



API Suppliers
0

US DMFs Filed
0

CEP/COS Certifications
0

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
0
Other Suppliers
0
0
0

USA (Orange Book)
0

Europe
0

Canada
0

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
0
U.S. Medicaid
0
Annual Reports
0
0
USFDA Orange Book Patents
0
USFDA Exclusivities
0
Blog #PharmaFlow
0
News
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Other Listed Suppliers
0
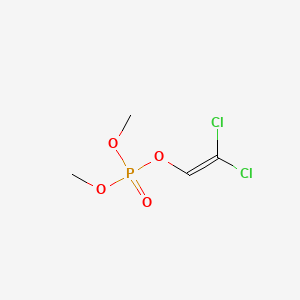

1. Ddvp
2. Dichlofos
3. Dichlorophos
4. Dimethyl Dichlorovinyl Phosphate
5. Divipan
6. Novotox
7. Phosphoric Acid 2,2 Dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Ester
8. Phosphoric Acid 2,2-dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Ester
1. 62-73-7
2. Ddvp
3. 2,2-dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Phosphate
4. Dichlorophos
5. Divipan
6. Vapona
7. 2,2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Phosphate
8. Chlorvinphos
9. Brevinyl
10. Canogard
11. Dichlorphos
12. Equigard
13. Krecalvin
14. Lindanmafu
15. Atgard
16. Bibesol
17. Equigel
18. Fecama
19. Herkal
20. Herkol
21. Nerkol
22. Phosvit
23. Unifos
24. Nogos
25. Nuvan
26. Dichlorman
27. Dichlorovos
28. Estrosel
29. Szklarniak
30. Vaponite
31. Vinylofos
32. Vinylophos
33. Winylophos
34. Dedevap
35. Fekama
36. Marvex
37. Mopari
38. Novotox
39. Tenac
40. Task
41. Atgard C
42. Atgard V
43. Nogos G
44. Vapona Insecticide
45. Dichloorvo
46. Astrobot
47. Cekusan
48. Dichlofos
49. Panaplate
50. Tetravos
51. Apavap
52. Benfos
53. Cypona
54. Unitox
55. Ddvp (insecticide)
56. Insectigas D
57. Dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinyl Phosphate
58. Nogos 50
59. Unifos (pesticide)
60. Derribante
61. Dichlorfos
62. Diclorvos
63. Equiguard
64. Estrosol
65. Nefrafos
66. Deriban
67. Devikol
68. Phosphoric Acid, 2,2-dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Ester
69. Tap 9vp
70. Fly Fighter
71. Mafu Strip
72. Phosphoric Acid, 2,2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Ester
73. No-pest Strip
74. Fly-die
75. No-pest
76. Vapora Ii
77. Dimethyldichlorovinyl Phosphate
78. Nuvan 7
79. O,o-dimethyl Dichlorovinyl Phosphate
80. Oms 14
81. Xlp 30
82. Dichlorovas
83. Duravos
84. Equigand
85. Verdican
86. Verdipor
87. Verdisol
88. Algard
89. Dimethyl 2,2-dichloroethenyl Phosphate
90. Unifos 50 Ec
91. Sd 1750
92. Sd-1750
93. Nci-c00113
94. Nogos 50 Ec
95. Nuvan 100ec
96. Task Tabs
97. Nsc-6738
98. Bay-19149
99. Dimethyl Dichlorovinyl Phosphate
100. Bayer 19149
101. Brevinyl E-50
102. Ddvf
103. Phosphoric Acid 2,2-dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Ester
104. Nsc 6738
105. Ethenol, 2,2-dichloro-, Dimethyl Phosphate
106. Dimethyl-2,2-dichlorovinyl Phosphate
107. (2,2-dichloro-vinil)dimetil-fosfato
108. Brevinyl E 50
109. (2,2-dichlor-vinyl)-dimethyl-phosphat
110. Atgard (tn)
111. Phosphate De Dimethyle Et De 2,2-dichlorovinyle
112. Vinyl Alcohol, 2,2-dichloro-, Dimethyl Phosphate
113. O,o-dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinyl Phosphate
114. Nuvan 100 Ec
115. Ent-20738
116. Phosphoric Acid 2,2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Ester
117. Phosphate, 2-2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl
118. 2,2-dichloroethenyl Phosphoric Acid Dimethyl Ester
119. (2,2-dichloor-vinyl)-dimethyl-fosfaat
120. Chembl167911
121. Chebi:34690
122. O,o-dimethyl-o-(2,2-dichlor-vinyl)-phosphat
123. Nsc6738
124. (2,2-dichloor-vinyl)-dimethyl-fosfaat [dutch]
125. 7u370bps14
126. 2,2-dimethyldichlorovinyl Phosphate
127. Oko
128. Ncgc00090997-02
129. Denkavepon
130. Uniphos
131. Dsstox_cid_449
132. O-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-o,o-dimethylphosphate
133. Des (phosphate)
134. Dsstox_rid_75598
135. Dsstox_gsid_20449
136. Brevinyl E50
137. Dichloorvo [dutch]
138. Dichlorfos [polish]
139. Caswell No. 328
140. Dichlorvosum
141. Delevap
142. Derriban
143. Mafu
144. Nuva
145. Diclorvos [inn-spanish]
146. Dichlorvosum [inn-latin]
147. Cas-62-73-7
148. Dichlorvos [iso]
149. Ccris 230
150. Dichlorvos [usan:inn:ban]
151. Dichlorvos (ddvp)
152. Udvf
153. Hsdb 319
154. Bay-b 4986
155. (2,2-dichloor-vinyl)-dimethyl-fosfaat (dutch)
156. Dichlorvos [bsi:iso]
157. Einecs 200-547-7
158. Ent 20738
159. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 084001
160. Brn 1709141
161. Dichlorovinphos
162. Aquaguard
163. Nuvos
164. Unii-7u370bps14
165. Ai3-20738
166. O,o-dimethyl O-2,2-dichlorovinyl Phosphate
167. Dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Phosphate
168. Prima U
169. (2,2-dichloro-vinil)dimetil-fosfato [italian]
170. (2,2-dichlor-vinyl)-dimethyl-phosphat [german]
171. O,o-dwumetylo-o-dwuchlorowinylofosforan [polish]
172. Dichlorvos (vapona)
173. O-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-o,o-dimethylphosphat [german]
174. Dichlorfos(polish)
175. 2,2-dichloroethenol Dimethyl Phosphate
176. O,o-dimethyl-o-(2,2-dichlor-vinyl)-phosphat [german]
177. O,o-dwumetylo-o-dwuchlorowinylofosforan
178. Phosphate De Dimethyle Et De 2,2-dichlorovinyle [french]
179. Spectrum_001779
180. Dimethyl O,2-phosphate
181. 2,2-dichlorovinyl-o,o-dimethyl Phosphate
182. Dichlorvos [mi]
183. Specplus_000360
184. Dichlorvos [inn]
185. Dichlorvos (usan/inn)
186. O-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-o,o-dimethylphosphat
187. O-(2,o-dimethylphosphat
188. Spectrum2_001227
189. Spectrum3_000810
190. Spectrum4_000650
191. Spectrum5_001930
192. Dichlorvos [hsdb]
193. Dichlorvos [iarc]
194. Dichlorvos [usan]
195. 2,2-dichlorovinyl Alcohol Dimethyl Phosphate
196. Dichlorvos [mart.]
197. 0,2-dichlorovinyl Phosphate
198. 2,2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Phosphoric Acid Ester
199. Dichlorvos [usp-rs]
200. Dichlorvos [who-dd]
201. Schembl25067
202. Bspbio_002279
203. Kbiogr_000999
204. Kbioss_002260
205. O,2-dichlor-vinyl)-phosphat
206. Mls002222471
207. Bidd:er0583
208. Divk1c_006456
209. Spbio_001074
210. Dichlorvos [green Book]
211. Wln: Gygu1opo&o1&o1
212. Dtxsid5020449
213. Kbio1_001400
214. Kbio2_002259
215. Kbio2_004827
216. Kbio2_007395
217. Kbio3_001779
218. Oebrkcosufcwjd-uhfffaoysa-
219. Hms2091c21
220. Dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinylphosphate
221. Zinc1853865
222. Tox21_111052
223. Tox21_201617
224. Tox21_300840
225. Bdbm50286926
226. Ccg-39147
227. Mfcd00036123
228. P5d635
229. (2, 2-dichloro-vinil)dimetil-fosfato
230. (2,2-dichlorovinyl)-dimethyl-fosfate
231. Akos005111045
232. Tox21_111052_1
233. Db11397
234. Dichlorvos 100 Microg/ml In N-hexane
235. Dichlorvos 1000 Microg/ml In Acetone
236. Ethenol,2-dichloro-, Dimethyl Phosphate
237. (2, 2-dichlor-vinyl)-dimethyl-phosphat
238. Ncgc00090997-01
239. Ncgc00090997-03
240. Ncgc00090997-04
241. Ncgc00090997-05
242. Ncgc00090997-06
243. Ncgc00090997-07
244. Ncgc00090997-08
245. Ncgc00090997-09
246. Ncgc00090997-11
247. Ncgc00254743-01
248. Ncgc00259166-01
249. Dichlorvos 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
250. Dimethyl O,o-dichlorovinyl-2,2-phosphate
251. Smr000777927
252. Sbi-0052506.p003
253. 2,2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Phosphate, 8ci
254. Db-054265
255. Dimethyl O, O-dichlorovinyl-2,2-phosphate
256. 2,2-bis(chloranyl)ethenyl Dimethyl Phosphate
257. O-(2, 2-dichlorvinyl)-o,o-dimethylphosphat
258. O-o-dimethyl-o(2,2-dichlorovinyl)phosphate
259. Dichlorvos, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
260. Ethenol, 2, 2-dichloro-, Dimethyl Phosphate
261. Phosphoric Acid,2-dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Ester
262. Vinyl Alcohol,2-dichloro-, Dimethyl Phosphate
263. 0, 0-dimethyl 0-2,2-dichlorovinyl Phosphate
264. D03791
265. Ab00053012_02
266. O,o-dimethyl-o-(2, 2-dichlor-vinyl)-phosphat
267. Phosphoric Acid,2-dichloroethenyl Dimethyl Ester
268. A833962
269. Q420622
270. Sr-05000001548
271. Sr-05000001548-1
272. O-(2,2-dichloroethenyl) O,o-dimethyl Phosphate, 9ci
273. Dichlorvos, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 220.97 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H7Cl2O4P |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 219.9459011 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 219.9459011 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 44.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 181 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anthelmintics; Cholinesterase Inhibitors; Insecticides
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Chloramphenicol. Online file (MeSH, 2017). Available from, as of May 17, 2017: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2017/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
VET: Anthelmintic; ectoparasiticide.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 558
VET: Dichlorvos is used primarily to treat intestinal parasites. Parasites that may be treated include Toxocara canis and Toxascaris leonina (roundworms), Ancylostoma caninum, Uncinaria stenocephala (hookworms), and Trichuris vulpis (whipworms). However, efficacy against T. vulpis may be erratic. In horses, it may be used for the removal and control of bots (Gastrophilus intestinalis, G. nasalis), large strongyles (Strongylus vulgaris, S. equinus, S. edentatus), small strongyles (of the genera Cyathostomum, Cylicocerus, Cylicodontophorus, Triodontophorus, Poteriostomum), pinworms (Oxyuris equi), and large roundworm (Parascaris equorum). In pigs, it is used to treat and control mature, immature, and/or fourth-stage larvae of the whipworm (Trichuris suis), nodular worm (Oesophagostomum sp.), large roundworm (Ascaris suum), and the thick stomach worm (Ascarops strongylina).
Papich, M.G. Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs Small and Large Animal. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders, 2011, p. 221
VET: A cholinesterase inhibitor, it is used in flea (pest) collars for pets.
Lewis, R.J. Sr. (ed) Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. 11th Edition. Wiley-Interscience, Wiley & Sons, Inc. Hoboken, NJ. 2004., p. 1223
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Dichlorvos (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
VET: Overdoses can cause organophosphate intoxication (treat with pralidoxime chloride and atropine). Signs of toxicity include salivation, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, and muscle twitching.
Papich, M.G. Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs Small and Large Animal. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders, 2011, p. 222
VET: Do not use in patients with heartworms. Do not administer within 2 days of administration of a cholinesterase-inhibiting drug. Use a split-dosage schedule in animals that are old, heavily parasitized, anemic, or otherwise debilitated. Do not use in young foals, kittens, or puppies. Its use may exacerbate clinical signs in animals with respiratory disease, such as bronchitis and obstructive pulmonary disease. Do not allow birds access to feed containing this preparation or to fecal excrement from treated animals.
Papich, M.G. Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs Small and Large Animal. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders, 2011, p. 222
Do not use with other anticholinesterase drugs. Do not use with other antifilarial agents, muscle relaxants, CNS depressants, or tranquilizers.
Papich, M.G. Saunders Handbook of Veterinary Drugs Small and Large Animal. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders, 2011, p. 222
Anthelmintics
Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of HELMINTHIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Anthelmintics.)
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
At least 85% of an oral dose of dichlorvos is absorbed. Dichlorvos is well absorbed following inhalation exposure based on the occurrence of toxic symptoms associated with inhalation exposures and the detection of specific dichlorvos metabolites (dichloroethanol and dimethyl phosphate) in urine of individuals exposed to dichlorvos.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 820
An elimination half-life of 13.5 min was estimated based on dichlorvos concentration in rat kidney after 2 or 4 hr exposure to 5 mg/cu m. In mice and rats given single oral doses of dichlorvos, 59-65% was eliminated in urine, 3-7% was eliminated in feces, 14-18% was eliminated as CO2 by 4 days after dosing, and the vast majority was eliminated by 24 hr. Retained dichlorvos following either oral or inhalation exposure is high because it is incorporated into intermediary metabolism.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 820
The vinyl moiety of the dichlorvos molecule undergoes two routes of biotransformation: conversion to dichloroethanol and subsequent formation of dichloroethanol glucuronide; or dehalogenation and incorporation of the carbon atoms into various metabolic pathways in the body. These pathways result in the production of hippuric acid, urea, carbon dioxide, and other endogenous compounds that result in a prolonged half-life of radioactivity in the tissues following the administration of [vinyl-C14] dichlorvos. Both radiolabelled dichloroethanol glucuronide and urea have been identified in the urine of men treated with [vinyl-C14] dichlorvos indicating that both pathways occur in humans.
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Dichlorvos p.71 (PB/98/101124/AS) (September 1997)
Dichlorvos was undetectable (<0.1 mg/liter) in the blood of two men immediately after exposure, one to air concentrations of 0.25 mg dichlorvos/cu m for 10 hours and one to 0.7 mg dichlorvos/cu m for 20 hours.
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 79: Dichlorvos p.37 (1988)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Dichlorvos (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Dichlorvos binds to acetylcholinesterase forming dimethoxy-phosphorylated acetycholinesterase and dichloroacetaldehyde. Alternatively, it is metabolized (primarily in the liver but also in the blood, adrenal, kidney, lung, and spleen) via 2 pathways. The major pathway is catalyzed by A-esterases and produces dimethyl phosphate and dichloroacetaldehyde. Dichloroacetaldehyde is converted to dichloroethanol which is then excreted as the glucuronide. Alternatively, dichloroacetaldehyde is dehalogenated and the carbon atoms are incorporated into normal tissue constituents via intermediary metabolism. The second minor pathway is catalyzed by glutahione-S-transferase and produced desmethyl dichlorvos and S-methyl glutathione. Subsequent degradation of desmethyl dichlorvos to dichloroacetaldehyde and monomethyl phosphate is catalyzed by A-esterases. S-methyl glutathione is broken down to methylmercapturic acid and excreted in urine. CO2 is also the major metabolite following inhalation exposures. The major urinary metabolite following either oral or inhalation exposures is dichloroethanol glucuronide.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 820
Dichlorvos is rapidly metabolized in human blood by A-esterases ... Dichlorvos A-esterase appears to be normally distributed. Half-lives for degradation of dichlorvos in whole blood after inhalation were 8.1 min for men and 11.2 min for women.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 820
Dichlorvos (DDVP) is a methylating agent. DNA from mice given 1.9 x 10-6 mol/kg of DDVP, degree of alkylation of guanine-n-7 accounting to 8 x 10-13 mol methyl per gram of DNA was found. Rate of clearance was (estimated) to be 29 hr .
Segerback D, Ehenberg L; Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 49 (Suppl 5): 56-66 (1981)
Dichlorvos, one of the active metabolites of trichlorofon ... is hydrolyzed to give dimethyl phosphate and dichloroacetaldehyde. The latter is subsequently reduced to beta,beta-dichloroethyl alcohol, characteristically converted by rats when administered intraperitoneally. After hydrolysis to a two-carbon fragment, dichloroacetaldhyde is able to enter a pathway of intermediary metabolism, and carbon dioxide is the major radioactive metabolic.
Aizawa, H. Metabolic Maps of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, 1982., p. 154
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Dichlorvos (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Half-lives for degradation of dichlorvos in whole blood after inhalation were 8.1 min for men and 11.2 min for women.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 820
An elimination half-life of 13.5 min was estimated based on dichlorvos concentration in rat kidney after 2 or 4 hr exposure to 5 mg/cu m.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 820
Like other organophosphate agents, dichlorvos inhibits acetylcholinesterase interfering with neuromuscular transmission in susceptible parasites.
Plumb D.C. Veterinary Drug Handbook. 8th ed. (pocket). Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015., p. 431
Dichlorvos is the active molecule of the pro-drug metrifonate used to revert the cognitive deficits associated with Alzheimer's disease. A few years ago it was reported that dichlorvos inhibits the enzyme acylpeptide hydrolase at lower doses than those necessary to inhibit acetylcholinesterase to the same extent. Therefore, the aim of our investigation was to test the hypothesis that dichlorvos can enhance synaptic efficacy through a mechanism that involves acylpeptide hydrolase instead of acetylcholinesterase inhibition. We used long-term potentiation induced in rat hippocampal slices as a model of synaptic plasticity. Our results indicate that short-term exposures (20 min) to 50 uM dichlorvos enhance long-term potentiation in about 200% compared to the control condition. This effect is correlated with approximately 60% inhibition of acylpeptide hydrolase activity, whereas acetylcholinesterase activity remains unaffected. Paired-pulse facilitation and inhibition experiments indicate that dichlorvos does not have any presynaptic effect in the CA3-->CA1 pathway nor affect gabaergic interneurons. Interestingly, the application of 100 nM methyllicaconitine, an alpha(7) nicotinic receptor antagonist, blocked the enhancing effect of dichlorvos on long-term potentiation. These results indicate that under the exposure conditions described above, dichlorvos enhances long-term potentiation through a postsynaptic mechanism that involves (a) the inhibition of the enzyme acylpeptide hydrolase and (b) the modulation of alpha(7) nicotinic receptors.
PMID:19379766 Olmos C et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238 (1): 37-46 (2009)
Exposure to dichlorvos (DDVP), an organophosphorus pesticide, is known to result in neurotoxicity as well as other metabolic perturbations. However, the molecular causes of DDVP toxicity are poorly understood, especially in cells other than neurons and muscle cells. To obtain a better understanding of the process of non-neuronal DDVP toxicity, we exposed zebrafish to different concentrations of DDVP, and investigated the resulting changes in liver histology and gene transcription. Functional enrichment analysis of genes affected by DDVP exposure identified a number of processes involved in energy utilization and stress response in the liver. The abundance of transcripts for proteins involved in glucose metabolism was profoundly affected, suggesting that carbon flux might be diverted toward the pentose phosphate pathway to compensate for an elevated demand for energy and reducing equivalents for detoxification. Strikingly, many transcripts for molecules involved in beta-oxidation and fatty acid synthesis were down-regulated. We found increases in message levels for molecules involved in reactive oxygen species responses as well as ubiquitination, proteasomal degradation, and autophagy. To ensure that the effects of DDVP on energy metabolism were not simply a consequence of poor feeding because of neuromuscular impairment, we fasted fish for 29 or 50 hr and analyzed liver gene expression in them. The patterns of gene expression for energy metabolism in fasted and DDVP-exposed fish were markedly different. We observed coordinated changes in the expression of a large number of genes involved in energy metabolism and responses to oxidative stress. These results argue that an appreciable part of the effect of DDVP is on energy metabolism and is regulated at the message level. Although we observed some evidence of neuromuscular impairment in exposed fish that may have resulted in reduced feeding, the alterations in gene expression in exposed fish cannot readily be explained by nutrient deprivation.
PMID:26499117 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4619386 Bui-Nguyen TM et al; BMC Genomics 16: 853 (2015)
The main target of neurotoxins is neurons because they comprise the main part of neural function, but glial cells may be indirect targets because they support the function of neurons. Among the glial cells, astrocytes in particular act as "nurse cells", regulating neuronal survival and functions. In the present study, to reveal whether a known neurotoxic substance, organophosphate dichlorvos (DDVP), affects the differentiation of astrocytes, we used an astrocyte differentiation model in rat glioma C6 cells. Morphological change and induction of GFAP expression in the differentiating C6 cells were suppressed by DDVP treatment. The known potential targets of DDVP are acetylcholine esterase (AChE), fatty acid amide hydrolase and methyl guanine methyl transferase. Among the specific inhibitors against these enzymes, the AChE inhibitor paraoxon successfully suppressed the cellular morphological changes and the induction of GFAP expression in differentiating C6 cells. These results indicate that DDVP inhibits differentiation in the C6 astrocyte-differentiation model, in which at least AChE inhibition is involved and that AChE is a potent regulator of the differentiation. Furthermore, considering that the main substrate of AChE is ACh, thus, ACh may act as regulators of astrocyte differentiation.
PMID:24001591 Ozawa A et al; Brain Res 1537: 37-45 (2013)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Dichlorvos (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.


