



API Suppliers

US DMFs Filed

CEP/COS Certifications

JDMFs Filed
0
Other Certificates
Other Suppliers
0

USA (Orange Book)

Europe

Canada

Australia
0

South Africa
0
Uploaded Dossiers
U.S. Medicaid
Annual Reports
0
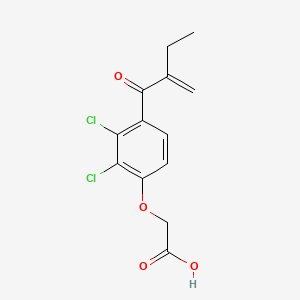

1. Acid, Etacrynic
2. Acid, Ethacrinic
3. Acid, Ethacrynic
4. Edecrin
5. Etacrynic Acid
6. Ethacrinic Acid
7. Ethacrynate Sodium
8. Ethacrynic Acid, Sodium Salt
9. Hydromedin
10. Sodium, Ethacrynate
1. Etacrynic Acid
2. 58-54-8
3. Ethacrynate
4. Edecrin
5. Etacrinic Acid
6. Hydromedin
7. Taladren
8. Crinuryl
9. Edecril
10. Edecrina
11. Endecril
12. Hidromedin
13. Otacril
14. Mingit
15. Reomax
16. Uregit
17. Etakrinic Acid
18. Methylenebutyrylphenoxyacetic Acid
19. Mk-595
20. Ethacrinique (acide)
21. Acido Etacrinico
22. Acide Etacrynique
23. Acidum Etacrynicum
24. Kyselina Ethakrynova
25. Kyselina Ethakrynova [czech]
26. 2-[2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylidenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid
27. Acide Etacrynique [inn-french]
28. Acido Etacrinico [inn-spanish]
29. Acidum Etacrynicum [inn-latin]
30. (2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy)acetic Acid
31. Methylenebutyryl Phenoxyacetic Acid
32. [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy]acetic Acid
33. 2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyl)phenoxyacetic Acid
34. Mk 595
35. Nsc 85791
36. (2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy)acetic Acid
37. Nsc 624008
38. Brn 1915060
39. Acetic Acid, (2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy)-
40. Etacrynic Acid [inn]
41. 2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy Acetic Acid
42. (4-(2-methylenebutyryl)-2,3-dichlorophenoxy)acetic Acid
43. 2-(2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutanoyl)phenoxy)acetic Acid
44. Nsc-85791
45. Chembl456
46. Nsc-624008
47. Acetic Acid, [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy]-
48. Kyselina 4-(2-(1-butenyl)karbonyl)-2,3-dichlorfenoxyoctova [czech]
49. M5dp350vzv
50. 58-54-8 (free Acid)
51. Mls000069535
52. Mls002701928
53. Chebi:4876
54. [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylidenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid
55. Kyselina 4-(2-(1-butenyl)karbonyl)-2,3-dichlorfenoxyoctova
56. Acetic Acid, (2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy)-
57. Nsc85791
58. Nsc624008
59. Cas-58-54-8
60. [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid
61. [4-(2-methylenebutyryl)-2,3-dichlorophenoxy]acetic Acid
62. Ncgc00016260-05
63. 2-[2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutanoyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid
64. Smr000058600
65. [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid
66. Ethacryinic Acid
67. Dsstox_cid_5257
68. Dsstox_rid_77718
69. Dsstox_gsid_25257
70. Ethacrynic Acid [usan:ban]
71. Ccris 4638
72. Hsdb 2136
73. Ethacrynic Acid (usp)
74. Sr-01000003010
75. Einecs 200-384-1
76. Unii-m5dp350vzv
77. Etacrynicacid
78. Etacrynsaure
79. Crinuril
80. Acetic Acid, [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy]-
81. Etacrynic-acid
82. Ethacrynic Acid [usan:usp]
83. 1gsf
84. 2gss
85. Prestwick_671
86. Opera_id_61
87. Spectrum_000813
88. Prestwick0_000259
89. Prestwick1_000259
90. Prestwick2_000259
91. Prestwick3_000259
92. Spectrum2_000097
93. Spectrum3_000425
94. Spectrum4_000544
95. Spectrum5_000680
96. E0526
97. Bmse000134
98. Schembl26353
99. Bspbio_000078
100. Bspbio_002010
101. Etacrynic Acid [jan]
102. Ethacrynic Acid [mi]
103. Kbiogr_001207
104. Kbioss_001293
105. Mls002548854
106. Divk1c_000900
107. Etacrynic Acid (jp17/inn)
108. Spectrum1500287
109. Spbio_000054
110. Spbio_002297
111. Ethacrynic Acid [hsdb]
112. Ethacrynic Acid [usan]
113. 2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxyacetic Acid
114. Bpbio1_000086
115. Gtpl7179
116. Zinc1382
117. Etacrynic Acid [mart.]
118. Ethacrynic Acid [vandf]
119. Dtxsid3025257
120. Etacrynic Acid [who-dd]
121. Hms502m22
122. Kbio1_000900
123. Kbio2_001293
124. Kbio2_003861
125. Kbio2_006429
126. Kbio3_001230
127. Ninds_000900
128. Hms1568d20
129. Hms1920m16
130. Hms2089n17
131. Hms2091d17
132. Hms2095d20
133. Hms3259g03
134. Hms3712d20
135. Pharmakon1600-01500287
136. Hy-b1640
137. Ethacrynic Acid, >=97% (hplc)
138. Tox21_110335
139. Tox21_201102
140. Bdbm50186231
141. Ccg-38915
142. Etacrynic Acid [ep Impurity]
143. Mfcd00056693
144. Nsc757026
145. S5561
146. Wln: Qv1or Bg Cg Dvy2&u1
147. Etacrynic Acid [ep Monograph]
148. Ethacrynic Acid [orange Book]
149. Gst Inhibitor-2 (ethacrynic Acid))
150. Akos003404732
151. Tox21_110335_1
152. Db00903
153. Ethacrynic Acid [usp Monograph]
154. Ks-1453
155. Nc00450
156. Nsc-757026
157. Idi1_000900
158. Ncgc00016260-01
159. Ncgc00016260-02
160. Ncgc00016260-03
161. Ncgc00016260-04
162. Ncgc00016260-06
163. Ncgc00016260-07
164. Ncgc00016260-08
165. Ncgc00016260-09
166. Ncgc00016260-10
167. Ncgc00016260-11
168. Ncgc00016260-13
169. Ncgc00022601-03
170. Ncgc00022601-04
171. Ncgc00022601-05
172. Ncgc00258654-01
173. Nci60_041898
174. Sbi-0051374.p003
175. Db-053221
176. Ab00051988
177. Cs-0013591
178. A51097
179. D00313
180. Ab00051988-19
181. Ab00051988_20
182. A831918
183. Q418571
184. Sr-01000003010-2
185. Sr-01000003010-3
186. Brd-k63630713-001-05-0
187. Brd-k63630713-001-15-9
188. [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-ethylacryloyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid #
189. Acetic Acid,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy]-
190. 2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenebutyryl)phenoxy)acetate
191. 4-(methylenebutyryl)-2,3-dichlorophenoxy)acetic Acid
192. Acetic Acid,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy]-
193. Ethacrynic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
194. Ethacrynic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
195. 2-(2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy)acetic Acid
196. Etacrynic Acid For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 303.13 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H12Cl2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 302.0112642 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 302.0112642 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 370 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Edecrin |
| PubMed Health | Ethacrynic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Ethacrynic acid is an unsaturated ketone derivative of an aryloxyace -tic acid. It is designated chemically as [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy] acetic acid, and has a molecular weight of 303.14. Ethacrynic acid is a white, or practica... |
| Active Ingredient | Ethacrynate sodium; Ethacrynic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Tablet |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; eq 50mg base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aton |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Edecrin |
| PubMed Health | Ethacrynic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Ethacrynic acid is an unsaturated ketone derivative of an aryloxyace -tic acid. It is designated chemically as [2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy] acetic acid, and has a molecular weight of 303.14. Ethacrynic acid is a white, or practica... |
| Active Ingredient | Ethacrynate sodium; Ethacrynic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Tablet |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; eq 50mg base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aton |
Diuretics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
A major use of loop diuretics is in the treatment of acute pulmonary edema. A rapid incr in venous capacitance in conjunction with a brisk natriuresis reduces left ventricular filling pressures and thereby rapidly relieves pulmonary edema. Loop diuretics also are widely used for the treatment of chronic congestive heart failure when diminution of extracellular fluid volume is desirable to minimize venous and pulmonary congestion. Diuretics are widely used for the treatment of hypertension, and controlled clinical trials demonstrating reduced morbidity and mortality have been conducted with Na+-Cl- symport (thiazides and thiazide-like diuretics), but not Na+-K+-2Cl- symport, inhibitors. Nonetheless, Na+-K+-2Cl- symport inhibitors appear to lower blood pressure as effectively as Na+-Cl- symport inhibitors while causing smaller perturbations in the lipid profile. /Loop diuretics/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 773
The edema of nephrotic syndrome often is refractory to other classes of diuretics, and loop diuretics often are the only drugs capable of reducing the massive edema associated with this renal disease. Loop diuretics also are employed in the treatment of edema and ascites of liver cirrhosis; however, care must be taken not to induce encephalopathy or hepatorenal syndrome. In patients with a drug overdose, loop diuretics can be used to induce a forced diuresis to facilitate more rapid renal elimination of the offending drug. /Loop diuretics/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 773
Loop diuretics- combined with isotonic saline admin to prevent volume depletion- are used to treat hypercalcemia. Loop diuretics interfere with the kidney's ability to produce a concentrated urine. Consequently, loop diuretics combined with hypertonic saline are useful for the treatment of life-threatening hyponatremia. /Loop diuretics/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 773
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ETHACRYNIC ACID (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Vet: Rapid ototoxicity in cats. Do not admin in cases of decr renal function.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 203
Not recommended for routine use /in pregnancy/. /Loop diuretics/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1230
Geriatric patients may be more sensitive to the effects of the usual adult dose.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1232
Ethacrynic acid may cause adverse GI effects, including anorexia, abdominal discomfort or pain, nausea, vomiting, malaise, diarrhea, and dysphagia. Adverse GI effects occur most frequently when large doses are employed or after 1-3 months of continuous therapy and may necessitate discontinuing the drug. Severe, profuse, watery diarrhea may occur; the drug should be permanently discontinued if this occurs. GI bleeding has been reported, most frequently in patients receiving IV ethacrynate sodium therapy and especially in patients receiving heparin sodium concomitiantly. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis, with an incr in serum amylase, has been reported.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2564
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ETHACRYNIC ACID (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of high blood pressure and edema caused by diseases like congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure.
FDA Label
Ethacrynic acid is a monosulfonamyl loop or high ceiling diuretic. Ethacrynic acid acts on the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and on the proximal and distal tubules. Urinary output is usually dose dependent and related to the magnitude of fluid accumulation. Water and electrolyte excretion may be increased several times over that observed with thiazide diuretics, since ethacrynic acid inhibits reabsorption of a much greater proportion of filtered sodium than most other diuretic agents. Therefore, ethacrynic acid is effective in many patients who have significant degrees of renal insufficiency. Ethacrynic acid has little or no effect on glomerular filtration or on renal blood flow, except following pronounced reductions in plasma volume when associated with rapid diuresis.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03C - High-ceiling diuretics
C03CC - Aryloxyacetic acid derivatives
C03CC01 - Etacrynic acid
Absorption
Onset of action is rapid, usually within 30 minutes after an oral dose of ethacrynic acid or within 5 minutes after an intravenous injection of ethacrynic acid.
Thirty-five % or less of ethacrynic acid was excreted in urine of rats and dogs, regardless of mode of admin and 50% or more appeared in feces, suggesting hepatic elimination of the drug.
PMID:4427293 Klaasen CD, Fitzgerald TJ; J Pharmacol Exp Ther 191: 548 (1974)
Renal elimination (67%), biliary/fecal (33%), 20% unchanged. /From table/
Ford MD, Delaney KA, Ling LJ, Erickson T; Clinical Toxicology. W.B. Saunders Company., Philadelphia, PA. 2001, p. 398
Ethacrynic acid is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. Following oral admin, the diuretic effect occurs within 30 min and reaches a peak in approx 2 hr. The duration of action following oral admin is usually 6-8 hr but may continue up to 12 hr. Following IV admin of ethacrynate sodium, diuresis usually occurs within 5 min, reached a max within 15-30 min, and persists for approx 2 hr. In animals, substantial quantities of ethacrynic acid accumulate only in the liver. The drug does not enter the CSF. It is not known whether ethacrynic acid crosses the placenta or is distributed into milk in humans. ... Approx 30-65% of an IV dose of ethacrynate sodium is secreted by the proximal renal tubules and is excreted in urine; approx 35-40% is excreted in bile, partially as the cysteine conjugate. In dogs, approx 30-40% of the drug excreted in urine is unchanged, 20-30% is the cysteine conjugate, and 33-40% is an unstable, unidentified compound. The rate of urinary excretion of ethacrynic acid increases as urinary pH increases and is decreased by probenecid.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2566
Hepatic.
After iv admin (5 or 50 mg/kg) of (14)C-ethacrynic acid to rats 60-70% was excreted into bile within 4 hr; <25% was ethacrynic acid, the remainder was biotransformation products. The 2 major metabolites in bile were identified; one was the glutathione adduct (ethacrynic acid-GSH) and the other was ethacrynic acid-mercapturate. Approx 40% of either dose was excreted as ethacrynic acid-GSH. Ethacrynic acid-mercapturate accounted for 18% of the low dose and 30% of the high dose excreted into bile. Dogs given a 5 mg/kg dose (iv) excreted 25, 11, and 9% of the dose as ethacrynic acid-mercapturate, ethacrynic acid-cysteine and ethacrynic acid-GSH, respectively.
PMID:4427293 Klaasen CD, Fitzgerald TJ; J Pharmacol Exp Ther 191: 548 (1974)
Animal studies indicate that ethacrynic acid is metabolized to a cysteine conjugate (which may contribute to the pharmacologic effects of the drug) and to an unstable, unidentified compound.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2566
Ethacrynic acid inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. Diuretics also lower blood pressure initially by reducing plasma and extracellular fluid volume; cardiac output also decreases, explaining its antihypertensive action. Eventually, cardiac output returns to normal with an accompanying decrease in peripheral resistance. Its mode of action does not involve carbonic anhydrase inhibition.
Optimal diuretic activity depends on at least 2 structural requirements: (1) methylene and adjacent ketone groups capable of reacting with sulfhydryl radicals of presumed receptor, and (2) substituents on aromatic nucleus.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 903
In vitro, ethacrynic acid inhibits the active transport of chloride in the lumen of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, thereby diminishing reabsorption of sodium and chloride at that site. Because this inhibition occurred with lower concns of ethacrynic acid in the presence of cysteine, it has been proposed that the ethacrynate-cysteine metabolite is the most active form of the drug. The drug increases potassium excretion in the distal renal tubule. Ethacrynic acid does not inhibit carbonic anhydrase, and it is not an aldosterone antagonist. Aldosterone secretion may incr during therapy with the drug and may contribute to the hypokalemia caused by ethacrynic acid.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2565
...IRREVERSIBLY COMBINES WITH 2 THIOL GROUPS OF GLYCERALDEHYDE 3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE, THUS INACTIVATING THE ENZYME. HOWEVER, IT IS NOT POSSIBLE TO ATTRIBUTE DIURETIC ACTION TO THIS TYPE OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTION...
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 905






