Fact Sheet No. 125 (1987)
Rats dosed via a stomach tube with 20 mg (14)C-mancozeb per day for 7 days (equivalent to approx 100 mg/kg body weight) were killed one day after the last dose and the radioactivity in excreta and organs was measured. In the feces, urine, organs and tissues, and carcass, 71%, 16%, 0.31%, and 0.96% of the total radioactivity was detected, respectively. Specifically, the liver contained 0.19%, the kidneys, 0.076%, the thyroid gland, 0.003%, and all other organs, < 0.01%. Most of the labeled material in the feces was mancozeb, indicating that mancozeb was poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract ...
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 78: Dithiocarbamate Pesticides, Ethylenethiourea and Propylenethiourea (1988). Available from, as of March 2, 2017: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
The pharmacokinetics of (14)C-mancozeb (11.54 mCi/g = 25,619 dpm/ug; suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose in distilled water) were studied in Sprague-Dawley CD rats (both sexes) treated with a single oral dose of 1.5 (Group A) or 100 mg/kg (Group B) or a pulse (oral) dose of 1.5 mg/kg (14)C-mancozeb (Group C) which followed 2 weeks of dietary administration of nonradiolabelled mancozeb (84% pure; 15 ppm a.i.). Rats were terminated 96 hours after (14)C-mancozeb treatment. Bile cannulation occurred in both sexes of rat treated at 1.5 (Group D) and 100 mg/kg (Group E) for assessment of excretion in bile at 24 hours. Approximately half of the oral dose of mancozeb was absorbed in rats. Results showed non-linear kinetics occurred between 100 and 1.5 mg/kg. Absorption was moderately rapid (peak levels in 3 and 6 hours at 1.5 and 100 mg/kg, respectively). Elimination was biphasic. Most of the oral dose was eliminated in excreta within 24 hours-evenly divided between feces and urine. Small amounts were excreted in the bile (2-9%). Thyroid contained the greatest concentrations and peak concentrations in thyroid were not proportional to dose. Thyroid (14)C-concentrations were disproportionately less than the respective peak blood levels after 100 mg/kg than after 1.5 mg/kg (14)C-mancozeb indicating saturation at the high dose. Pretreatment with dietary nonradiolabelled mancozeb did not significantly affect the disposition or excretion of (14)C-mancozeb. The in vivo conversion of mancozeb to ETU was determined to be 6.8%.
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Summary of Toxicology Data for Mancozeb, Chemical Code No.000211 p.17 (December 1, 1986, Revised February 10, 2000). Available from, as of March 2, 2017: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/risk/toxsums/toxsumlist.htm
... Mancozeb /is/ metabolized to the degradation product ethylene thiourea, which may have toxic properties of its own.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency/Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances. Roberts, J.R., Reigart, J.R. Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings. 6th ed. 2013. EPA Document No. EPA 735K13001, and available in electronic format at: https://www2.epa.gov/pesticide-worker-safety, p. 148
In oral rat metabolism studies conducted with radiolabeled mancozeb and other /ethylenebisdithiocarbamate compounds (EBDC)/, the in vivo metabolic conversion of EBDC to ETU (ethylenethiourea) was 7.5% on a weight-to-weight basis.
USEPA/Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Mancozeb EPA 738-R-04-012 p.12 (September 2005). Available from, as of March 1, 2017: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
In plants, the principal metabolite is ethylenethiourea, which undergoes further metabolism. Ethylenethiuram monosulfide, ethylenethiuroum disulfide, and sulfur are also metabolites.
Tomlin, C.D.S. (ed.). The Pesticide Manual - World Compendium. 10th ed. Surrey, UK: The British Crop Protection Council, 1994., p. 636
The major metabolite is ethylene thiourea comprising almost 24% of the bio-available dose in urine and bile. Ethylene thiourea residues in the thyroid and the liver were less than 1 ppm and were nondetectable after 24 hr.
Purdue University; National Pesticide Information Retrieval System, Mancozeb Fact Sheet No. 125 (1987)
... This study demonstrates that non-toxic doses of pesticides can induce cellular changes that increase cell sensitivity to other toxins or stress. Pesticide exposure is an environmental risk factor for Parkinson's disease. Manganese (Mn) is essential but high dose exposure may result in neurological dysfunction. Mn-containing dithiocarbamates, maneb (MB) and mancozeb (MZ), are primarily used as pesticides. Studies have shown that MB can augment dopaminergic damage triggered by sub-toxic doses of Parkinsonian mimetic MPTP. However, the mechanism underlying this effect is not clear. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) has been implicated in MPTP toxicity. Mn stimulates the activation of NF-kB and subsequently induces neuronal injury via an NF-kB dependent mechanism. We speculate that MB and MZ enhance MPTP active metabolite (methyl-4-phenylpyridine ion, MPP(+)) toxicity by activating NF-kB. The activation of NF-kB was observed using Western blot analysis and NF-kB response element driven Luciferase reporter assay. Western blot data demonstrated the nuclear translocation of NF-kB p65 and the degradation of IkB-alpha after MB and MZ 4-hr treatments. Results of NF-kB response element luciferase reporter assay confirmed that MB and MZ activated NF-kB. The NF-kB inhibitor (SN50) was also shown to alleviate cytotoxicity induced by co-treatment of MB or MZ and MPP(+). This study demonstrates that activation of NF-kB is responsible for the potentiated toxic effect of MB and MZ on MPP(+) induced cytotoxicity.
PMID:23744253 Williams CA et al; Cell Mol Neurobiol 33 (6): 815-23 (2013)
Mancozeb (manganese/zinc ethylene bis-dithiocarbamate) is an organometallic fungicide that has been associated with human neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. In a high-throughput screen for modulators of KCNQ2 channel, a fundamental player modulating neuronal excitability, Mancozeb, was found to significantly potentiate KCNQ2 activity. Mancozeb was validated electrophysiologically as a KCNQ2 activator with an EC50 value of 0.92 +/- 0.23 uM. Further examination showed that manganese but not zinc ethylene bis-dithiocarbamate is the active component for the positive modulation effects. In addition, the compounds are effective when the metal ions are substituted by iron but lack potentiation activity when the metal ions are substituted by sodium, signifying the importance of the metal ion. However, the iron (Fe(3+)) alone, organic ligands alone or the mixture of iron with the organic ligand did not show any potentiation effect, suggesting as the active ingredient is a specific complex rather than two separate additive or synergistic components. Our study suggests that potentiation on KCNQ2 potassium channels might be the possible mechanism of Mancozeb toxicity in the nervous system.
PMID:23542819 Li P et al; Toxicol Lett 219 (3): 211-7 (2013)
Toxicogenomics has the potential to elucidate gene-environment interactions to identify genes that are affected by a particular chemical at the early stages of the toxicological response and to establish parallelisms between different organisms. The fungicide mancozeb, widely used in agriculture, is an ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate complex with manganese and zinc. Exposure to this pesticide has been linked to the development of idiopathic Parkinson's disease and cancer. Given that many signaling pathways and their molecular components are substantially conserved among eukaryotic organisms, we used Saccharomyces cerevisiae to get insights into the molecular mechanisms of mancozeb toxicity and adaptation based on expression proteomics. The early global response to mancozeb was analyzed by quantitative proteomics using 2-DE. The target genes (e.g. TSA1, TSA2, SOD1, SOD2, AHP1, GRE2, GRX1, CYS3, PRE3, PRE6, PRE8, PRE9, EFT1, RPS5, TIF11, HSP31, HSP26, HSP104, HSP60, HSP70-family) and the putative main transcription activators (e.g. Yap1, Msn2/Msn4, Met4, Hsf1, Aft1, Pdr1, Skn7, Rpn4p, Gcn4) of the complex mancozeb-induced expression changes are related with yeast response to stress, in particular to oxidative stress, protein translation initiation and protein folding, disassembling of protein aggregates and degradation of damaged proteins. ...
PMID:19137554 Santos PM et al; Proteomics 9 (3): 657-70 (2009)
Animal studies offer evidence for the basis of a mechanistic association with some pesticides and the development of PD or Parkinsonian features. Two fungicides, mancozeb and maneb, have dose-dependent toxicity on dopaminergic cells in rats. Both the organic component of the fungicide as well as the manganese ion contributed to the toxicity ...
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency/Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances. Roberts, J.R., Reigart, J.R. Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings. 6th ed. 2013. EPA Document No. EPA 735K13001, and available in electronic format at: https://www2.epa.gov/pesticide-worker-safety, p. 218
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Mancozeb (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.


